What Is Atopic Dermatitis What Is Eczema
Atopic dermatitis and eczema both refer to skin conditions. Atopic dermatitis is a cause of eczema, which refers to skin conditions that cause inflammation and irritation. The terms are sometimes used interchangeably.
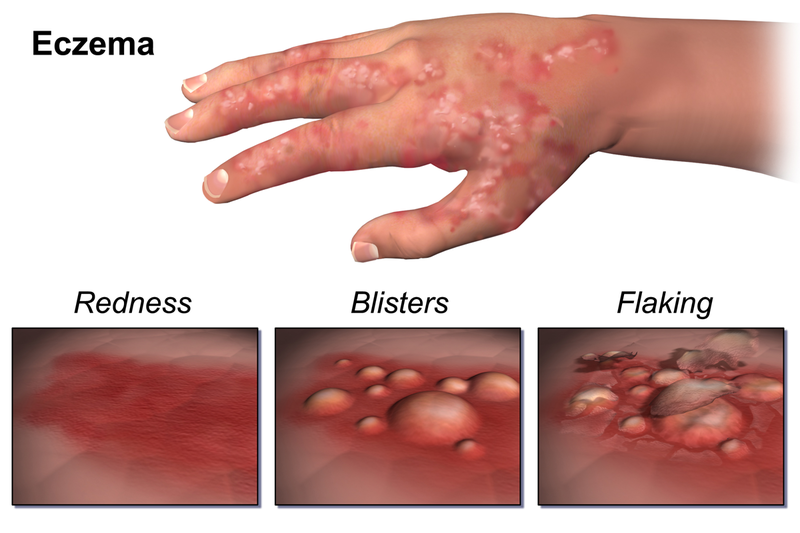
Atopic dermatitis is a common chronic skin condition that results in red, inflamed, dry, and itchy skin. Other symptoms of atopic dermatitis include blisters , skin cracking, crusting, weeping, and scaling. Atopic dermatitis can affect adults, but it is most commonly seen in babies and young children. Triggers that may cause or worsen atopic dermatitis include low humidity, cold weather, seasonal allergies, and exposure to harsh soaps and detergents. Atopic dermatitis treatment involves use of moisturizers such as petroleum jelly and topical steroids to reduce inflammation and itching.
Eczema is not a condition in itself, but a description for a group of skin diseases that cause skin inflammation and irritation. Eczema itself is not contagious however, if the blisters become infected, that infection may spread. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema. Symptoms of eczema include itching along with blisters that ooze and eventually produce crusted, thickened plaques of skin. A rash may appear on the face, wrists, hands, feet, scalp, or the back of the knees. Use of creams, lotions, and other moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated can help manage symptoms.
Infantile Seborrheic Dermatitis Vs Eczema
Infantile seborrheic dermatitis, more commonly known as Cradle cap, is a scalp condition in young infants .
This condition usually presents as thick and greasy scales on the scalp. These scales eventually become waxy and and yellowy which causes them to stick to a babies head. The result will usually look like crusting.
In more severe conditions, the crusting can spread wider across the forehead, neck, behind your babies ears and the temples.
Though this looks painful, it generally isnt an issue for the babies comfort.
Treatment usually consists of mild, unperfumed shampoo and brushing with a very soft brush to slowly remove the scales. A gentle massage may also help, but never pick or force the scales out. This may cause infection.
This should outline the differences between infantile seborrheic dermatitis vs generalised eczema.
Choice Of Topical Corticosteroid
There are different strengths of topical corticosteroids that can be prescribed depending on the severity of your eczema. Discoid eczema usually needs a stronger type of corticosteroid than other types of eczema.
You might be prescribed a cream to be used on visible areas, such as face and hands, and an ointment to be used at night or for more severe flare-ups.
Read Also: Prescription Hand Cream For Eczema
What Are Common Fungal Skin Infections
Common fungal skin infections are caused by yeast, such as a candida infection, or dermatophytes, like ring worm. People who are overweight or patients with diabetes tend to be more likely to develop fungal skin infections. With fungal infections, patients sometimes can develop rashes on other parts of the body that are not infected by the fungus. A fungal foot infection may lead to a bumpy or itchy rash on the fingers, for example. These are usually due to an allergic reaction to the fungus, not from touching the infected area.3,4
Can You Have More Than One Type Of Eczema At The Same Time
For many patients, the challenging truth is that you can experience more than one type of eczema at the same time. Not only that, you can experience all of the different types of eczema, at different times, throughout the course of your lifetime. Dr. Lio explained that he frequently sees allergic contact dermatitis and atopic dermatitis in the same patient. Its very tough to separate them sometimes, he said, but that is why patch testing is so important.
Knowing that each type of eczema has a unique profile, its especially important to connect with a dermatologist who can recognize and diagnose all seven types of eczema. Check out our summary of each type of eczema for more information about symptoms and triggers.
Read Also: Best Non Prescription Eczema Cream
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
What Tests Are Done To Diagnose Dermatitis
Usually your healthcare provider will be able to diagnose dermatitis based on examining your skin. However, when there is doubt, they may perform the following tests:
- Blood tests to check for causes of the rash that might be unrelated to dermatitis.
- A skin biopsy to distinguish one type of dermatitis from another.
- An allergy skin test.
Recommended Reading: Tubby Todd Cream For Eczema
Can You Have Atopic Dermatitis And Symptoms Of Other Types Of Eczema At The Same Time
It is possible to have more than one type of eczema at a time, especially because dyshidrotic dermatitis and neurodermatitis often result from other forms of eczema like atopic dermatitis. You can also have atopic dermatitis and develop other types of eczema if your skin comes in contact with an allergen, irritating substance, or fungus.
How Is Contact Dermatitis Treated
Dermatologists commonly prescribe steroids to treat symptoms of contact dermatitis, which can mimic several other skin conditions. Its important to see a board-certified dermatologist to rule out other conditions.
Topical steroids may resolve itching and other contact dermatitis symptoms, but if the rash is widespread, dermatologists may prescribe a short-term course of oral or injectable corticosteroids.
Preventing future outbreaks depends on pinpointingand then avoidingthe irritant or allergen that triggers flares.
With irritant contact dermatitis, the trigger is usually easy to identify, as stinging, pain or discomfort usually happens within minutes of contact.
For allergic contact dermatitis, knowing what to avoid often requires an in-office procedure called patch testing. This is when the doctor applies patches with small amounts of various allergens to the patients arm or back and then evaluates skin after about 48 hours.
Dermatologists who are members of the American Contact Dermatitis Society are recognized experts in contact dermatitis and patch testing.
Read Also: Can You Get Eczema On Your Eyelids
Lets Get The Basics On The Seven Different Types Of Eczema
Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema, affecting more than 9.6 million children and 16.5 million adults in the United States. For complex reasons that researchers are still studying, the immune system becomes overactive, triggering inflammation that damages the skin barrier, leaving it dry and prone to itching, rashes and infection. AD is usually treated with moisturizing lotions, topic corticosteroids, non-steroidal topicals and biologics. Lifestyle changes to lower stress and ensure regular sleep and healthy dietary habits can also help.How to know if you have it: AD can appear anywhere on the body and at any time of life, but it often appears in childhood and tends to be chronic. It can be hereditary and it is more likely to happen to people who have asthma, hay fever and/or food allergy.
Contact dermatitisoccurs when your skin becomes irritated or inflamed in response to physical contact with an allergen unlike atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis does not run in families and isnt associated with other allergic conditions such as asthma or allergic rhinitis. Standard treatments include topical steroids, as well as patch testing to determine the source of the allergen.How to know if you have it: Contact dermatitis can appear out of the blue and typically disappears when the allergen or irritant is removed. It usually occurs in the spot where your body comes into contact with the allergen or irritant.
Preventing Eczema Flare Ups
There is no cure for atopic dermatitis, but there are things you can do to prevent outbreaks, and treatments are available for when outbreaks happen.1 For the prevention of atopic dermatitis, doctors recommend that patients keep the skin well moisturized. It can also help to try and identify what might be triggering outbreaks, such as certain skin products or allergens, and avoid exposure if possible. Shorter baths or showers with warm waternot hot and gentle, eczema-friendly soaps are also recommended.1
You May Like: Prescription Strength Hydrocortisone Cream For Eczema
Is There A Difference Between Eczema And Dermatitis
Although the terms dermatitis and eczema may overlap in how theyre used, specific types of skin conditions are better known by just one of the names. For example, many doctors use the terms atopic dermatitis and eczema interchangeably but wouldnt use the term contact dermatitis in place of eczema.
Dermatitis means inflammation of the skin. Eczema is inflamed skin that has other symptoms like itching, a flaky or scaly rash, and dry skin.
The table below compares the two conditions, with the bolded terms signifying differences.
| Dermatitis |
|---|
Are There Any Universal Triggers To All The Different Types Of Eczema

According to Dr. Lio, soaps and detergents can trigger almost anyone to flare up in the right context. I would also argue that stress is a fairly universal trigger, he added. Allergens are much more nuanced and individualized. Environmental stressors like heat and cold are fairly common, but not universal.
You May Like: Can You Suddenly Get Eczema
Who Gets Dermatitis
Anyone young and old can get dermatitis. Some examples include:
- Your baby can get cradle cap and diaper rash.
- Atopic dermatitis usually begins in childhood, but anyone at any age can get it.
- Anyone can get contact dermatitis as it just involves skin to substance contact.
- Individuals with celiac disease are prone to dermatitis herpetiformis.
There are several factors that put you at risk of getting dermatitis. Some examples include:
Atopic dermatitis risk factors include:
- A family history of dermatitis, hay fever or asthma.
- Being female.
Contact dermatitis risk factors include:
- If you work around chemicals such as in a factory, restaurant or garden.
Periorificial dermatitis risk factors include:
- Being female.
- Being ages 15 to 45.
Dyshidrotic dermatitis risk factors include:
- If you sweat a lot.
- Prolonged exposed to water and/or irritants.
- If you live in a warmer climate.
Who Gets It And Why
The condition affects 1-3% of the adult population and is more common in men than women. The adult form of seborrhoeic dermatitis can develop from puberty but more usually occurs in adulthood prevalence rises sharply over the age of 20, with a peak at 30 years for men and 40 years for women.
Although this condition affects the areas of skin with grease glands and can lead to the development of a greasy-looking scale, greasy skin is not the cause of seborrhoeic dermatitis. Typically, the skin is, in fact, quite dry, as in all forms of eczema. Adult seborrhoeic dermatitis is believed to be an inflammatory reaction related to an overgrowth of normal skin inhabitants species of Malassezia yeasts . The yeasts are part of normal skin flora but for an unknown reason they trigger seborrhoeic dermatitis in certain individuals.
Seborrhoeic dermatitis is not contagious or related to diet, but it may be aggravated by illness, psychological stress, fatigue, change of season and a general deterioration of health. Those with an immunodeficiency , heavy alcohol intake, and neurological disorders such as Parkinsons disease and stroke are particularly prone to it. It may or may not be itchy and can vary from day to day.
Once the skin has become inflamed with any form of eczema, any exposure to detergents, soaps, shampoos etc. will aggravate the irritation in the skin and scalp. This can be a major factor in causing the seborrhoeic dermatitis to become more severe and persistent.
You May Like: What’s The Best Laundry Detergent For Eczema
How Is Dermatitis Treated What Medications Are Used
The type of treatment depends on the type of dermatitis and its location. Step number one is to avoid whatever triggers the dermatitis. That may be stress, a chemical, tobacco smoke and/or a number of other irritants that cause or worsen your dermatitis. Step number two is to try remedies on your own. Step number three is medication prescribed by your healthcare provider.
How Can You Differentiate Between Eczema And Dermatitis
Sure, eczema and dermatitis refer to the same types of skin conditions, but just like with the different forms of acne, there are discrepancies among them. “Different types of dermatitis have different causes and appear in different locations of the body,” says Sadick. “For example, atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition that begins at infancy, which usually affects the elbows, knees, and neck, and is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.”
On the other hand, Sadick says dermatitis is spurred by direct exposure to a particular allergen or irritant, like poison ivy, nickel, or perfumes. And as for seborrheic dermatitis, Sadick says it generally affects areas of the body that produce more oil, such as the face, upper chest, and back, and can also be triggered by yeast. All this to say: Despite these distinctions, each condition technically falls under the umbrella of eczema, but can also be called dermatitis, too.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Dyshidrotic Eczema Fast
Dermatitis Herpetiformis Vs Eczema Herpeticum
It is not just conditions like dermatitis herpetformis that eczema herpeticum is confused with.
For example, because when it first develops there are visible small red-coloured spots, it is misdiagnosed as chickenpox often.
Its easy to tell the difference though, as eczema herpeticum consists of multiple minuscule red-coloured spots close together whereas chickenpox only has larger red-coloured spots that are spaced more further apart.
As its also mistaken for dermatitis herpetiformis, its worth noting that although they are similar, they differ in that one has rashes and flareups that are itchy, whereas the other has flareups that are very painful.
Other Types Of Eczema
Eczema is the name for a group of skin conditions that cause dry, irritated skin.
Other types of eczema include:
- discoid eczema a type of eczema that occurs in circular or oval patches on the skin
- contact dermatitis a type of eczema that occurs when the body comes into contact with a particular substance
- varicose eczema a type of eczema that most often affects the lower legs and is caused by problems with the flow of blood through the leg veins
- seborrhoeic eczema a type of eczema where red, scaly patches develop on the sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears and scalp
- dyshidrotic eczema a type of eczema that causes tiny blisters to erupt across the palms of the hands
Page last reviewed: 05 December 2019 Next review due: 05 December 2022
Also Check: How Can I Cure Eczema
Questions To Ask Your Childs Doctor
After your child is diagnosed with atopic dermatitis, you may feel overwhelmed with information. It can be easy to lose track of the questions that occur to you.
Lots of parents find it helpful to jot down questions as they arise- that way, when you talk to your childs doctors you can be sure that all of your questions are answered. If your child is old enough, you may want to suggest that she writes down what she wants to ask her health care provider too.
The commitment and compassion with which we care for all children and families is matched only by the pioneering spirit of discovery and innovation that drives us to think differently, to find answers, and to build a better tomorrow for children everywhere.
What Is A Fungal Skin Infection
Fungal skin infections are different from atopic dermatitis, though at first glance they can sometimes appear similar. Fungal infections are not chronic or genetic conditions they are caused by common fungi found in the environment. These skin infections typically appear on moist areas of the body, such as between the toes, under the arms, under the breasts, or in the genital area.1,3
Read Also: How To Remove Eczema From Face
What Gets Rid Of Dermatitis
These self-care habits can help you manage dermatitis and feel better:
- Moisturize your skin. …
- Use nonprescription anti-inflammation and anti-itch products. …
- Apply a cool wet cloth. …
- Take a comfortably warm bath. …
- Use medicated shampoos. …
- Take a dilute bleach bath. …
- Avoid rubbing and scratching. …
- Wear cotton clothing.
How Can I Prevent Or Reduce My Risk Of Dermatitis
Do your best to avoid what triggers your dermatitis. That might be foods youre sensitive or allergic to, chemicals that irritate your skin and/or soaps that do the same. Moisturize your skin regularly. Dont overheat. Use a humidifier to keep the air from getting too dry. Try not to scratch. Reduce your stress.
Don’t Miss: Eczema On Face During Pregnancy
Causes & Strategies For Prevention
A combination of genetic and environmental factors appears to be involved in the development of eczema. Children whose parents have asthma and allergies are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis than children of parents without allergic diseases. Approximately 30 percent of children with atopic dermatitis have food allergies, and many develop asthma or respiratory allergies. People who live in cities or drier climates also appear more likely to develop the disease.
Is Eczema And Dermatitis The Same Thing
Eczema and dermatitis are both generic terms for skin inflammation and are often used interchangeably. There are a number of types of eczema and dermatitis that have different causes and symptoms, but most can be managed with a good skin care regimen and by avoiding irritants that cause flare-ups.
Don’t Miss: How Do I Treat Eczema On My Hands