Causes Of Discoid Eczema
The cause of discoid eczema is unknown, although it may happen as a result of having particularly dry skin.
When your skin is very dry it cannot provide an effective barrier against substances that come into contact with it. This could allow a previously harmless substance, such as soap, to irritate your skin.
Its important to look carefully at all the chemicals in cosmetics and toiletries that may have come into contact with your skin. Contact dermatitis, a type of eczema caused by coming into contact with a particular irritant, may have a role in discoid eczema.
Some people with discoid eczema also have a history of atopic eczema, which often happens in people who are prone to asthma and hay fever. However, unlike atopic eczema, discoid eczema does not seem to run in families.
Read Also: Is Eczema An Autoimmune Disease
What Is Yale Medicines Approach To Treating Allergic Contact Dermatitis
According to Dr. Choate, one thing that sets Yale Medicine dermatologists apart is their willingness to aggressively pursue results.
Our physicians are really dedicated to getting answers, Dr. Choate says. “If a patient is having recurrent episodes and comes to us, we look at the rash and say, ‘Gosh, that has features of allergic contact dermatitis.’ Then we actually go and we find the answer to what is causing the reaction by using the patch-test approach.
Eczema Coping Tips Diet
In most cases, eczema isnt caused or made worse by diet. If you notice that your eczema seems to get worse after eating a particular food, you may be an exception to this. See your doctor or dietitian for proper allergy testing and dietary advice.Never self-diagnose or you risk depriving yourself of enjoyable and nutritious foods for no good reason. Unnecessarily avoiding certain foods can lead to nutritional deficiencies.
You May Like: How To Treat Eczema On Breast
Conditions That Can Look Like Eczema But Arent
Evan Starkman Brunilda Nazario, MD
Eczema is the name for a group of conditions that can make your skin irritated, inflamed, and itchy. Your doctor may call it atopic dermatitis, which is also the most common type of eczema. Youâre more likely to get eczema when youâre a child, but adults can get it, too.
The symptoms you have and where they show up on your body vary from person to person. You might have one or more of these signs:
- Red patches on white skin
- Gray or violet-brown patches on dark skin
- Oozing or crusty skin from scratching
- Swelling
Several health problems can bring on similar symptoms, so itâs important to talk to your doctor, a dermatologist, or an allergist to find out whatâs going on with your skin. They might tell you that you have one of these conditions that looks like eczema but isnât:
Psoriasis. This long-term condition is partly due to your immune system attacking your skin by mistake. Both psoriasis and eczema can bring on symptoms like:
- Red, scaly patches
- Dry, cracked skin
- Itching
Eczema patches tend to be thinner than psoriasis patches. Another difference: Fluid can ooze from your skin with eczema.
Scabies. This contagious condition happens when tiny bugs called mites burrow into the top layer of your skin and lay eggs. You might have symptoms like bad itching and a rash that looks like pimples. Like eczema, you could also get scaly-looking patches.
Acne. This skin condition can take several forms, including:
Show Sources
Causes Of Atopic Eczema
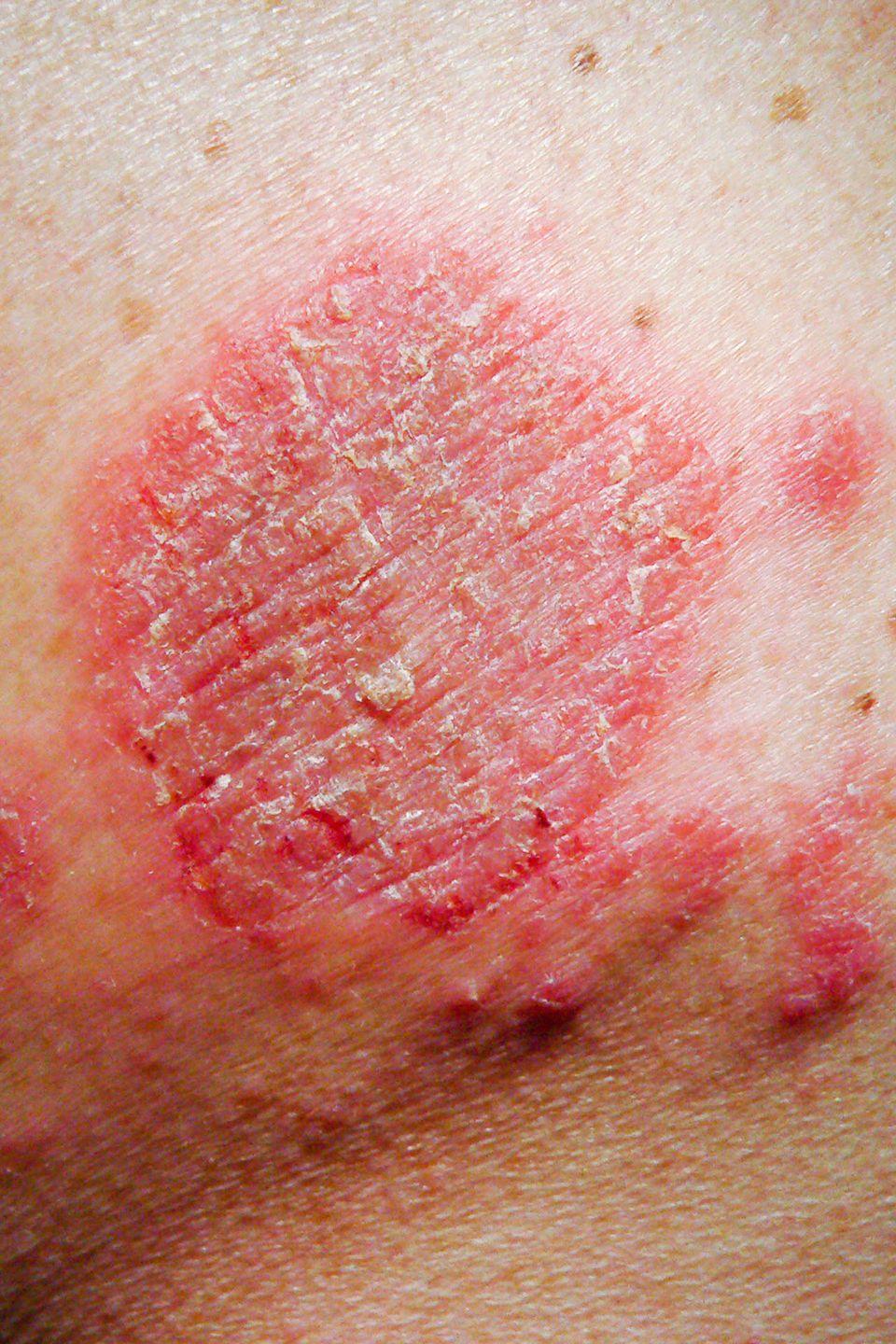
The exact cause of atopic eczema is unknown, but it’s clear it is not down to one single thing.
Atopic eczema often occurs in people who get allergies. “Atopic” means sensitivity to allergens.
It can run in families, and often develops alongside other conditions, such as asthma and hay fever.
The symptoms of atopic eczema often have certain triggers, such as soaps, detergents, stress and the weather.
Sometimes food allergies can play a part, especially in young children with severe eczema.
You may be asked to keep a food diary to try to determine whether a specific food makes your symptoms worse.
Allergy tests are not usually needed, although they’re sometimes helpful in identifying whether a food allergy may be triggering symptoms.
Don’t Miss: What Kind Of Doctor To See For Eczema
What Do All Of The Seven Types Of Eczema Have In Common
If you live with eczema, you probably know the answer to this one: they itch! All different types of eczema share the universal symptom of pruritus, or itchiness. But thats not all. Dr. Lio explained that all seven types of eczema are also type 2 inflammatory skin conditions that share some of the same signalling molecules such as IL-4, IL-13 and IL-31. In other words, there is a biological commonality underlying all seven types of eczema. For more information about itch, check out our recent article The Complex Science of Itch.
An Emollient Cream Or Ointment
An emollient cream or ointment helps moisturize the dry, scaly, eczema-ridden skin to make it less irritated and itchy. Moisturizing the skin religiously also helps strengthen its natural barrier function to prevent further damage or infections.
You must continue applying the emollient even after the rash clears and other medications have been stopped as part of your daily skin care routine.
In fact, the doctor may even recommend emollient soaps instead of the regular detergent-based soaps that can strip the moisture from your skin and make it even more irritated.
Also Check: How To Get Rid Of Eczema On Feet
Types Of Eczema & Dermatitis
Eczema and dermatitis are common conditions that cause skin inflammation. This inflammation can affect people of all ages and may result in redness, bumps, dryness, cracking, or a scaly texture. Often, skin affected by eczema and dermatitis is so intensely itchy that people may not be able to resist scratching, especially at night.
Eczema and dermatitis are neither contagious nor life threatening. But skin inflammation may cause physical and social discomfort. Rashes may develop anywhere on the body but can be especially uncomfortable when they appear on the face and hands.
Understanding the types of eczema and dermatitis can be difficult sometimes, the terms eczema and dermatitis are used interchangeably in casual conversation. Our dermatologists differentiate between them because treatments may differ.
Other Types Of Eczema
Eczema is the name for a group of skin conditions that cause dry, irritated skin. Other types of eczema include:
- atopic eczema the most common type of eczema, it often runs in families and is linked to other conditions such as asthma and hay fever
- contact dermatitis a type of eczema that happens when the skin comes into contact with a particular substance
- varicose eczema a type of eczema that usually affects the lower legs and is caused by problems with the flow of blood through the leg veins
Page last reviewed: 30 October 2019 Next review due: 30 October 2022
Anyone young and old can get dermatitis. Some examples include:
- Your baby can get cradle cap and diaper rash.
- Atopic dermatitis usually begins in childhood, but anyone at any age can get it.
- Anyone can get contact dermatitis as it just involves skin to substance contact.
- Individuals with celiac disease are prone to dermatitis herpetiformis.
There are several factors that put you at risk of getting dermatitis. Some examples include:
Atopic dermatitis risk factors include:
- A family history of dermatitis, hay fever or asthma.
- Being female.
Contact dermatitis risk factors include:
- If you work around chemicals such as in a factory, restaurant or garden.
Periorificial dermatitis risk factors include:
- Being female.
- Being ages 15 to 45.
Dyshidrotic dermatitis risk factors include:
- If you sweat a lot.
- Prolonged exposed to water and/or irritants.
- If you live in a warmer climate.
Also Check: Topical Zinc Oxide For Eczema
How Is Eczema Treated
There is no cure for eczema. But treatments can help with symptoms. The doctor will recommend different treatments based on how severe the symptoms are, the child’s age, and where the rash is. Some are “topical” and applied to the skin. Others are taken by mouth.
Topical moisturizers. Skin should be moisturized often . The best time to apply moisturizer is after a bath or shower, with the skin patted dry gently. Ointments and creams are best because they contain a lot of oil. Lotions have too much water to be helpful.
Topical corticosteroids, also called cortisone or steroid creams or ointments. These ease skin inflammation. It’s important not to use a topical steroid prescribed for someone else. These creams and ointments vary in strength, and using the wrong strength in sensitive areas can damage the skin, especially in infants.
Other topical anti-inflammatory medicines. These include medicines that change the way the skin’s immune system reacts.
Medicine taken by mouth. These can include antihistamines to help itchy kids sleep better at night, antibiotics if a rash gets infected by bacteria, and corticosteroid pills or other medicines that suppress the immune system.
Other types of treatment can include:
- wet wraps: damp cloths placed on irritated areas of skin
- bleach baths: bathing in very diluted bleach solution
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider About Eczema
- How can you tell that I have eczema?
- If I dont have eczema, what other skin condition might I have?
- Is there a specific brand of moisturizer that you recommend?
- Is there a prescription cream that you can prescribe?
- How often should I see a dermatologist regarding my eczema?
- What soaps, lotions, makeup, etc. should I avoid?
- What medications do you recommend?
- What at-home treatments do you recommend?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Eczema is very normal, very common, and very, very uncomfortable. It can affect your quality of life. At its worse it can keep you from sleeping, distract you and make you feel self-conscious in public. See your dermatologist or other healthcare provider as soon as you start to see signs of it. Explore at-home remedies and prescribed treatments.
Youre not alone! 15% to 20% of people experience eczema or another type of dermatitis at some point in their lives.
Recommended Reading: What Is Eczema And What Causes It
Whats Eczema And What Does It Look Like
Unlike heat rash which usually clears up fairly quickly, eczema is a long-term, chronic condition that needs treatment and ongoing management.
It tends to develop in infancy or childhood, and is very common in children. In fact, it affects between 10 and 20 percent of children.
Eczema, which is also known as atopic dermatitis, can and does persist into adulthood for more than 16 million adults. If you first developed eczema in childhood, you may have learned to recognize the hallmarks of an eczema flare-up by now.
But it might be harder for an adult who develops what dermatologists call adult-onset atopic dermatitis. It may also be more challenging for a parent whos not sure whether their child has eczema or just a heat rash.
The Different Types Of Eczema
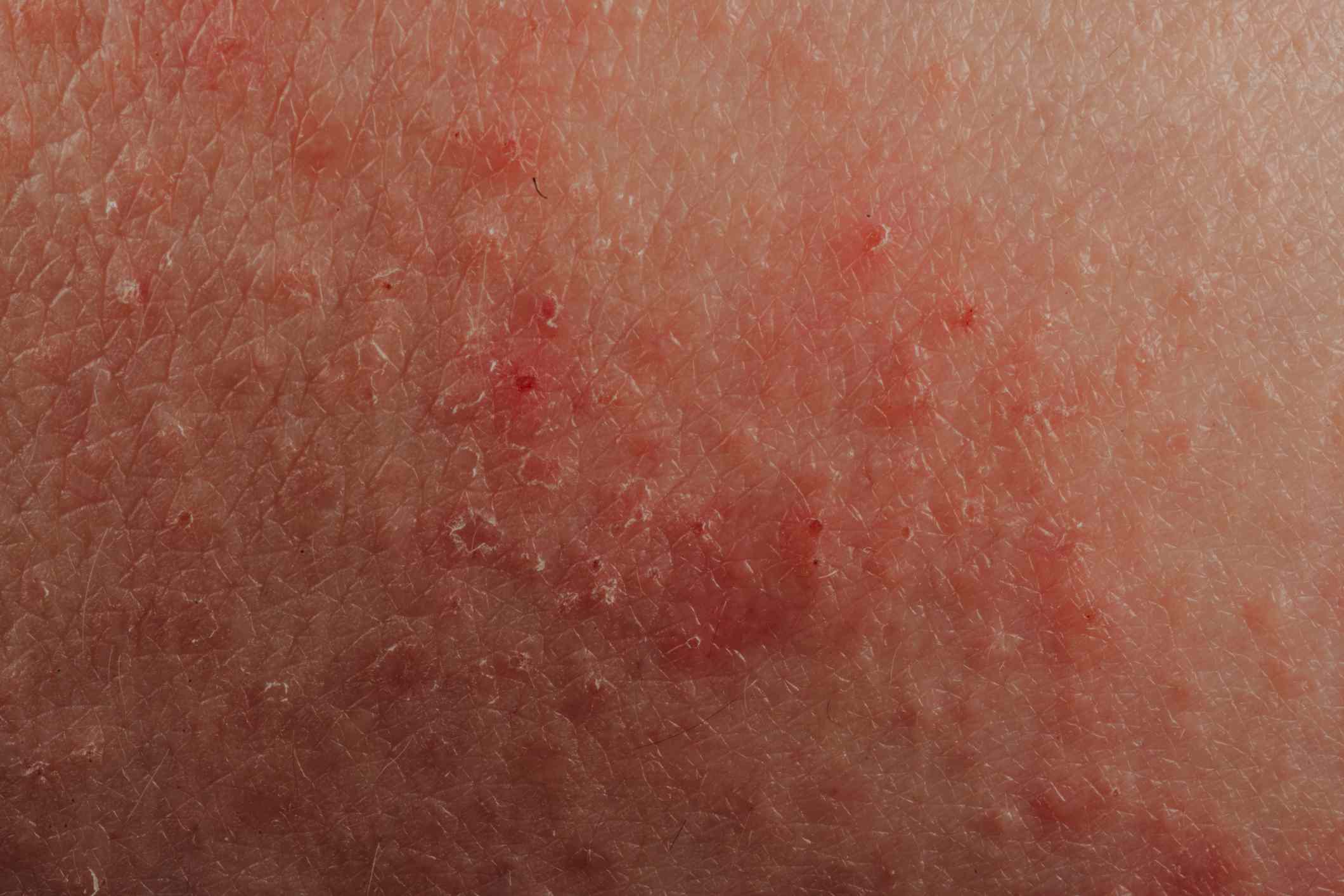
There are actually many different kinds of eczema. In fact, experts tend to group them into seven specific types.
The most common is called atopic dermatitis. It affects more than 26 million people in the United States. Atopic dermatitis tends to develop in the first 6 months of life, but it can also develop later.
Atopic dermatitis is characterized by dry, itchy skin. The color of the rash tends to be:
- reddish in people with lighter skin tones
- brown or gray in people with darker skin
Sometimes your skin will get thicker in patches where the rash appears. It has a genetic component, but your immune system and environmental triggers may also play a role.
According to the National Eczema Association, the other six types of eczema include:
Its important to note that different kinds of eczema can overlap. In other words, you could have more than one kind at the same time. And they may require different treatment or management strategies.
Because heat rash and eczema can look similar to each other, its not always easy to tell them apart. If you cant tell by looking at the rash, its important to consider the following factors.
Read Also: Is Ice Good For Eczema
Where Does Dermatitis Form On The Body
The location of your dermatitis depends on the type. For example, atopic dermatitis can appear anywhere on your skin. But, in teens and adults, its typically on the hands, inner elbows, neck, knees, ankles, feet and around the eyes. Seborrheic dermatitis and cradle cap are typically on your scalp, face and ears. Periorificial dermatitis is found around your eyes, mouth, nostrils and sometimes the genitals.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Eczema On Lips
Helping Your Child Feel Better
If your child has eczema, keep their fingernails short and their skin moisturized. Dress them in loose-fitting clothes and make sure they dont get overheated. Depending on how severe their eczema is, your doctor may recommend wet wraps, a diluted bleach bath, over-the-counter or prescription medications, and/or light therapy to help.
Read Also: Http Healthh Com Dyshidrotic Eczema
Also Check: Best Medication For Eczema And Psoriasis
What Is Eczema What Does It Look And Feel Like
Eczema is a condition that causes your skin to become dry, red, itchy and bumpy. Its one of many types of dermatitis. Eczema damages the skin barrier function . This loss of barrier function makes your skin more sensitive and more prone to infection and dryness.
Eczema doesnt harm your body. It doesnt mean that your skin is dirty or infected, and its not contagious. There are treatments that can help manage your symptoms.
In the word dermatitis, derm means skin and itis means inflammation. The word as a whole means inflammation of the skin. Eczema originates from the Greek word ekzein which means to boil over or break out.
Read Also: What Is The Best Treatment For Eczema
How Is Eczema Treated What Medications Are Used
Treating eczema can be difficult if the cause is something you cant control, like genetics. Fortunately, you may have some influence over your environment and stress levels. Do your best to figure out what triggers or worsens your eczema, and then avoid it. The goal is to reduce itching and discomfort and prevent infection and additional flare-ups.
Consider these treatment tips:
If your child has skin problems, such as eczema, you can:
- Avoid long, hot baths, which can dry the skin. Use lukewarm water instead and give your child sponge baths.
- Apply lotion immediately after bathing while the skin is still moist. This will help trap moisture in the skin.
- Keep the room temperature as regular as possible. Changes in room temperature and humidity can dry the skin.
- Keep your child dressed in cotton. Wool, silk and manmade fabrics such as polyester can irritate the skin.
- Use mild laundry soap and make sure that clothes are well rinsed.
- Watch for skin infections. Contact your healthcare provider if you notice an infection.
- Help them avoid rubbing or scratching the rash.
- Use moisturizers several times daily. In infants with eczema, moisturizing on a regular basis is extremely helpful.
Don’t Miss: Get Rid Of Eczema Scars
What Questions Might My Healthcare Provider Ask To Diagnose Eczema
The conversation with your healthcare provider will need to cover a lot of information. Be sure to be specific about your symptoms.
- Where is your eczema located?
- What have you used to try to treat your eczema?
- What medical conditions do you have? Allergies? Asthma?
- Is there a history of eczema in your family?
- How long have you had symptoms of eczema?
- Do you take hot showers?
- Is there anything that makes your symptoms worse?
- Have you noticed that something triggers or worsens your eczema? Soaps? Detergents? Cigarette smoke?
- Is there so much itchiness that you have trouble sleeping? Working? Living your normal life?
How Is Atopic Eczema Diagnosed
There is no single test used to diagnose eczema, but there are a few things doctors use to tell if you have eczema:
Physical exam and review of medical history. Along with examining the rash, your doctor may ask when symptoms appeared and what happened around that time. For example, did you:
- Go hiking?
- Use a new product, like laundry detergent?
- Go to the hairdresser for hair color, a perm or other treatment?
Patch test. Certain types of dermatitis might suggest contact allergy. If your doctor suspects contact dermatitis, they may ask you to wear skin patches containing small amounts of possible allergens for two days. If you are allergic to the substance, you should develop a local itchy rash. The doctor will do a follow-up exam to check your reaction, usually two days after you remove the patch.
The doctor may need to see you more than once to make an accurate diagnosis. If you are seeing a general doctor, they may refer you to a specialist like a dermatologist or allergist.
Read Also: What Can Stop Eczema Itching
Is Eczema Contagious
No. You canât catch eczema from someone or pass it on to others. Eczema doesnât mean that your skin is infected or that it spreads from person to person. Some people might assume that eczema may be contagious because it often tends to run in families. But eczema can arise from several factors, including your immune system, your genes, the environment, and other things that cause your skin barrier to be faulty.
Still, eczema can lead to skin infections from scratching or cracking. That can break down your skinâs barrier against bacteria and other germs.
What To Watch For
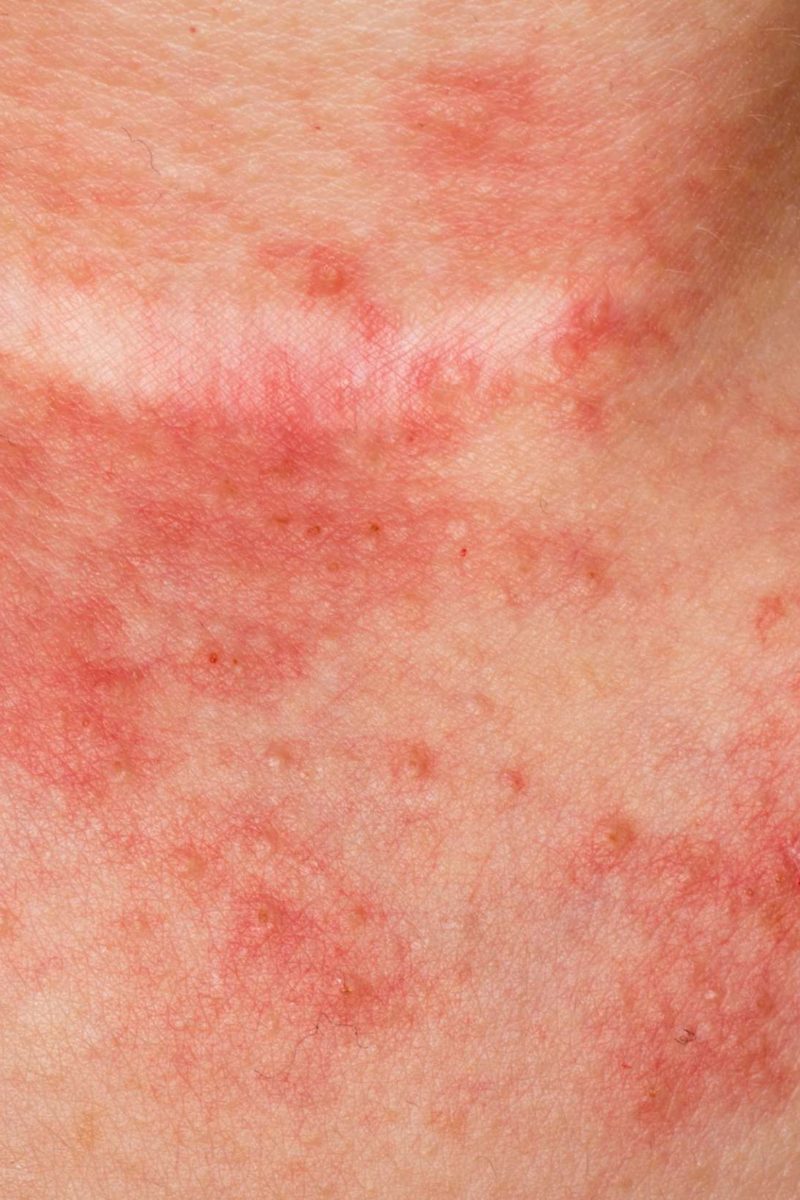
When atopic dermatitis gets out of control, serious complications can occur. You may get bacterial or viral skin infections that can spread over large parts of the body. When atopic dermatitis isnt well controlled, it can lead to nighttime scratching, poor sleep, learning difficulties, and behavior problems. Severe cases can even lead to growth problems over time.
It is incredibly important to seek care from a dermatologist who can help establish best practices to keep it as well controlled as possible, says Dr. Browning.
kitzcorner/ Shutterstock
You May Like: How Do You Treat Eczema On Your Face
You May Like: Best Over The Counter Medicine For Eczema