How Can I Help Prevent Hand
Good handwashing is important to stop the disease from being spread to other children. To help prevent the spread of the illness to others:
-
Wash your hands before and after caring for your child. Use soap and warm water and scrub for at least 20 seconds. Rinse well and air dry or use a clean towel.
-
If you are not able to wash your hand, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer and follow instructions for its use.
-
Make sure your child washes his or her hands often.
-
Make sure your childcare center encourages handwashing.
Also make sure to:
-
Clean contaminated surfaces with a disinfectant.
-
Stay away from infected people. An infected person can still transmit viruses for 1 to 2 weeks after he or she no longer has symptoms.
When Should I Call My Childs Primary Care Provider
If you are worried, you are never wrong to call or make an appointment with your childs provider. Call your pediatrician immediately if your child:
- Is dehydrated: Look for dry lips and mouth or decrease in urine output
- Is listless or you are concerned about how sick your child looks, especially if he/she does not perk up after a dose of ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- Has a stiff neck
- Has a fever above 105 degrees, a fever that lasts more than two to three days, or is younger than 3 months old with a fever higher than 100.3 degrees
Remember: if your childs fingernails or toenails seem to be coming off a couple months after having HFMD, dont worry. You dont need to see your doctor for this unless the child is in pain or the skin around the nails looks infected.
What Causes Eczema Coxsackium
Coxsackievirus A6 and A16 are the most common causes of eczema coxsackium.
The reason why the enterovirus localises to sites with atopic dermatitis remains unclear. It is thought the mechanism is similar to eczema herpeticum, where afflicted patients appear to have impaired immunity to the virus and barrier dysfunction at the affected sites . This mechanism may explain how non-eczematous conditions such as Darier disease have also presented with a widespread viral infection that preferentially erupts at the sites of the skin disease .
Read Also: Dyshidrotic Eczema On Bottom Of Feet
Who Does Dyshidrotic Eczema Affect
Dyshidrotic eczema can affect anyone. However, it most commonly affects people:
- Between the ages of 20 and 40.
- Assigned female at birth.
- With a personal or family history of eczema.
- With a personal or family history of contact dermatitis.
- Who develop allergic reactions when they touch an antigen, which is a foreign substance that causes an allergic reaction.
- Who receive immunoglobulin infusions. Intravenous immunoglobulin is an injection of antibodies for people with an immune deficiency.
About 50% of dyshidrotic eczema cases occur in people who have allergic reactions when they touch an antigen. Researchers think that people assigned female at birth may be more likely to develop dyshidrotic eczema because they more frequently interact with certain antigens, like nickel and cobalt in jewelry.
What Is Eczema Coxsackium
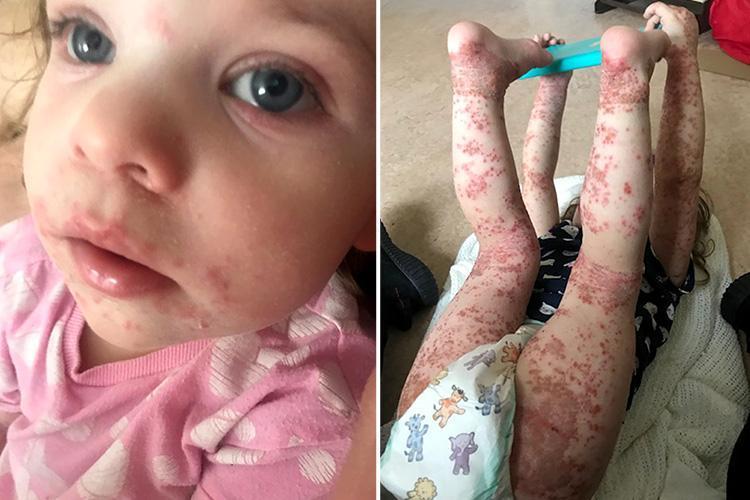
Eczema coxsackium is an enteroviral infection typically affecting children with atopicdermatitis . It is characterised by an eruption of vesicles, bullae, and erosions affecting areas of active or inactive atopic dermatitis.
Eczema coxsackium is a form of Kaposi varicelliform eruption, and has been described as atypicalhand, foot and mouth disease . Both conditions are caused by enterovirus. However, eczema coxsackium is more widespread than hand, foot and mouth disease, and presents with vesiculobullouslesions that ulcerate and scab. The term eczema coxsackium was coined by Nahmias et al in 1968 .
See Hand foot and mouth disease images.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Eczema On Face
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Eczema herpeticum is considered a medical emergency and should be treated promptly with systemic antivirals, as misdiagnosis and delay in treatment can result in serious complications. An ophthalmologic evaluation is warranted in cases of EH involving the face and eyelids. A dermatology consult may be beneficial to confirm the diagnosis. Clinicians should be aware of the risk factors associated with EH, including severe or poorly controlled atopic dermatitis, food and environmental allergies, asthma, the onset of atopic dermatitis before age five, and history of S. aureus and molluscum contagiosum infections.
Patients with systemic symptoms or widespread involvement should be promptly referred to the Emergency Department. To improve patient outcomes and prevent morbidity and mortality, healthcare providers should have a high index of suspicion for EH in patients with a history of atopic dermatitis presenting with a sudden onset, vesicular, monomorphic rash in areas of pre-existing dermatitis.
Measles And Morbilliform Rashes
Measles is a highly contagious paramyxovirus infection with respiratory droplet and occasionally, conjunctival spread. The incubation period is 10-14 days.
It has become relatively rare in the UK owing to herd immunity resulting from MMR vaccination. In 2011, 258,000 measles deaths were recorded worldwide. Measles vaccination has resulted in a 71% reduction in deaths from 2000 to 2011.
Koplik spots in the mouth: highly suggestive of measles
Diagnosis and managementVaccination status should be checked, because the classical presentation is unlikely in those who have been vaccinated.
Prodromal symptoms include the three Cs: cough, coryza and non-purulent conjunctivitis, which occur two to four days before the rash develops.
Koplik spots are highly suggestive of measles. These are white/grey spots with an erythematous halo on the buccal mucosa opposite the molars, often described as looking like grains of salt.
There is a short period of overlap with the exanthem occurring 24-48 hours beforehand and lasting two to three days. The exanthem, which consists of red maculopapular lesions, some of which may be confluent , starts on the face and neck and spreads downwards. Fine desquamation may occur as the rash resolves.
- Scarlet fever
- Graft versus host disease
- Viral exanthema, including German measles, adenovirus, roseola infantum, echovirus, Epstein-Barr virus and many more
- Drug hypersensitivity, including antiretrovirals
- Syphilis
- Toxic shock syndrome
Don’t Miss: Body Wash For Sensitive Skin Eczema
What Are The Clinical Features Of Eczema Coxsackium
Eczema coxsackium presents with vesicles, bullae, and erosions.
- The vesicles are relatively monomorphous and can be painful, but are generally not pruritic.
- Bullae are more common in infants under one year of age compared to older children, who present with vesicles .
- The vesicles and bullae can progress to erosions and scabs.
- Any site can be affected but hands, feet, face, torso, and buttocks/groin are usually involved.
- Lesions preferentially localise to sites affected by atopic dermatitis or another skin disease. Lesions may also be present on unaffected skin or skin previously affected by eczema.
- Oral ulcers can be present. These are less common than with hand, foot and mouth disease.
- Fever and oropharyngeal pain are common.
- The course of illness is similar to the classical hand, foot and mouth disease with no serious long-term sequelae.
About Author: Luke Legner
Luke Legner is a writing coordinator at OSF HealthCare. He joined the Ministry in April 2021 after several years working in corporate communications in the heavy equipment industry. A Pontiac native, he graduated from Illinois State University in 2002 where he earned a bachelors degree in mass communication.Luke and his wife, Ashley, reside in Bloomington and have one son and two daughters. When hes not tackling a home improvement project, you can usually find Luke watching his beloved Chicago Cubs or The Andy Griffith Show.
You May Like: What Is Good For Eczema Skin
What Causes Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is caused by either coxsackieviruses or human enteroviruses. Its found in the digestive tract, including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
The virus is spread from person to person when a sick person sneezes, coughs, or blows their nose. You can get it if you touch your nose, eyes, or mouth after touching something contaminated with the virus, such as a toy. You can also get it if you touch the stool or blisters of a person who is infected.
What Is The Prognosis For Coxsackievirus Vs Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Coxsackievirus
Most people who get coxsackievirus infections have no symptoms or are only mildly ill and soon recover. People who have fever or feel ill should stay home, because the infection is contagious.
Most patients with myopericarditis recover completely, but up to one-third will continue to have some degree of heart failure. Children with myopericarditis usually fare better than adults. Severe coxsackievirus infections in newborns are fatal in approximately one-half of cases.
Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
Appropriate infection control practices are recommended to prevent the spread of hand, foot, and mouth disease. Good hand hygiene is always important. Children infected with the virus causing hand, foot, and mouth disease generally have mild illness and recover within one week of developing symptoms. There is no vaccine however, the illness is typically mild and self-limited, and children generally cannot develop the illness twice. In addition, most adults have persistent immunity and cannot become infected either.
Read Also: Natural Eczema Treatment For Adults
What Is The Cause Of Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Hand foot and mouth disease is due to an enterovirus infection, usually Coxsackie virus A16. Other viruses causing HFM include:
- Enterovirus 71, linked with severe infections that may involve the nervous system
- CVA6, causing increasingly common and severe infection worldwide
- CV A5, A7, A9, A10, B2, and B5
- Echovirus
- Coxsackievirus.
Could It Really Be Monkeypox
The first thing to ask yourself is – do you think you could have been exposed? It takes close, prolonged contact – often skin-to-skin – with an infected person. There are very few people in the world who currently have it, meaning there are not that many opportunities to catch it.
Even in remote parts of some African countries where it can sometimes circulate, children rarely contract it.
If you were to get sick with monkeypox, the first thing you would notice is flu-like symptoms – feeling tired, generally unwell and feverish. It’s what doctors call the “invasion period” of the disease, when the virus enters your cells.
Your glands would feel swollen because your immune system is ramping up to fight the infection.
Next comes the rash, which goes through different “skin eruption” phases. It starts off flat and red, but then gets bumpy and blistered, before forming scabs.
Dr Rosamund Lewis from the World Health Organization’s Emergencies Programme explains: “It starts with what we call macules. These are just red areas. Then it progresses to papules. This is something you can feel. It’s raised.”
Those red lumps and bumps then start to blister, and fill with a whitish fluid that looks like pus.
These pustules then begin to dry out and scab over. Eventually, the scabs will heal and drop off.
“This is why it can be confused with chickenpox,” says Dr Lewis.
The rash – which may look slightly different on different skin tones – can contaminate bedsheets and clothes.
Recommended Reading: Tea Tree Oil For Eczema For Babies
Living With Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Living with hand, foot, and mouth disease is a short-term challenge since the symptoms go away in about a week. As a parent caring for a child who has the virus, your primary goals are to keep your child comfortable and hydrated. It is best to keep them at home to rest and to avoid situations that will infect others.
Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
| Hand, foot, and mouth disease |
|---|
| Other names |
| Based on symptoms, viral culture |
| Prevention |
| As outbreaks |
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common infection caused by a group of enteroviruses. It typically begins with a fever and feeling generally unwell. This is followed a day or two later by flat discolored spots or bumps that may blister, on the hands, feet and mouth and occasionally buttocks and groin. Signs and symptoms normally appear 36 days after exposure to the virus. The rash generally resolves on its own in about a week. Fingernail and toenail loss may occur a few weeks later, but they will regrow with time.
The viruses that cause HFMD are spread through close personal contact, through the air from coughing and the feces of an infected person. Contaminated objects can also spread the disease.Coxsackievirus A16 is the most common cause, and enterovirus 71 is the second-most common cause. Other strains of coxsackievirus and enterovirus can also be responsible. Some people may carry and pass on the virus despite having no symptoms of disease. Other animals are not involved. Diagnosis can often be made based on symptoms. Occasionally, a throat or stool sample may be tested for the virus.
Recommended Reading: Early Signs Of Eczema In Toddlers
Staying Off School Or Nursery
Keep your child off school or nursery while they’re feeling unwell.
But as soon as they’re feeling better, they can go back to school or nursery. There’s no need to wait until all the blisters have healed.
Keeping your child away from other children for longer is unlikely to stop the illness spreading.
Is There A Treatment For Hfmd
Unfortunately, no. There is no anti-viral medicine to treat coxsackie virus. Managing HFMD includes use of fever-reducers/pain-relievers such as acetaminophen , and emphasizing/monitoring hydration. Typically the rash is not painful or itchy, so you dont need to put anything on it. If it does seem to itch, you can apply 1% hydrocortisone ointment .
Don’t Miss: What To Do If I Have Eczema
Check If It’s Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
The first signs of hand, foot and mouth disease can be:
- a sore throat
- not wanting to eat
After a few days mouth ulcers and a rash will appear.
The symptoms are usually the same in adults and children, but they can be worse in babies and children under 5.
It’s possible to get hand, foot and mouth disease more than once.
From Hand Foot And Mouth To Influenza There A A Few Nasty Daycare Bugs You Need To Look Out For Heres How To Spot Them
When Huxley woke up on Thursday morning cranky and covered in a bright red rash, Teala knew exactly what she was dealing with.
After working for years as an administrator at a childcare centre, the Victorian mum-of-two has seen her fair share of hand, foot and mouth disease .
She headed to her local doctor with the 11-month-old in tow, expecting to be home within the hour with instructions to keep Huxley home until the blisters healed.
But instead I was told it was just his eczema, Teala tells Kidspot.
I instantly thought its not eczema because Ive seen flare-ups of his eczema and its nothing like it, she adds.
I told her I believed it was HFM but she just kept saying it was just his eczema.
She said he had all the signs of an eczema flare-up and to put cream on it and it will improve my concerns certainly werent listened to.
With two boys, 4 and 11 months, and a career in childcare, Teala has seen her fair share of infections. Source: Madeline Cox
Don’t Miss: Eczema White Patches On Skin
What Is The Fastest Way To Get Rid Of Dyshidrotic Eczema
Your body is unique. You may respond well to an at-home skin care routine and OTC medications, or you may require prescription-strength corticosteroid creams or ointments, like clobetasol .
Dyshidrotic eczema usually goes away with treatment, but it may come back later. You may need to follow a specific skin care routine at home or continue using medication to reduce your symptoms.
It Could Have Been So Much Worse
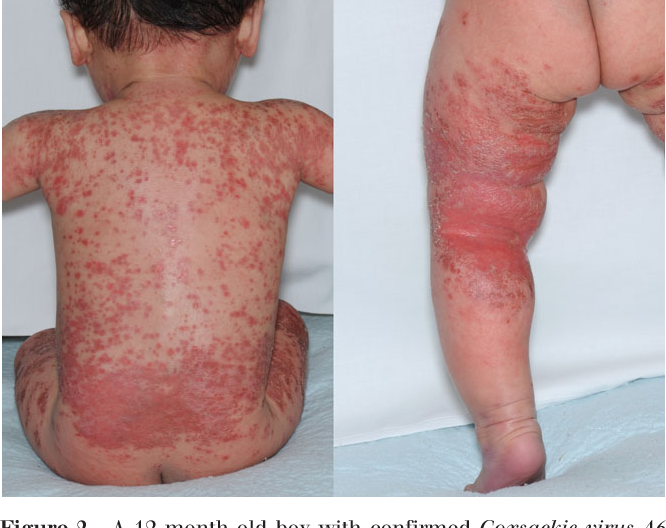
Its one thing to get a diagnosis wrong, but what is especially concerning to Teala is thinking about what might have happened if she hadnt trusted her gut and asked for a second opinion.
I was told the cream that the first doctor prescribed would have killed the bacteria trying to heal the HFM, she says.
The rash could have spread, causing the infection to get worse he might have needed to be admitted to hospital.
If it had gotten any worse he would have needed fluids and a tube to help feel him HFM can develop inside the mouth making it too painful for kids to eat and drink.
If I hadnt gotten a second opinion and applied the cream we were prescribed I may have been sitting in the hospital with my little boy as we speak.
Teala just knew the rash wasnt eczema. Source: Madeline Cox
Read Also: Best Organic Eczema Cream For Babies
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
- How can you tell that I have dyshidrotic eczema?
- If I dont have dyshidrotic eczema, what other skin condition might I have?
- Is there a cream or ointment that you can prescribe?
- What medications do you recommend?
- What at-home treatments do you recommend?
- Is there a specific brand of moisturizer that you recommend?
- Should I see a dermatologist or another specialist?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Dyshidrotic eczema is a common skin condition that can be painful and itchy. You may only have it once, or you may have it off and on throughout your life. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have painful blisters and itchy skin. Over-the-counter creams, ointments and medications can treat mild cases of dyshidrotic eczema. More severe cases of dyshidrotic eczema may require prescription medications or other therapies. With a proper skin care routine, you can reduce the impact of dyshidrotic eczema.
Girl 2 Left Scarred By Blisters From Hand Foot And Mouth Disease That Medics Thought Was Eczema
Aubrey Weatherall, from Stoke-on-Trent, was left squirming and screaming in agony suffering the worst case of the disease one nurse has ever seen
- 14:48, 26 Oct 2016
AT the age of just two, Aubrey Weatheralls tiny body was covered in painful blisters, her skin peeling off like a snake.
Though medics first feared she was suffering an eczema flare up, the toddler was diagnosed with the worst case of hand, foot and mouth disease.
The nurse who spotted the common infection, which causes mouth ulcers as well as spots on the hand and feet, claims it was the most severe case she has seen in her 20 years of nursing.
Such was the severity of her condition, her mum Danielle fears she will be left scarred for life.
The mum-of-two said: It was horrific.
She had a temperature but no other symptoms. When I put her to bed at 6pm she suddenly started scratching and itching uncontrollably.
She has eczema and chronic idiopathic urticaria where her skin can flare up from an allergen but she has never scratched like this before.
Don’t Miss: Anti Aging For Eczema Skin