Emollients And Fire Safety
Lotions, creams or ointments used to moisturise your childs skin are also known as emollients.
Emollients are very effective at treating chronic dry skin conditions, such as eczema.
But it is important to be aware of the fire risk linked with them.
Emollients won’t cause a fire on their own. But if there is a build-up of emollient residue on clothing and bedding, this can quicken the speed of a fire.
Do not smoke near your baby or allow them near naked flames:
- while they are wearing emollient
- if they are wearing clothes or bandages that may have emollient on them
There is a fire risk with all paraffin-containing emollients. There may also even be a fire risk with paraffin-free emollients. There might also be a fire risk with other products that you put on skin over large body areas for more than a few days.
Washing clothing or fabric at a high temperature may reduce emollient build-up. But it might not totally remove it.
Aveeno Eczema Therapy Daily Moisturizing Cream For Sensitive Skin
- 12-fluid ounce bottle of Aveeno Eczema Therapy Daily Moisturizing Cream eczema moisturizer brand is clinically-proven to relieve dry, itchy, and irritated skin due to eczema.
- This breakthrough eczema cream has been awarded the National Eczema Association Seal of Approval and is clinically shown to help relieve the key symptoms of eczema, including itchiness, the appearance of redness, dryness and irritation.
- The nourishing formula of this moisturizing lotion is enriched with colloidal oatmeal and contains ceramides, essential lipids naturally found within skin, to enhance and restore skins protective function.
- Our daily eczema cream is also designed to help prevent the recurrence of extra-dry skin.
- Aveeno uses the goodness of nature and the power of science to keep your skin looking and feeling healthy and balanced.
Dont Shy Away From Topical Steroids
Steroids, which are the standard treatment for eczema, still make many parents nervous, said Dr. Cheryl Bayart, M.D., a pediatric dermatologist at the Cleveland Clinic. People hear the word steroids and they automatically think about taking steroids by mouth, which does carry a high risk of side effects like mood swings, and even stunting a childs growth, she explained. But far less steroid enters the bloodstream through the skin, which makes topicals safer.
Most doctors dont recommend topical steroids for more than a couple of weeks at a time, since long term use can cause the skin to thin, said Dr. Kirkorian. They should also never be used around the eyes, which may increase the risk of glaucoma and cataracts later in life. There are three non-steroidal topical medications that are Food-and-Drug-Administration-approved for children over 2: tacrolimus , pimecrolimus or crisaborole . Protopic or Elidel are good for sensitive areas such as the eyes, face, armpit or groin, added Dr. Kirkorian. Eucrisa is best for children with frequent flareups, instead of keeping them on topical steroids.
You May Like: Best Pajamas For Babies With Eczema
How Is Atopic Dermatitis Treated In A Child
Treatment will depend on your childs symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is. There is no cure for atopic dermatitis. The goals of treatment are to ease itching and inflammation, add moisture, and prevent infection.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis includes:
-
Staying away from irritants, as advised by your child’s healthcare provider
-
Bathing with a gentle cleaner or body wash advised by the healthcare provider
-
Keeping your child’s fingernails short, to help prevent scratching that can cause skin irritation and infection
-
Using moisturizing lotion advised by the healthcare provider
Your child’s healthcare provider may also prescribe medicines. They may be used alone or together. The following are most commonly used to treat atopic dermatitis:
Good Bacteria Might Help Restore The Skins Natural Oils
If you examine the skin of someone with eczema when everything is going great for them when they still may need medicine, but their disease is well controlled the main thing that is still abnormal compared to healthy people is the lipid profile of their skin, says Myles.
In the context of eczema, the term lipid refers to the skins natural oils , Myles explains. Your skin needs specific kinds of the right oils in the right amounts to have it function the way its supposed to, he says.
According to Myles, theres no evidence that for people with eczema, the skin itself is unable to produce the right lipids. That led us to suspect that maybe its the bacteria on their skin that are failing to make the correct lipids, he says.
Also Check: Is Eczema An Inflammatory Condition
Puriya Cream For Eczema
Puriya cream is tagged as the Mother of All Creams as it proves to be helpful for skin rashes, dermatitis, shingles, rosacea, dermatitis, eczema and psoriasis. The cream comes in 13 in 1 unique natural solution to offer an instant relief to the itchy, dry, irritated and flaky skin.
The main ingredient is the Amarnath oil that has anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic properties to boost cell growth. Solution works by deeply hydrating the skin and locking in the moisture. Has proved to be effective skin care lotion to heal damaged and sore skin.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Eczema On Your Face
Gentle Soaps And Detergents
Laundry detergent can contain harsh chemicals that aggravate eczema.
Many body washes and cleansers contain detergents, which help provide a soapy lather. Detergents and other lathering agents can dry out the skin, especially in people with eczema.
Bar soaps can also be harsh on the skin because of their alkalinity.
Try using a gentle, no-lather, fragrance-free cleanser. Avoid products with rough particles for scrubbing or exfoliating, as these can further irritate the skin.
Many people with eczema also find that switching to a more gentle, fragrance- or color-free laundry detergent can help improve symptoms.
Additionally, try skipping fabric softener, which lingers on clothes and often contains fragrances and chemicals that can irritate the skin.
Sitting next to a fireplace or near a furnace may feel good, but it can worsen eczema symptoms. The hot, dry air can dehydrate the skin and aggravate the itchiness of eczema.
Use a humidifier during the dry winter months and avoid getting too close to heaters and fireplaces.
Read Also: How To Repair Damaged Skin From Eczema
What To Do About Itching
Try to keep your baby from scratching their itchy skin. Scratching can make the rash worse, lead to an infection, and cause the irritated skin to get thicker and more leathery.
Trim their nails often, and then take the edge off of them with a file if you can. Some parents also slip scratch mittens onto their little ones hands. Others try long socks, tucked in under a long-sleeved shirt, so theyre harder for a baby to remove. View a slideshow to get more eczema skin care tips.
Key Points About Atopic Dermatitis In Children
-
Atopic dermatitis is a long-term skin condition. It’s common in babies and children.
-
A child with allergies or family members with atopic dermatitis has a higher chance of having atopic dermatitis.
-
Itching, dryness, and redness are common symptoms.
-
The goals of treatment are to ease itching and inflammation of the skin, increase moisture, and prevent infection.
-
Staying away from triggers is important to manage the condition.
-
It usually gets better or goes away as a child gets older.
You May Like: Is Polyester Bad For Eczema
Referral To Nhs Eczema Specialists
Most cases of baby eczema/atopic dermatitis are successfully treated by parents and GPs using emollients, corticosteroids and, most importantly, by identifying and avoiding eczema triggers. However, some cases are more severe or slow to respond and need specialist treatment. The NHS eczema specialists work as hospital based multi-disciplinary teams usually made up of:
Eczema nurses Referrals to specialist eczema nurses are usually for demonstrations on how to use emollients and bandages effectively. Eczema nurses will also carry out regular treatment reviews for little ones who have previously been seen by a dermatologist. The eczema nurses are the backbone of NHS eczema services and are senior specialist nurses, specially trained to deal with skin conditions and allergy testing. Its worth remembering that they are part of a multi-disciplinary team and will know when something needs to be referred on to a specialist doctor . A lot of the more experienced eczema parents we talk to actually prefer appointments with the eczema nurses over those with dermatologists.
Allergy specialists if an allergy is suspected to be causing severe eczema, eczema babies and children can be referred to an allergy specialist for further investigation including allergy testing and dietary advice.
Progression Of Eczema In Infants And Children
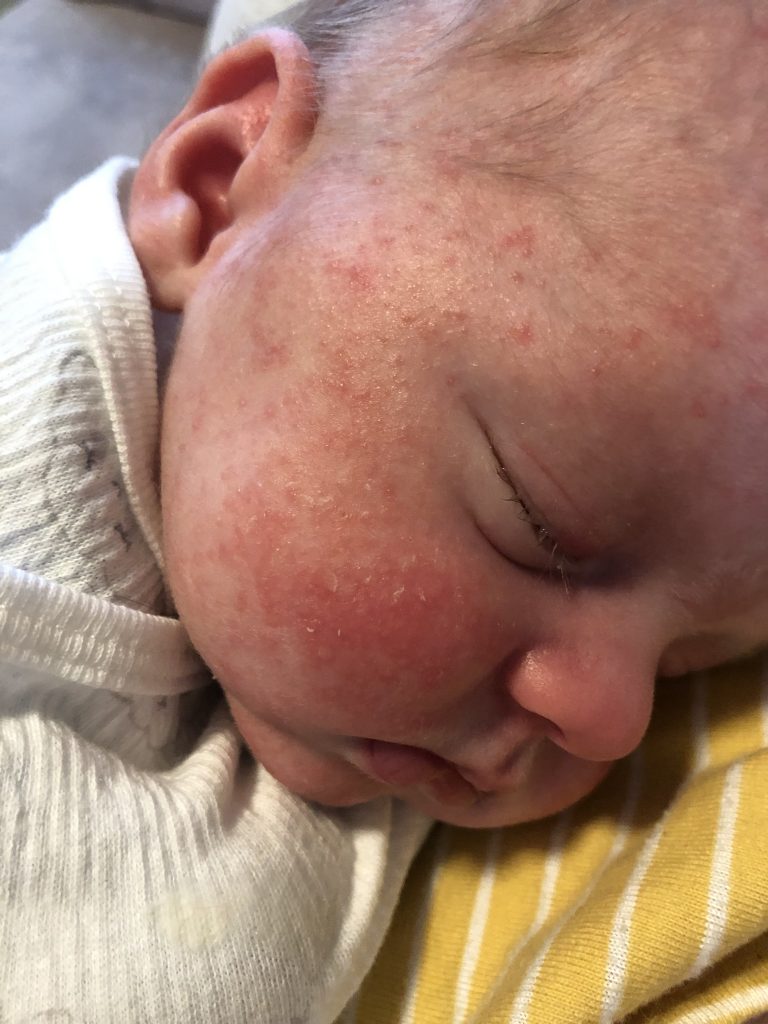
Baby eczema is most prominent on the cheeks, forehead, and scalp of an infant within the first few months of life, and often tends to make the skin look more red and weepy than at other ages.
The eczema can appear on other parts of the body as well, including the diaper area.
When the infant begins to crawl, usually between 6 and 12 months, eczema will typically affect the elbows and knees, which rub on the ground. The eczema rash can become infected, resulting in a yellowish crust or tiny bumps of pus.
When the child is around age 2, eczema may begin to appear on the inside of the elbows and behind the knees, as well as on the wrists, ankles, and hands. It may also appear around the mouth and eyelids.
This eczema tends to be drier, scalier, and thicker .
Don’t Miss: What Are The First Signs Of Eczema
What Do I Do When My Child Has A Flare
Your childs eczema will improve more quickly if it is treated soon after you first notice the rash. Prompt treatment will also reduce the likelihood of complications, so its best to see your doctor or pharmacist at the first sign of a flare-up.
Keep your childs fingernails short to avoid them scratching as much as possible.
Eczema is often treated using a steroid cream or ointment. You should get advice from your doctor or pharmacist about the best one to use for your specific case as different creams are used depending on the part of the body, the severity and the age of the child.
If your childs eczema does not improve after two days of regular treatment or if there are signs of infection, weepy, crusted or broken areas, it is important to see a doctor.
There are many treatments that can be used to treat eczema. For many children, eczema is a condition that comes and goes, and changes in intensity over time, so you may need to see your doctor a few times for the same condition.
What Are The Symptoms Of Atopic Dermatitis In A Child
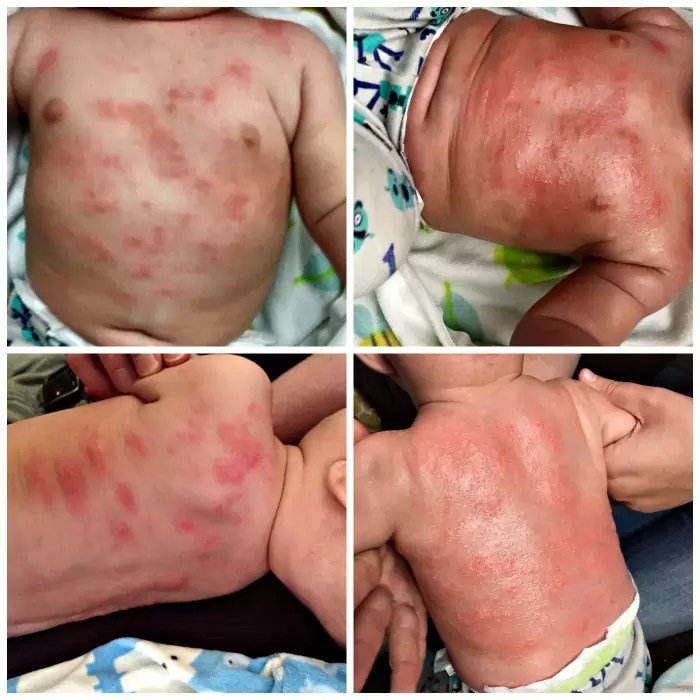
Symptoms may come and go, or occur most or all of the time. Any area of the body may be affected. In babies, symptoms usually affect the face, neck, scalp, elbows, and knees. In children, symptoms usually affect the skin inside the elbows, on the back of the knees, the sides of the neck, around the mouth, and on the wrists, ankles, and hands.
Symptoms can occur a bit differently in each child. They can include:
-
Dry, scaly skin
-
Pale skin on the face
-
Small, raised bumps that may become crusty and leak fluid if scratched
-
Rough bumps on the face, upper arms, and thighs
-
Darkened skin of eyelids or around the eyes
-
Skin changes around the mouth, eyes, or ears
-
Raised, red areas
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis can be like other health conditions. Make sure your child sees his or her healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Also Check: Why Do Newborns Get Eczema
What Causes Eczema In Toddlers
Before you panic that your child will have lifelong bouts of itchy rashes, its important to remember that some kids are just prone to eczema because of their unique skin makeup. And even thats not always fixed or permanent.
Theres no way to predict what will happen in the future, but lots of kids outgrow their eczema when they reach their preschool years.
Your child is more likely to have eczema if they also have:
- a family history of eczema
- asthma
Food allergies dont cause eczema, but they are related.
According to a , other conditions that may be related to eczema may include attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder.
For the most part, though, environmental triggers are the biggest cause of eczema flares. Common triggers include:
- excessive heat or sweating
Although eczema is bothersome and often hard to treat, you can take some steps to get your toddlers eczema under control.
Treating With Topical Steroids
The word topical means something that you apply at the site of the problem. Steroids are substances produced by the body to help the healing process. Steroids produced for medicinal purposes aim to have the same effect. They can be very helpful in treating all manner of illnesses, but taken orally they can have serious side effects, one of which is to restrict growth. This is very unlikely to happen with steroid formulations applied to the skin, but having said that, bear in mind that a babys skin is very permeable. This is why steroid creams and ointments prescribed for babies are usually of a very weak formulation unless there is a special reason for the extra strength in which case the treatment is likely to be only for a short time. Also, strong doses of steroids used over a long length of time can produce thinning, stretch marks and reddening of the skin.
However, topical steroids can reduce itchiness and speed up healing so they are extremely useful in controlling a flare-up of the condition. Used with caution, they can often spare both the baby and parents undue suffering.
If the eczema becomes infected you must see your Doctor straight away. Infected eczema can be tricky to treat on anybody, but a baby obviously has to be very closely monitored.
Recommended Reading: Red Light Therapy For Eczema
Seattle Children’s Urgent Care Locations
If your childâs illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
What Triggers Eczema
Each child with eczema has their own set of individual triggers, although sometimes the condition can flare and subside for no apparent reason.
Examples of common exacerbating factors and triggers in children include:
- Heat avoid overheating with blankets and long hot showers
- Irritants soaps, shampoos, chlorine, chemicals, fragrances, make-up, scratchy clothes and materials
- Allergens dust mite, moulds, grasses, plant pollens, pets, soaps and shampoos, foods
Recommended Reading: Best Moisturizer For Eczema And Acne
What Causes Eczema
The skin of people with eczema has cracks in the barrier so is more sensitive to irritants and more at risk of infection.
A child is more likely to develop eczema if there is a family history of eczema, asthma or hayfever.
Food allergies do not cause eczema although children with eczema have a higher risk of developing food allergy.
What Happens Next
If properly managed in early childhood, eczema can be cleared or well controlled, with minimal need for ongoing treatment. It is advisable to continue to consider the skin as delicate and avoid perfumed body sprays, deodorants, soaps, face wipes and body washes. In terms of employment, there should be few jobs that are unsuitable though hand eczema can be provoked by hairdressing, food preparation or the frequent hand washing required in healthcare professions.
Recommended Reading: Eczema Flare Up On Arms
What Not To Do
Wondering how to treat eczema in babies? Believe it or not, bathing babies or toddlers with eczema may not be as soothing for the skin as you might think. Constant washing can damage vulnerable baby skin, says Dr Hextall. But dont let that put you off enjoying what might be your babys favourite time of day. Lukewarm baths can be kinder and less drying to the skin, and always gently pat skin dry afterwards, she says.
Avoid harsh soaps and heavily fragranced products, too. I would never use a perfumed baby wipe on such vulnerable skin, she adds. Avoid known triggers, try to keep your babys room as cool as possible, and avoid direct sunlight, as heat and sweat can be triggers for eczema. Also, if youve been to the doctor and have been prescribed a topical steroid cream, ensure you apply it regularly and for as long as directed youll need to keep using it alongside their normal moisturisation . Its just as important to keep the skincare barrier hydrated during and post steroid treatment, she says.
How Is It Treated
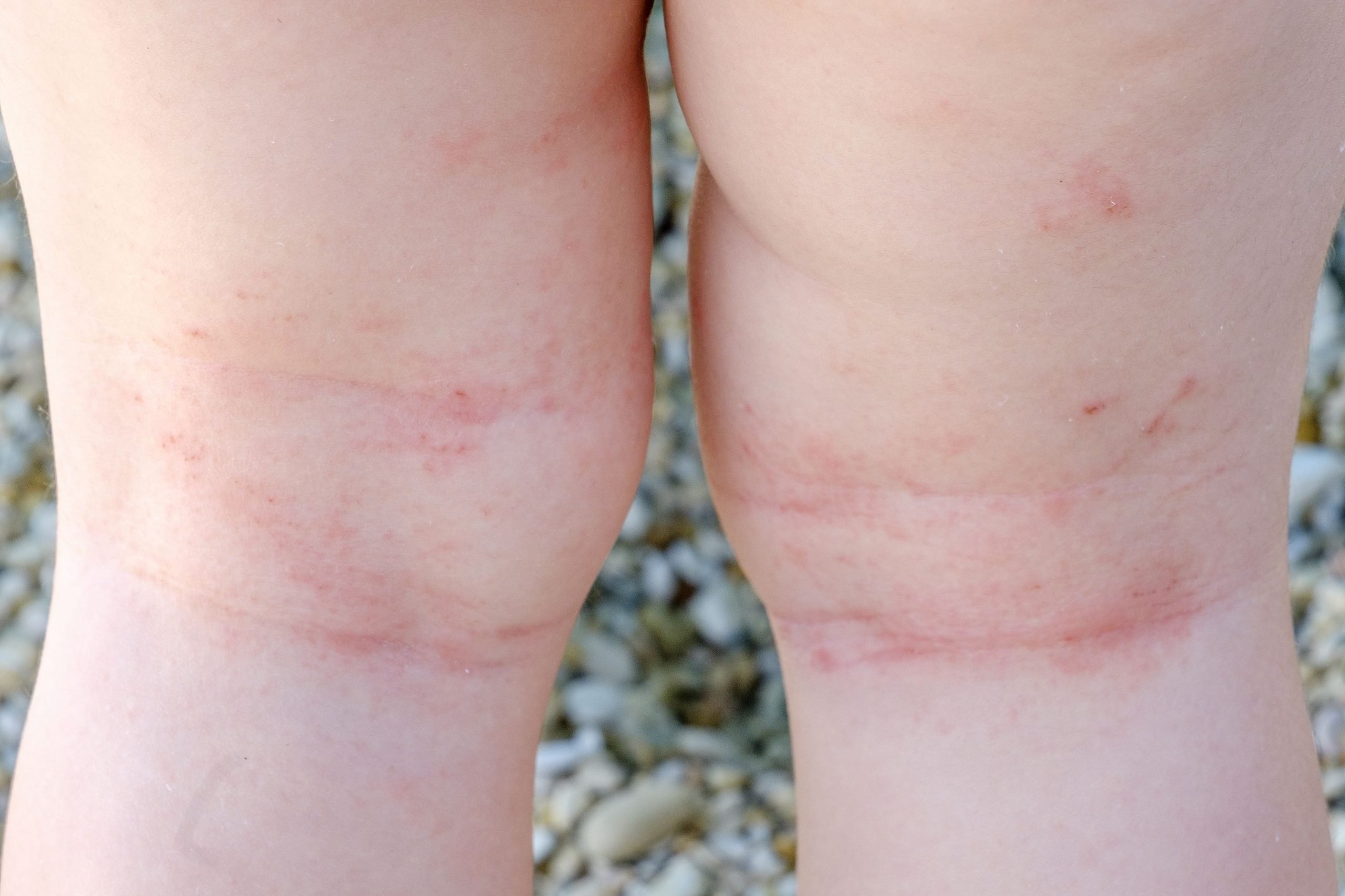
Because there is not yet a cure for eczema, our treatment goals are to reduce itching and skin inflammation, and to prevent infection. The best treatment for eczema is a proactive one, using gentle skin care and moisturizers to re-establish the skin barrier.
Infants and older childrens skin should be kept well moisturized, and washed with fragrance-free non-soap cleansers. We also recommend a fragrance-free ointment-based moisturizer, with petrolatum as either the only or the first ingredient. In young children and infants, it is reasonable to use an over-the-counter topical hydrocortisone ointment, which is a mild topical steroid, for up to a week.
But if the rash either persists or you find that you need to use the hydrocortisone more than one week out of the month, you should discuss further use with your childs pediatrician. You can apply the ointment, as prescribed, then a coat of petrolatum-based moisturizer, to help keep in the moisture.
If your childs skin does not respond well to any of these measures or becomes infected, contact your pediatrician, who can diagnose the condition and then prescribe another topical cream or antihistamine.
You May Like: I Think I Have Eczema