Emollients For Treating Eczema
Emollient creams add moisture to the skin. Apply moisturisers each day to clean, dry skin. It is especially important to moisturise after showering and bathing, and when living or working in an air-conditioned or heated environment. You may need to try several different brands until you find the emollient that works best for you. Ask your doctor, dermatologist or pharmacist for advice.
Chronic Or Severe Eczema
74% of the dysregulated genes in acute eczema remain impaired or further impaired by the chronic phase of eczema.
In chronic eczema, itching can intensify, and lesions may spread to cover larger areas of the skin. The skin may result in:
- thickening and cracks in the skin
- scaling being more prominent
on a persons age:
- Infants: Red, dry, scaly patches on the face, especially the cheeks, and widely distributed across the body.
- Toddlers and young children: The rash may become more localized and typically occurs on the:
How Is Eczema Diagnosed What Tests Are Done
Your healthcare provider will take a close look at your skin. They will look for classic signs of eczema such as a redness and dryness. They will ask about the symptoms youre experiencing.
Usually your healthcare provider will be able to diagnose eczema based on examining your skin. However, when there is doubt, they may perform the following tests:
- An allergy skin test.
- Blood tests to check for causes of the rash that might be unrelated to dermatitis.
- A skin biopsy to distinguish one type of dermatitis from another.
Recommended Reading: Baby Eczema Shampoo And Body Wash
Whats The Difference Between Eczema And Ad
Eczema refers to a group of conditions that cause inflamed skin. There are many types of eczema. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type.
Other types of eczema include contact dermatitis, nummular eczema, and dyshidrotic eczema. People often say eczema when referring to any one of these conditions.
While AD is only one type of eczema, it can develop on the skin in many ways. Youll see pictures of AD and the different ways that it can appear at: Atopic dermatitis: Symptoms
What Are The Symptoms Of Atopic Dermatitis
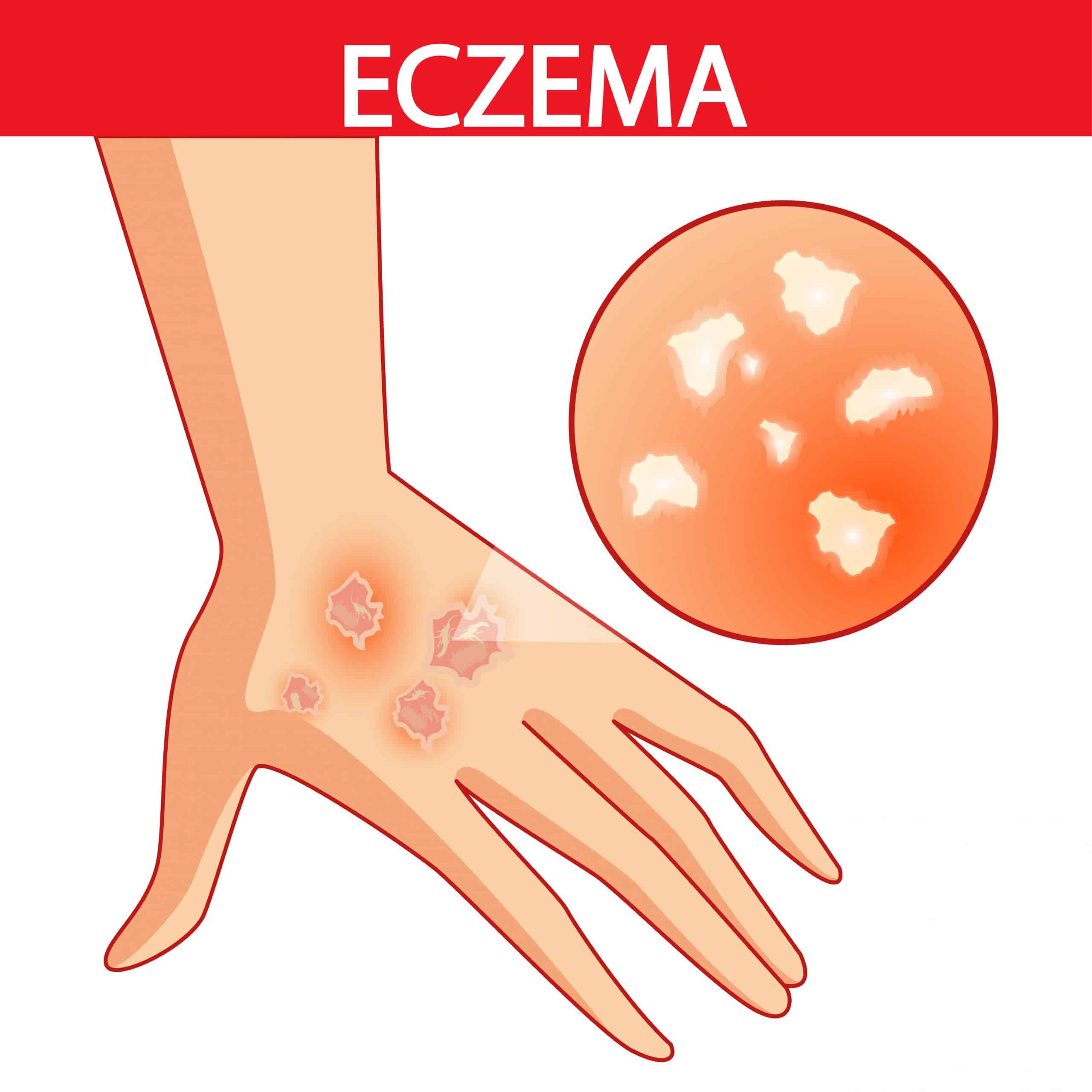
The area of the body affected by atopic dermatitis may change with age. In infants and young children, it usually affects the face, outside of the elbows, and on the knees. In older children and adults, it tends to be on the hands and feet, the arms, on the back of the knees, and the folds of the elbows.
Symptoms are slightly different for each person. Common symptoms include:
- Dry, scaly patches on the skin
- Small bumps that open and weep when scratched
- Redness and swelling of the skin
- A thickening of the skin
- Scratch marks on the skin
Too much rubbing and scratching can tear the skin and lead to infection.
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis may look like other skin conditions. Always talk with your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Recommended Reading: What Can You Do For Eczema
Causes & Strategies For Prevention
A combination of genetic and environmental factors appears to be involved in the development of eczema. Children whose parents have asthma and allergies are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis than children of parents without allergic diseases. Approximately 30 percent of children with atopic dermatitis have food allergies, and many develop asthma or respiratory allergies. People who live in cities or drier climates also appear more likely to develop the disease.
What Is Eczema What Does It Look And Feel Like
Eczema is a condition that causes your skin to become dry, red, itchy and bumpy. Its one of many types of dermatitis. Eczema damages the skin barrier function . This loss of barrier function makes your skin more sensitive and more prone to infection and dryness.
Eczema doesnt harm your body. It doesnt mean that your skin is dirty or infected, and its not contagious. There are treatments that can help manage your symptoms.
In the word dermatitis, derm means skin and itis means inflammation. The word as a whole means inflammation of the skin. Eczema originates from the Greek word ekzein which means to boil over or break out.
Also Check: How Long Does Eczema Rash Last
Eczema Coping Tips Good Hygiene
Skin affected by eczema is more vulnerable to a range of infections, including impetigo, cold sores and warts. The bacterium Staphylococcus aureus may cause a secondary infection of impetigo, and possibly contribute to the symptoms of eczema.Suggestions for washing include:
- Take lukewarm baths or showers, and avoid really hot showers.
- Dont use ordinary soap, as the ingredients may aggravate your eczema. Wash your body with warm water alone. For armpits and groin, use soap-free products, such as sorbolene cream.
- Bath oils can help to moisturise your skin while bathing.
- When towelling dry, pat rather than rub your skin.
How Do Clinical Features Vary In Differing Types Of Skin
There are ethnic variations in patterns of atopic dermatitis. In Mori, Pacific Islanders, and Africans, the papular variant is observed. Perifollicular and extensor, rather than flexural, patterns may also be more common in patients of African descent.
Conventional scoring systems for atopic dermatitis may underestimate the severity of disease in those with skin of colour due to the erythema appearing violaceous.
Patients with skin of colour appear to be at particular risk of developing lichen simplex and nodular prurigo with scratching and rubbing.
Postinflammatory hypo- and hyper-pigmentation occurs more commonly with skin of colour and can be more noticeable than in ethnic white skin, resulting in significant psychological distress.
Atopic dermatitis in skin of colour
Don’t Miss: Witch Hazel For Eczema In Babies
Whats The Difference Between Dermatitis And Psoriasis
Psoriasis and dermatitis can appear similar. Both cause patches of red skin. However, in psoriasis, the scales are thick and the edges of those scales are well-defined.
Discuss with your healthcare provider your questions about which type of skin condition you have. You can have more than one skin condition at a time. Treatments for one may not work for the other.
Living With Atopic Dermatitis
The following steps can help manage atopic dermatitis:
- Take brief baths or showers using lukewarm water.
- Practice good skin care.
- Dont use harsh soaps. Ask your healthcare provider to recommend a brand.
- Dress in light clothes. Sweating can make atopic dermatitis worse.
- Use a good moisturizer at least once a day. Ask your healthcare provider to recommend a brand.
- Avoid scratching the affected area.
- Minimize stress.
- Make lifestyle changes that prevent flare-ups.
- Avoid skin products that have fragrances and dyes
You May Like: How To Heal Eyelid Eczema
How Do You Get Rid Of Dyshidrotic Eczema
For many people, getting rid of dyshidrotic eczema starts with an at-home skin care routine. Home care may include:
- Using warm water instead of hot water when washing your hands.
- Soaking your hands and feet in cool water to improve your symptoms.
- Applying cool compresses as needed to relieve itching and irritation. Soak a clean washcloth with cool water and hold it to your skin for 10 to 15 minutes. Allow the water to partially evaporate and then immediately apply moisturizer. Repeat this three to four times per day.
- Applying moisturizers frequently each day to improve dry skin.
- Thoroughly drying your hands and feet after bathing or swimming.
- If possible, don’t wear gloves, socks or shoes. If you must, wear gloves that repel or absorb moisture, cotton or wool socks that absorb moisture and loose shoes.
Your healthcare provider may recommend over-the-counter medications such as topical corticosteroid creams or ointments that you rub directly on your skin. They may also recommend oral antihistamine pills, including fexofenadine or cetirizine , that you swallow with water. These medications help reduce inflammation and itching.
What Triggers Dyshidrosis
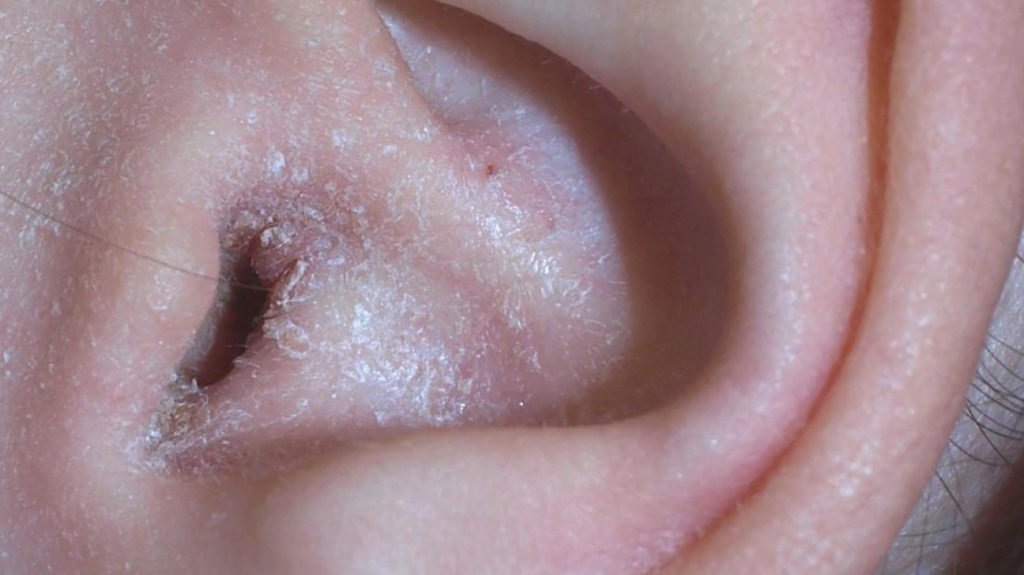
Healthcare workers and researchers dont know exactly what causes dyshidrosis. A combination of triggers can cause dyshidrosis flare-ups, including:
- Immune system activation: If you have dyshidrotic eczema, your immune system reacts to minor irritants or allergens. This overreaction can inflame your skin.
- Allergies: Exposure to certain substances, including cement, nickel, cobalt and chromium, may trigger dyshidrotic eczema. Other allergies, including hay fever or food allergies, may also cause flare-ups.
- Moisture: Frequently sweaty or wet hands or feet may trigger dyshidrotic eczema.
You May Like: How To Apply Wet Dressing For Eczema
Other Types Of Eczema
Eczema is the name for a group of skin conditions that cause dry, irritated skin.
Other types of eczema include:
- discoid eczema a type of eczema that occurs in circular or oval patches on the skin
- contact dermatitis a type of eczema that occurs when the body comes into contact with a particular substance
- varicose eczema a type of eczema that most often affects the lower legs and is caused by problems with the flow of blood through the leg veins
- seborrhoeic eczema a type of eczema where red, scaly patches develop on the sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears and scalp
- dyshidrotic eczema a type of eczema that causes tiny blisters to erupt across the palms of the hands
Page last reviewed: 05 December 2019 Next review due: 05 December 2022
Atopic Dermatitis Or Eczema
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition that requires symptom management. Its characterized by an itchy, red rash that usually appears at joints in your body, like knees or elbows, and even around the neck. But it can occur anywhere on the body.
This condition occurs in flare-ups or bouts, meaning that it gets worse and improves in irregular cycles. Symptoms include:
To determine what type of eczema you have, make an appointment with a doctor. Following your diagnosis, your doctor will provide a plan for treatment and management.
Also Check: What Helps Eczema Flare Ups
General Tips For Coping With Eczema
Other tips to manage your eczema include:
- Keep your fingernails short longer nails are more likely to injure your skin when you scratch.
- If the water in your area is hard or alkaline, consider installing a water-softening device.
- Swim in the sea in warm weather whenever you can seawater is known to reduce the symptoms of eczema.
- Use sun exposure for limited periods for example, when swimming at the beach. This can help relieve eczema symptoms. But be aware that ultraviolet radiation is a risk factor for skin cancer and premature ageing of the skin. Also, if sun exposure causes overheating, this can also aggravate eczema.
What To Look For
There are literally hundreds of different coal tar preparations found on drugstore shelves and online. When choosing a product, opt for one that has undergone testing with an independent certifying body like the U.S. Pharmacopeia , NSF International, or ConsumerLab. In this way, you will know for sure that the product contains the ingredients listed on the label in the declared potency level.
Read Also: Food To Avoid For Eczema Baby
How Is Atopic Dermatitis Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will ask about your health history and whether you have allergies or asthma. He or she will also ask about any family history of dermatitis, allergies, or asthma.
A healthcare provider can often diagnose atopic dermatitis by examining your skin. You may also have a patch test. This is used to find allergies by placing small amounts of allergens on the skin and watching for a response. A skin biopsy may also be done to rule out other causes of the rash.
What Questions Should I Ask My Doctor
- How can you tell that I have dyshidrotic eczema?
- If I dont have dyshidrotic eczema, what other skin condition might I have?
- Is there a cream or ointment that you can prescribe?
- What medications do you recommend?
- What at-home treatments do you recommend?
- Is there a specific brand of moisturizer that you recommend?
- Should I see a dermatologist or another specialist?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Dyshidrotic eczema is a common skin condition that can be painful and itchy. You may only have it once, or you may have it off and on throughout your life. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have painful blisters and itchy skin. Over-the-counter creams, ointments and medications can treat mild cases of dyshidrotic eczema. More severe cases of dyshidrotic eczema may require prescription medications or other therapies. With a proper skin care routine, you can reduce the impact of dyshidrotic eczema.
Read Also: How To Treat Eczema On Scalp Naturally
Cleaning And Personal Care Products
Experiment with using different laundry detergents, cleaning products, etc., to see if that may help. Some people with eczema are sensitive to substances found in these products. Take a look at conventional products, but also so-called natural products because these can be disease triggers as well. Avoiding a suspected substance for a period of time can give you an idea of whether it might be triggering your symptoms.
Start by staying away from scented products. You might want to experiment with products labeled hypoallergenic, which may be less likely to trigger symptoms.
Generally, fewer ingredients are a good sign. Some people also experiment with homemade products, or simple baking soda and vinegar rinses.
In general, once you have identified a triggering substance, youll know to avoid it in the future.
How Is Dermatitis Treated
General principles are covered here. Specific management of specific types of dermatitis are detailed on the relevant pages.
- Potential allergen identification and avoidance made on the basis of history e.g. hobbies, products used, and occupation. A patch test will confirm.
- Potential irritant identification and avoidance avoid soaps, shower gels, dust, organic solvents, and drying/desiccating agents.
- Protect the skin with personal protective equipment especially hand dermatitis, by the use of cotton gloves for dry work, and cotton with an occlusive glove appropriate to the suspected allergen or irritant.
Also Check: The Best Medicine For Eczema
What Are The Symptoms Of Dyshidrotic Eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema causes symptoms that come and go. These symptoms may last for several weeks at a time. The most common symptoms of dyshidrotic eczema include:
- Small, firm blisters on the sides of your palms, fingers and soles.
- Painful blisters.
- Itchy, scaly skin on or around your blisters.
- Increased sweat around your blisters.
- Dry, cracked skin that appears as blisters fade.
The skin on your fingers, hands and feet may thicken if you scratch them frequently. Large blisters or large areas of blisters may become infected.
Who Gets Acute Palmoplantar Eczema
People who develop acute palmoplantar eczema often have a history of this condition in their family. Even a personal or family history of other forms of eczema can increase your risk of developing the acute palmoplantar variety by about 50 percent.
Its more common in women than in men, and is more common before age 40. This condition is also more common in people with overactive sweat glands on the palms of their hands and in people who smoke tobacco.
A doctor may also recommend either an over-the-counter or prescription anti-itch cream.
Treatment is usually guided by how severe your symptoms are. More advanced cases of palmoplantar eczema could require additional medications like:
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Really Bad Eczema
Does Eczema Go Away
Theres no known cure for eczema, and the rashes wont simply go away if left untreated. For most people, eczema is a chronic condition that requires careful avoidance of triggers to help prevent flare-ups.
Age is also thought to play a role: About 60 percent of people who have eczema developing it as infants. If you develop eczema as a child, then you may experience improved symptoms as you get older.
Natural Treatments At Home
Aside from moisturizing your skin, some natural treatments may help heal your skin.
Oatmeal baths are one type of natural treatment that can soothe the itchiness and discomfort of eczema rashes. Be sure to use lukewarm water and follow up with a moisturizer immediately after.
Theres some evidence that both probiotics and prebiotics may stabilize your microbiome to help treat inflammation. However, more research is needed to support this approach in eczema treatment.
You May Like: What Is Eczema And Psoriasis
Diagnosis Of Atopic Dermatitis
The following features should be considered in the diagnosis of AD in accordance with the American Academy of Dermatology 2014 Guidelines :
Essential features are as follows:
- Eczema : Typical morphology and age-specific patterns chronic or relapsing history
Important features are as follows:
-
Early age of onset
-
Atopy: Personal and/or family history IgE reactivity
Associated features are as follows:
-
Atypical vascular responses
-
Keratosis pilaris/pityriasis alba/hyperlinear palms/ichthyosis
-
Other regional findings
-
Perifollicular accentuation/lichenification/prurigo
Exclusionary conditions are as follows:
Additional considerations in the diagnosis of AD are as follows:
-
No reliable biomarker exists for the diagnosis of AD
-
Laboratory testing is seldom necessary but a complete blood cell count can be useful to exclude immune deficiency an IgE level can be helpful to confirm an atopic pattern a swab of skin can be helpful to identify S aureus superinfection
-
Allergy and radioallergosorbent testing is of little value
-
Biopsy shows an acute, subacute, or chronic spongiotic dermatitis pattern that is nonspecific but can be helpful to rule out other conditions
See Workup for more detail.
What Are The Symptoms Of Acute Palmoplantar Eczema
Like other forms of eczema, acute palmoplantar eczema develops with some level of skin irritation.
The main feature of this type of eczema is the appearance of deep, fluid-filled blisters, referred to as a vesicular rash. The appearance of this rash is sometimes compared to tapioca pudding.
In addition to this blistered appearance, acute palmoplantar eczema can develop with symptoms like:
- intense burning
- red, dry cracks in the skin
Researchers believe there are likely many reasons that eczema develops, and its difficult to pinpoint an exact cause. Some common themes in people with acute palmoplantar eczema include:
- a family history of this or other types of eczema
- a history of inflammatory fungal infections of the skin
- medication reactions
Outside of the underlying cause, its also important to note that many forms of eczema flare up in the presence of certain triggers. Triggers of acute palmoplantar eczema can include things like:
- skin irritation from friction, chemicals, or detergents
- frequent handwashing
You May Like: Dairy And Eczema In Toddlers