Whats The Difference Between Eczema And Psoriasis
Diagnosing eczema can be tricky sometimes.
Other skin conditions can look like eczema, but a dermatologist can tell the difference. If there is a case where the doctor isnât quite sure, a new genetic test can help them make the appropriate diagnosis.
The underlying cause of the two conditions is different:
- Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition. This means the immune system is not working as it should and skin cells grow too fast, piling up.
- Eczema is more complicated and unknown. Both genetic and environmental factors may be involved.
Psoriasis itching tends to be on the mild side, whereas the itching associated with eczema can be intense.
In older adults, eczema is usually on the backs of the knees and inside of the elbows. Psoriasis is often found on the scalp, elbows, knees, buttocks, and face.
Eczema is more common than psoriasis in children.
Aside from psoriasis, other skin conditions can look like eczema but arenât. Knowing the underlying cause and identifying the condition correctly is the best way to get appropriate treatment.
A dermatologist will be able to diagnose the condition based on:
- your reported symptoms
There is no cure for eczema, but it can be treated and managed. By working with a dermatologist or allergist, you can help reduce your chances of flare-ups, minimize symptoms, and keep your skin healthy.
Treatment is based on three concepts, according to the NEA:
Medication may be OTC or prescription, depending on the type and severity of your eczema.
A Message From Dr Aron
Dr. John Van Wagoner, an eczema specialist for both adults and children, provides an outstanding service for patients in the United States of America. Dr. Van Wagoner has worked closely with me in studying the protocols of the regimen which I have developed for the management of Atopic Eczema. He has visited my clinic in Cape Town, South Africa on two separate occasions to study first hand the tools of management that I use in treatment. Dr. Van Wagoner provides a perfect balance between clinical expertise and compassion for each patient, and I am pleased to be able to say that any parent or patient who is battling atopic skin disease may consult with him in complete confidence.Dr. Van Wagoner is licensed to treat and prescribe in no fewer than thirty-five states and his remit will be extended to other states in the near future.Richard Aron, Creator of the Aron Regimen for the treatment of Atopic Eczema
Recommended Reading: Why Do I Have Eczema On My Arms
Avoiding Atopic Dermatitis Triggers
Everyoneâs eczema is different. Common triggers include stress, sweat, certain chemicals, dust, and pollen. Some foods can trigger flares in infants and children. A symptom diary can help you track your or your childâs triggers so you know what to avoid.
Try these tips to limit contact with triggers:
- Protect your skin, especially when the weather is cold and dry.
- Be careful with soaps, shampoos, and other commercial skin care items. Read the labels carefully.
- Rinse laundry twice to remove detergent residue.
View a slideshow to see top eczema triggers to avoid.
Also Check: Does Acupuncture Work For Eczema
What Are Five Types Of Eczema
Eczema is an inflammatory condition characterized by patches on the skin with severe itching, redness, and dryness anywhere on the body. It can occur in children, teenagers, or adults. Eczema is not contagious. It is a lifelong condition with multiple flare-ups and periods of remission .
There are five different types of eczema:
- Atopic dermatitis: It is the most common type of eczema. Hence, eczema is often called atopic dermatitis. The skin is extremely sensitive to certain substances.
- Contact dermatitis: This is caused by skin contact with irritants. It takes prolonged contact with the irritants for the rash to develop.
- Dyshidrotic dermatitis: It affects the fingers, palms, and soles. There are deep-seated blisters that cause pain. The causative agent may be stress, metal jewelry, or sweat.
- Nummular dermatitis: It usually occurs during the winter. Coin-shaped areas of itching and scaling are seen.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: More commonly called dandruff, it is caused by yeast and is characterized by yellowish flakes over the scalp. It occurs on the scalp and hair-bearing areas such as the eyebrows or eyelids.
Also Check: How To Treat Dyshidrotic Eczema At Home
Physical Examination And Medical History
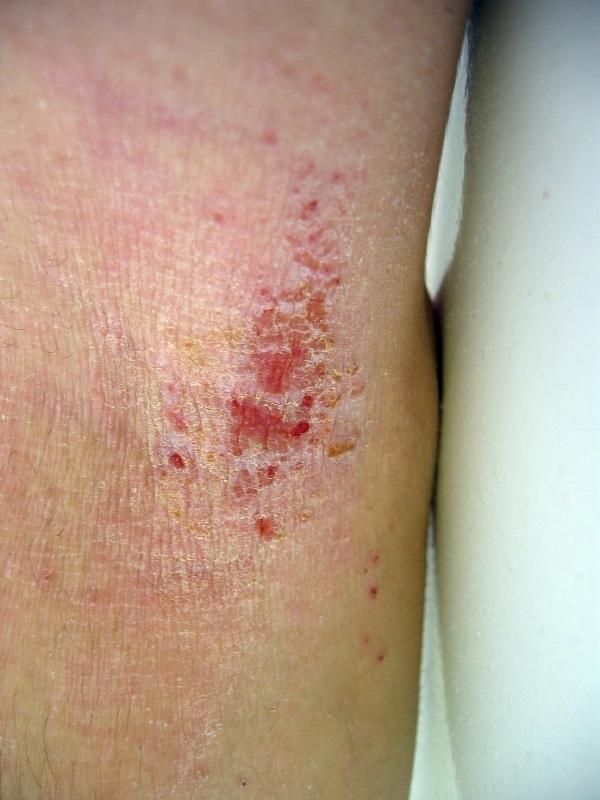
A dermatologist carefully examines your skin during a physical exam. The pattern, location, and appearance of a rash provide our doctors with important information about its causes.
Your doctor may ask questions about when symptoms appeared, what parts of the body they affect, and whether a rash is persistent or comes and goes. They also want to know if there are any noticeable patterns about when the rash appears, such as if there is a seasonal variation or if the rash appears when using certain perfumes or after exposure to certain metals or fabrics. Knowing whether anyone else in your family has been diagnosed with eczema or dermatitis may help doctors better understand your diagnosis.
Doctors may also ask about the personal hygiene products used in your household. Many cosmetics, moisturizers, and soaps contain irritating ingredients that may cause eczema and dermatitis. Our dermatologists can recommend nonirritating, fragrance-free products that have low levels of preservatives. Often, these are available at drugstores in a similar price range as the products you normally buy.
You May Like: Best Body Wash For Eczema Australia
Articles On Atopic Dermatitis
It can be hard to tell for sure if you have atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema. Youâll want to see a dermatologist or other doctor to find out.
At your appointment, your doctor will check your skin and talk with you about your symptoms, your health history in general, and any rashes or allergies that run in your family.
Based on that information, they’ll decide if itâs eczema or something else.
Seattle Childrens Urgent Care Locations
If your childâs illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
Read Also: Does Eczema Cause White Patches
Ask Your Doctor About Skin Infection Risk
Because eczema patients have a weak skin barrier, they are at greater risk for skin infections like staph or the herpes simplex virus.
Bacteria like to live on eczema-prone skin like a parasite, Kim says, adding that one sign of infection is when skin becomes oozy and crusted.
One remedy to treat infections is an antibiotic ointment like bacitracin or Neosporin, which you can find in most pharmacies. These ointments are able to kill bacteria like staph and allow skin to begin healing.
If topical antibiotics arent helping, your doctor may also prescribe oral antibiotics, Kim says. When using topical or oral antibiotics, you should always consult with your doctor to determine how often and how long you should take them.
Emollients For Treating Eczema
Emollient creams add moisture to the skin. Apply moisturisers each day to clean, dry skin. It is especially important to moisturise after showering and bathing, and when living or working in an air-conditioned or heated environment. You may need to try several different brands until you find the emollient that works best for you. Ask your doctor, dermatologist or pharmacist for advice.
Recommended Reading: Rodan And Fields Soothe For Eczema
How Is Contact Dermatitis Treated
Treatment involves working out what allergen or irritant is causing the contact dermatitis and then avoiding it. The rash should clear slowly once you avoid the trigger.
It is possible to have different types of contact dermatitis at the same time. You may need to avoid several different allergens or irritants.
Your doctor may recommend a moisturiser, steroid creams or tablets, or therapy such as ultraviolet light. In severe cases, immunosuppressant medication may be needed.
Try not to scratch the affected skin and keep your nails short so you dont accidentally scratch yourself and break the skin. Your pharmacist or doctor may be able to recommend some products which can help with dry, sore or itchy skin.
Why Choose Mount Sinai
At our Center of Excellence in Eczema directed by Dr. Emma Guttman, MD, we treat eczema patients from all over the world. Thanks to our research efforts, we can offer the most advanced therapies for this condition.
We can also test to see if you have an allergy that is making your eczema worse, or is causing contact dermatitis. We design our patch testing to meet your individual needs. Studies have found that food allergies can make eczema symptoms worse in some children. When appropriate, we may refer you to the food allergy experts of the Elliot and Roslyn Jaffe Food Allergy Institute at Mount Sinai.
We perform laboratory research and conduct clinical trials in eczema therapies. This means our patients have access to the very latest treatments.
Also Check: Is Citric Acid Bad For Eczema
Read Also: O Keeffe’s Working Hands For Eczema
What Are Some Types Of Eczema
There are many kinds of eczema and each has its own particular set of causes, symptoms, and treatments. Some types of eczema include:
- Atopic dermatitis. A type of eczema characterized by dry, itchy, inflamed skin. It is the most common form of eczema and most frequently occurs in children, but can develop in adults. It is associated with certain allergies and asthma.
- Contact dermatitis. This develops due to skin exposure to allergens, chemicals, materials, or other irritants. Symptoms vary depending on the allergen or irritant involved, but can range from reddening to blistering to a burning sensation.
- Dyshidrotic eczema. Also known as pompholyx, this type of eczema is characterized by tiny itchy blisters that resemble tapioca pudding on the palms, fingers, and soles of the feet. It typically occurs in young adults.
- Nummular eczema. Also called discoid dermatitis, this produces itchy, circular patches of inflamed skin that measure 2 to 3 centimeters in diameter. It usually affects the arms and legs.
- Seborrheic dermatitis. A chronic form of eczema that causes inflamed, scaly skin in parts of the body with a high concentration of sebaceous glandsglands that produce a kind of oil called sebumincluding the face, scalp, and chest.
- Lichen simplex chronicus. Also called neurodermatitis, this form of eczema develops as a result of chronic scratching which results in thickened, or lichenified, skin that is usually itchy, dry, and darker than surrounding skin.
Eczema Specialists And Care Centers
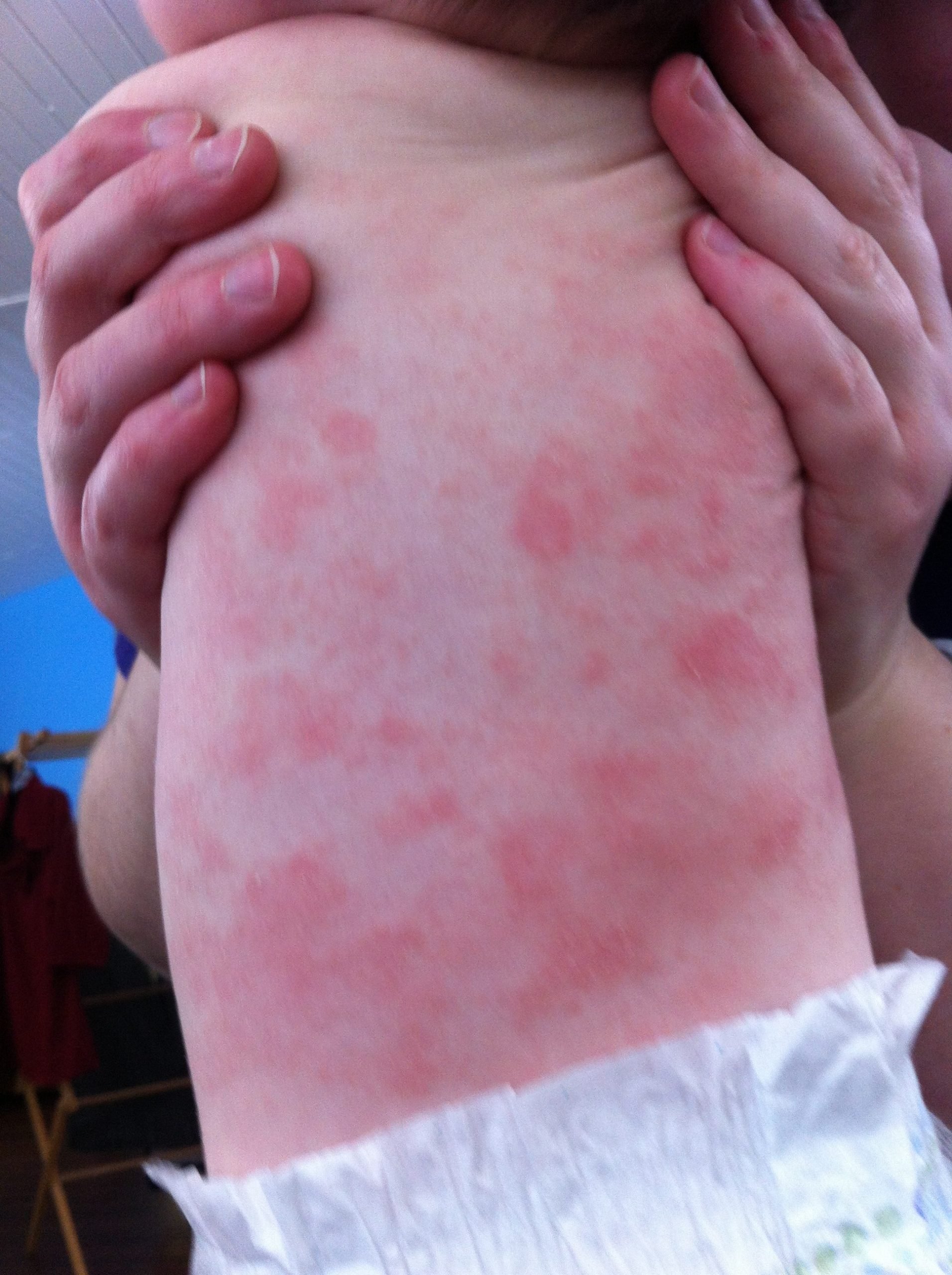
The Northwestern Medicine Multidisciplinary Eczema Center is committed to providing the highest level of care for adults with eczema and contact dermatitis in the Chicagoland area and throughout the Midwest.
NMEC comprises multiple specialty practices for adult eczema care. Our adult eczema practice provides the highest quality dermatologic care for all aspects of eczema skin care. Our Comprehensive Eczema Program provides multidisciplinary care for patients whose eczema is accompanied by certain other medical disorders.
We offer a comprehensive array of diagnostic procedures and consultation including:
- Eczema education and management
You May Like: How To Treat Eczema Under Eyes
Read Also: Can Eczema Be Under The Skin
Best Treatments For Eczema
There is no cure for eczema, and eczema treatment can be complex. There are many types of eczema that all might need a different treatment. However, there may be some self-care and home care practices that you can do to manage your skin and your symptoms.
Medications
- Antibiotics
Home care and remedies
A significant part of eczema treatment is caring for the skin at home and avoiding allergens and triggers. It is important to establish a regular bathing and moisturizing routine to maintain skin health.
To manage your eczema at home, you can:
- Bathe in lukewarm water
- Use a gentle, unscented, fragrance-free cleanser
- Gently pat the skin dry without rubbing
- Apply any topical medications to the area
- Apply a liberal amount of moisturizer all over your body within 3 minutes of your shower
- Apply a dressing or wet wrap
- Avoid scratching the skin
- Avoid harsh soaps, lotions, or detergents
You may find that a bath soothes the skin. Some bath treatments that might help include soaking in a full tub of lukewarm water with one of the following:
- ¼ cup of baking soda to relieve itching
- ½ cup of regular bleach to help with skin infections
- 1 cup table salt to relieve stinging
Managing stress is also an important piece of your eczema treatment.
Alternative therapies
Some complementary therapies may also help eczema. These include:
- Coconut oil as a moisturizer
- Sunflower oil as a moisturizer
- Topical vitamin B12
Eczema Support Team Assemble
OKyouve got your primary care physician and hopefully your eczema specialist, such as a dermatologist or allergist. Now who are some other people you can add to your eczema support team?
- Nurses, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, or pharmacists: You can gain valuable insights by talking to these medical professionals about medication or skin care.
- Dietitians: If youve found that food can trigger symptoms or youre looking for nutrition tips, it might help to consult a registered dietitian.
- Therapists or counselors: If eczema is affecting your emotional well-being, a trusted counselor or mental health professional can be a great additional resource.
Get started now and
You May Like: Does Stress Cause Eczema To Flare Up
Other Types Of Eczema
Eczema is the name for a group of skin conditions that cause dry, irritated skin.
Other types of eczema include:
- discoid eczema a type of eczema that occurs in circular or oval patches on the skin
- contact dermatitis a type of eczema that occurs when the body comes into contact with a particular substance
- varicose eczema a type of eczema that most often affects the lower legs and is caused by problems with the flow of blood through the leg veins
- seborrhoeic eczema a type of eczema where red, scaly patches develop on the sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears and scalp
- dyshidrotic eczema a type of eczema that causes tiny blisters to erupt across the palms of the hands
Page last reviewed: 05 December 2019 Next review due: 05 December 2022
What Is The Underlying Cause For Eczema
Medical researchers acknowledge the fact that there is no proven cause of eczema. However, most of them believe that a combination of genes and an external or internal trigger can lead to eczema.
Research shows that most of the patients who suffer from this condition tend to have an over-reactive immune system that produces the inflammation when triggered by either internal environment or external substances. It is this inflammation that causes the itchy and sometimes painful symptoms of eczema.
Research has also revealed that some patients with dermatitis have a gene mutation responsible for creating filaggrin a special protein which primary role is to help your body maintain a healthy and protective barrier on the top layer of your skin.
If your body fails to produce enough filaggrin to build the protective layer, you end up losing a lot of moisture, letting in bacteria and other viruses ultimately leading to chronic inflammation. This is the primary reason why many individuals with dermatitis have dry and infection-prone skin.
Don’t Miss: Eczema Around Eyes And Mouth
Allergist Or Dermatologist In Sarasota Florida
Whether you want to see an allergist or a dermatologist, you can find the care you need at Intercoastal Medical Group. All allergists in our practice are highly skilled and will get to the root of your symptoms. Alternatively, our board-certified dermatologists can diagnose and treat any skin-related problem you are experiencing.
If you need help selecting which physician to see, we are happy to help. We have multiple locations throughout Sarasota and Bradenton to serve you. Call one of them today, or use our convenient online appointment request form.
You May Like: What Causes Eczema Flare Ups On Arms
Medicines For Atopic Dermatitis
If your doctor decides you need meds to treat your eczema, those may include:
Hydrocortisone. Over-the-counter cream or ointment versions of it may help mild eczema. If yours is severe, you may need a prescription dose.
Antihistamines. Ones you take by mouth are available over-the-counter and may help relieve symptoms. Some of these make you drowsy, but others donât.
Corticosteroids. Your doctor may prescribe these if other treatments donât work. Always follow your doctor’s directions when taking steroids by mouth.
Drugs that work on your immune system. Your doctor may consider these medicines — such as azathioprine, cyclosporine, or methotrexate — if other treatments donât help. There are also prescription creams and ointments that treat eczema by controlling inflammation and reducing immune system reactions. Examples include pimecrolimus , which is a cream, and crisaborole and tacrolimus , which are ointments. You should only use these for a short time if other treatments don’t work — and you should never use them on kids younger than 2, according to the FDA.
Injectables. Dupilumab is an injectable medicine for moderate to severe eczema. It works by controlling the bodyâs inflammatory response. This medicine is given every 2 weeks as an injection and should only be used by people 12 and older.
Prescription-strength moisturizers. These support the skinâs barrier.
Find out which eczema treatment is right for you.
Also Check: What To Do If You Have Eczema On Your Eyelids