Atopic Dermatitis And Eczema Are Often Used Interchangeablybut They’re Not The Same Thing
Your skin is the largest organ in your entire bodyand because it’s essentially that body’s protective outside layer, there are a number of conditions that can affect it .
Two more of those skin conditions are atopic dermatitis and eczema, and while the two terms are commonly used interchangeably, they’re not necessarily the same thing. Here, dermatologist help to break down how atopic dermatitis and eczema differand what other conditions might present similarly.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Eczema
The signs of eczema :
- are mainly dry, itchy skin. Because it is so itchy, it is often called “the itch that rashes.”
- include redness, scales, and bumps that can leak fluid and then crust over
- tend to come and go. When they get worse, it is called a flare-up.
- may be more noticeable at night
Symptoms can vary:
- Infants younger than 1 year old usually have the eczema rash on their cheeks, forehead, or scalp. It may spread to the knees, elbows, and trunk .
- Older kids and teens usually get the rash in the bends of the elbows, behind the knees, on the neck, or on the inner wrists and ankles. Their skin is often scalier and drier than when the eczema first began. It also can be thicker, darker, or scarred from all the scratching .
How Can Parents Help
Help prevent or treat eczema by keeping your child’s skin from getting dry or itchy and avoiding triggers that cause flare-ups. Try these suggestions:
- Kids should take short baths or showers in warm water. Use mild unscented soaps or non-soap cleansers and pat the skin dry before putting on cream or ointment. Teens should use unscented makeup and oil-free facial moisturizers.
- Ask your doctor if it’s OK to use oatmeal soaking products in the bath to help control itching.
- Kids should wear soft clothes that “breathe,” such as those made from cotton. Wool or polyester may be too harsh or irritating.
- Keep your child’s fingernails short to prevent skin damage from scratching. Try having your child wear comfortable, light gloves to bed if scratching at night is a problem.
- Kids should avoid becoming overheated, which can lead to flare-ups.
- Kids should drink plenty of water, which adds moisture to the skin.
- Get rid of known allergens in your household and help your child avoid others, like pollen, mold, and tobacco smoke.
- Stress can make eczema worse. Help your child find ways to deal with stress .
Recommended Reading: Why Does Eczema Get Itchy At Night
Signs And Symptoms Of Atopic Dermatitis
Incessant pruritus is the only symptom of AD. The disease typically has an intermittent course with flares and remissions occurring, often for unexplained reasons.
Primary physical findings include the following:
-
Xerosis
-
Lichenification
-
Eczematous lesions
The eczematous changes and its morphology are seen in different locations, depending on the age of the patient .
The following is a constellation of symptoms and features commonly seen in AD:
-
Pruritus
-
Peripheral eosinophilia
-
Staphylococcus aureus superinfection
-
Personal history of asthma or hay fever or a history of atopic diseases in a first-degree relative
See Clinical Presentation for more detail.
What Is Eczema In Skin Of Color
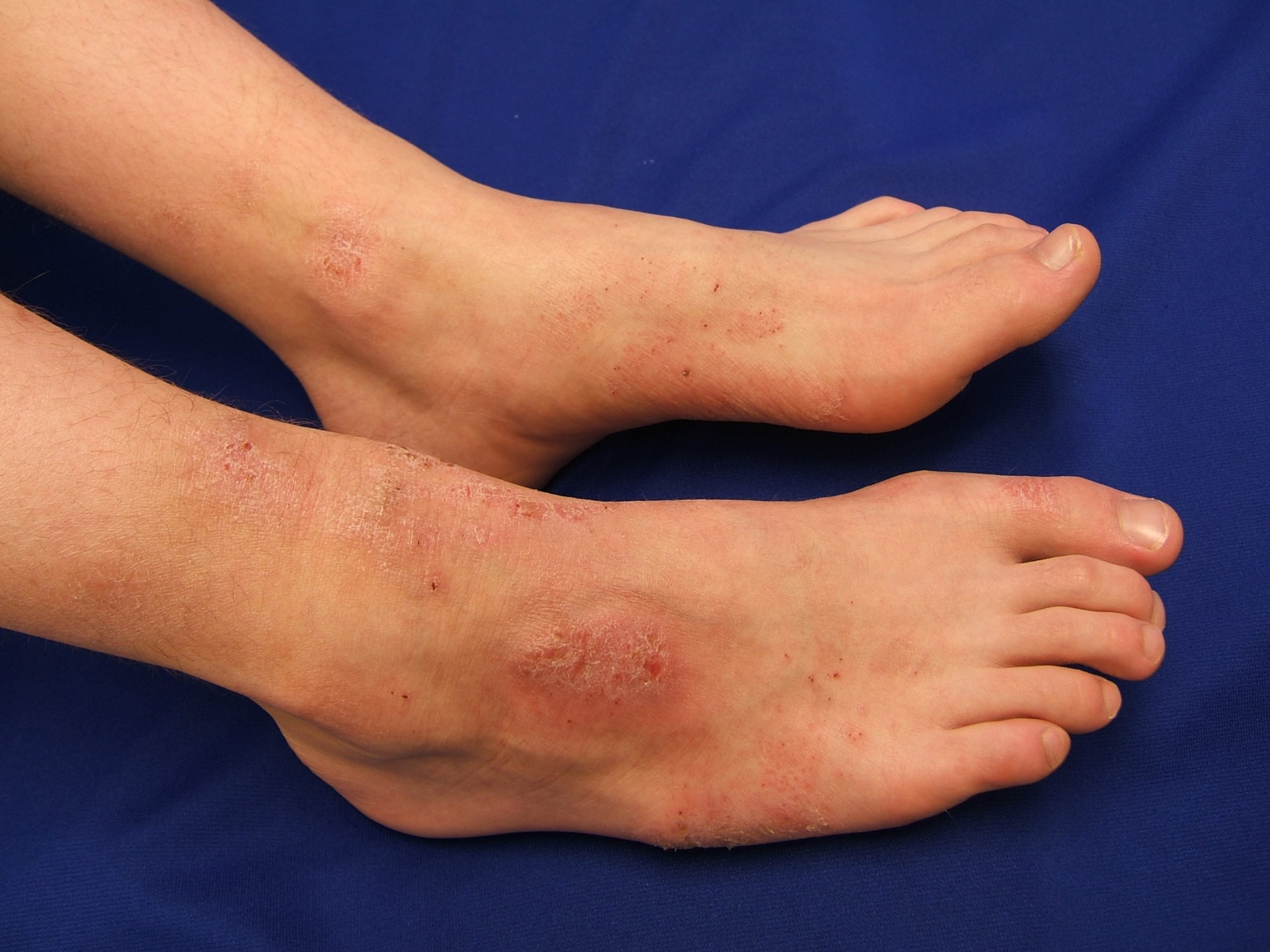
Eczema is more common in Black Americans, especially children. They may experience more itchiness and skin inflammation that require higher doses of medications to get relief.
Black and Hispanic children tend to develop more severe cases of eczema compared to white children. They are also more likely than white children to miss school due to eczema.
Recommended Reading: Is Charcoal Good For Eczema
Other Types Of Eczema
Eczema is the name for a group of skin conditions that cause dry, irritated skin.
Other types of eczema include:
- discoid eczema a type of eczema that occurs in circular or oval patches on the skin
- contact dermatitis a type of eczema that occurs when the body comes into contact with a particular substance
- varicose eczema a type of eczema that most often affects the lower legs and is caused by problems with the flow of blood through the leg veins
- seborrhoeic eczema a type of eczema where red, scaly patches develop on the sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears and scalp
- dyshidrotic eczema a type of eczema that causes tiny blisters to erupt across the palms of the hands
Page last reviewed: 05 December 2019 Next review due: 05 December 2022
How Common Is Atopic Dermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis is very common worldwide and increasing in prevalence.
- It affects males and females equally and accounts for 10%-20% of all referrals to dermatologists .
- Atopic dermatitis occurs most often in infants and children, and its onset decreases substantially with age.
- Of those affected, 65% of patients develop symptoms in the first year of life, and 90% develop symptoms before the age of 5.
- Onset after age 30 is uncommon and often occurs after exposure of the skin to harsh conditions.
- People who live in urban areas and in climates with low humidity seem to be at an increased risk for developing atopic dermatitis.
- About 10% of all infants and young children experience symptoms of the disease.
- Roughly 60% of these infants continue to have one or more symptoms of atopic dermatitis even after they reach adulthood.
- This means that more than 15 million people in the United States have symptoms of the disease.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Eczema From Spreading
Diagnosis Of Atopic Dermatitis
The following features should be considered in the diagnosis of AD in accordance with the American Academy of Dermatology 2014 Guidelines :
Essential features are as follows:
- Pruritus
- Eczema : Typical morphology and age-specific patterns chronic or relapsing history
Important features are as follows:
-
Early age of onset
-
Atopy: Personal and/or family history IgE reactivity
-
Xerosis
Associated features are as follows:
-
Atypical vascular responses
-
Keratosis pilaris/pityriasis alba/hyperlinear palms/ichthyosis
-
Other regional findings
-
Perifollicular accentuation/lichenification/prurigo
Exclusionary conditions are as follows:
- Scabies
Additional considerations in the diagnosis of AD are as follows:
-
No reliable biomarker exists for the diagnosis of AD
-
Laboratory testing is seldom necessary but a complete blood cell count can be useful to exclude immune deficiency an IgE level can be helpful to confirm an atopic pattern a swab of skin can be helpful to identify S aureus superinfection
-
Allergy and radioallergosorbent testing is of little value
-
Biopsy shows an acute, subacute, or chronic spongiotic dermatitis pattern that is nonspecific but can be helpful to rule out other conditions
See Workup for more detail.
What Questions Might My Healthcare Provider Ask To Diagnose Eczema
The conversation with your healthcare provider will need to cover a lot of information. Be sure to be specific about your symptoms.
- Where is your eczema located?
- What have you used to try to treat your eczema?
- What medical conditions do you have? Allergies? Asthma?
- Is there a history of eczema in your family?
- How long have you had symptoms of eczema?
- Do you take hot showers?
- Is there anything that makes your symptoms worse?
- Have you noticed that something triggers or worsens your eczema? Soaps? Detergents? Cigarette smoke?
- Is there so much itchiness that you have trouble sleeping? Working? Living your normal life?
Don’t Miss: How To Deal With Eczema On Scalp
What Are The Symptoms And Signs Of Atopic Dermatitis
Although symptoms and signs may vary from person to person, the most common symptoms are dry, itchy, red skin.
- Itch is the hallmark of the disease.
- Typically, affected skin areas include the folds of the arms, the back of the knees, wrists, face, and neck.
- The itchiness is an important factor in atopic dermatitis, because scratching and rubbing can worsen the skin inflammation that is characteristic of this disease.
- People with atopic dermatitis seem to be more sensitive to itching and feel the need to scratch longer in response.
- They develop what is referred to as the “itch-scratch” cycle.
- The extreme itchiness of the skin causes the person to scratch, which in turn worsens the itch, and so on. Itching is particularly a problem during sleep, when conscious control of scratching decreases and the absence of other outside stimuli makes the itchiness more noticeable.
Causes And Risk Factors Of Eczema
Skin affected by eczema is unable to retain moisture well, possibly because of low production of fats and oils. It is also caused by a disrupted skin barrier, allowing whatever moisture the skin has to freely evaporate into the air. This causes it to become dry and lose its protective properties.
It’s not clear what causes certain people to develop eczema, specifically atopic dermatitis.
Children are more likely to develop eczema if other allergic diseases such as hay fever and asthma run in the family, which suggests that there may be a genetic component to the condition. Read more about conditions related to eczema below.
Though dermatologists dont necessarily consider eczema an autoimmune disorder, the symptoms of atopic dermatitis are thought to be the result of an immune system overreaction or dysfunction.
Indian Journal of Dermatology
In addition to genetic and immune system factors, environmental factors also play a role in worsening or triggering eczema.
Philipp Oscity/Alamy
Also Check: How To Avoid Itching Eczema
Atopic Dermatitis And Eczema
Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory, allergic, non-contagious skin disorder that causes itchy, scaly, flaky skin.
- is the most common chronic skin disorder in children
- occurs in 10 to 20 percent of children
- usually affects babies or very young children
- may last until adolescence or adulthood
- causes the skin to itch, scale and flake
- can lead to permanent scars if your child scratches too much
- lowers a childs quality of life because the itching feeling is constant
- is not curable
- can get better as a child grows older
Atopic dermatitis is a type of inflammation of the skin often connected to allergies. Physicians often use the terms eczema and atopic dermatitis interchangeably because most cases of eczema in children are caused by atopic dermatitis. Eczema is a general term for inflamed, itchy skin, which can sometimes be caused by something other than atopic dermatitis.
Food allergies are a trigger for some patients with atopic dermatitis.
When To See A Doctor
Usually, minor cases of dermatitis can be resolved with self-care. Still, if your symptoms dont improve, you should visit a dermatologist to determine the best course of action for symptom management of eczema or dermatitis.
If your skin becomes painful, infected, or very uncomfortable, you should make a doctors appointment as soon as possible.
Recommended Reading: Home Remedies For Eczema On Feet
What Food Allergies Trigger Atopic Dermatitis
Allergens are substances from foods, plants, or animals that provoke an overreaction of the immune system and cause inflammation . The importance of food allergy in atopic dermatitis is controversial. Although not all researchers agree, most experts think that breastfeeding the infant for at least four months may have a protective effect for the child. New lines of evidence even support exposing young children to normal environmental contaminants such as peanuts. Although such exposures may prevent the development of atopic dermatitis, there is no consensus on how to prevent the development of atopic diseases.
If a food allergy is suspected, it may be helpful to keep a careful diary of everything the patient eats, noting any reactions. Identifying the food allergen may be difficult and require supervision by an allergist if the patient is also being exposed to other allergens. One helpful way to explore the possibility of a food allergy is to eliminate the suspected food and then, if improvement is noticed, reintroduce it into the diet under carefully controlled conditions. A two-week trial is usually sufficient for each food. If the food being tested causes no symptoms after two weeks, a different food can be tested in like manner afterward. Likewise, if the elimination of a food does not result in improvement after two weeks, other foods may be eliminated in turn.
Living With Eczema And Atopic Dermatitis
Eczema can flare up when you are under stress. Learn how to recognize and cope with stress. Stress reduction techniques can help. Changing your activities to reduce daily stress can also be helpful.
The area where you had the eczema may easily get irritated again, so it needs special care. Continue to follow the tips provided here even after your skin has healed.
You May Like: Can I Use Aveeno Eczema Therapy On My Baby
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is often called the itch that rashes because it begins with itchy skin. Scratching the itchy skin causes a rash to appear.
This rash also tends to be very itchy.
AD causes itchy skin
No matter your age or where the AD appears on your skin, AD tends to itch.
AD can develop on any area of your skin at any age. However, at certain ages, its more likely to appear on certain areas of your body and have a unique appearance.
Heres whats most common during each stage of life.
Dermatitis Or Eczema Prevention
Most forms of dermatitis and eczema are chronic conditions. One exception is contact dermatitis. It can be prevented by finding and avoiding the irritant that caused the skin condition.
Its important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis, then try to avoid triggers for your type of eczema or dermatitis .
Other forms of dermatitis can usually be avoided or managed with proper self-care, which includes the following:
- Avoid long showers or baths, which can dry out the skin.
- Use moisturizers like oils, lotions, or creams.
- Avoid irritants that make your skin more susceptible to breakouts, like scented products.
- Dont scrub your skin too hard.
- Use topical steroids to help with itching.
- Keep your fingernails short if you have a habit of scratching.
- Avoid stressful situations that may cause a flare-up.
Establishing a skincare routine can help you manage your atopic dermatitis or eczema symptoms. A doctor can help you come up with a regimen that works for you. You should also take note of things that may have caused your breakouts.
You May Like: Is Eczema And Dermatitis The Same
Millions Live With Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is common worldwide. People of all ages from newborns to adults 65 years of age and older live with this condition. Symptoms range from excessively dry, itchy skin to painful, itchy rashes that cause sleepless nights and interfere with everyday life.
Atopic dermatitis is common
1 in 10 Americans has atopic dermatitis.
In the United States, research indicates that African American and Asian American children develop AD more often than white children.
When a child has deeply pigmented skin, AD tends to be diagnosed later in life. Sometimes, the condition is missed altogether because its less noticeable. In brown or black skin, you tend to see gray to violet-brown skin discoloration rather than red rashes.
Care For Your Skin In The Bath Or Shower
Bathe only with a mild unscented soap, such as Dove, Basis, or Olay. Use a small amount of soap. Keep the water temperature cool or warm, not hot. Soaking in the tub for a short time can be good for your skin. Doing so allows your skins outer layer to absorb water and become less dry. Soak for 15 to 20 minutes. Then use a soft towel to pat your skin dry without rubbing. Immediately after drying, apply a moisturizer to your skin. This helps seal in the moisture.
You May Like: What Is The Best Moisturizer For Eczema
Whats The Difference Between Eczema And Ad
Eczema refers to a group of conditions that cause inflamed skin. There are many types of eczema. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type.
Other types of eczema include contact dermatitis, nummular eczema, and dyshidrotic eczema. People often say eczema when referring to any one of these conditions.
While AD is only one type of eczema, it can develop on the skin in many ways. Youll see pictures of AD and the different ways that it can appear at: Atopic dermatitis: Symptoms
Favorite Annual Meetings For Eczema Patients
The NEAs annual expo provides a vacation retreat for people and families affected by eczema. The four-day event includes activities educational seminars camps for infants, children, and teens and hotel accommodations that are as free of potential allergens as possible. The next Eczema Expo is June 25 through 28, 2020, in Orlando, Florida. The organization offers a limited amount of needs-based scholarships to help people attend.
Recommended Reading: Best Cream For Toddler Eczema On Face
Eczema Symptoms Often Appear On The Following Parts Of The Body:
Eczema may also appear as dark circles under the eyes. This is not due to tiredness or a lack of sleep. In people of color, it could be eczema-related inflammation causing hyperpigmentation .
Atopic dermatitis is the most common form of eczema. Symptoms include:
- Itchy and red patches in lighter skin, itchy and dark brown, purple or gray patches on darker skin
- dry and scaly skin
- open, oozing, crusty sores, which could lead to infection
- ashy skin on skin of color
Points To Remember About Atopic Dermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis, often called eczema, is a chronic disease that causes the skin to become inflamed and irritated, making it extremely itchy.
- Atopic dermatitis is a common condition that usually begins in childhood however, anyone can get the disease.
- Living with atopic dermatitis can be hard, but treatment can help control symptoms.
- Treatments can include medications and skin care.
- You can help prevent flares of atopic dermatitis by caring for your skin, managing stress, following your doctors treatment plan, and keeping a cool temperature in your home.
Don’t Miss: Why Am I Getting Eczema On My Face