What About Babies With Eczema
It is easy for adults to change their diets. But it is a different story for breastfed babies with eczema.
You may be wondering what foods cause eczema in breastfed babies the truth is the mother’s diet could affect the baby.
Therefore, examine your diet if you notice an increase in your baby’s severity of eczema symptoms.
To be specific, tree nuts, cow’s milk, and peanuts are among foods that cause eczema in susceptible babies.
Also, baby formula products might contain eczema triggers. Therefore, you might want to switch from a milk-based formula to a hydrolyzed one. This type is less likely to cause eczema flare-ups.
The Sun Sweat And Sunscreen
You can be out in the sun, but your skin may not like getting hot and sweaty. If so, stay cool and seek out shade. Always wear sunscreen. Sunburns inflame your skin and can lead to an eczema flare. If youre sensitive to sunscreens, block out burning rays with mineral versions, like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide. Sunscreens made for the face may also give you gentle protection.
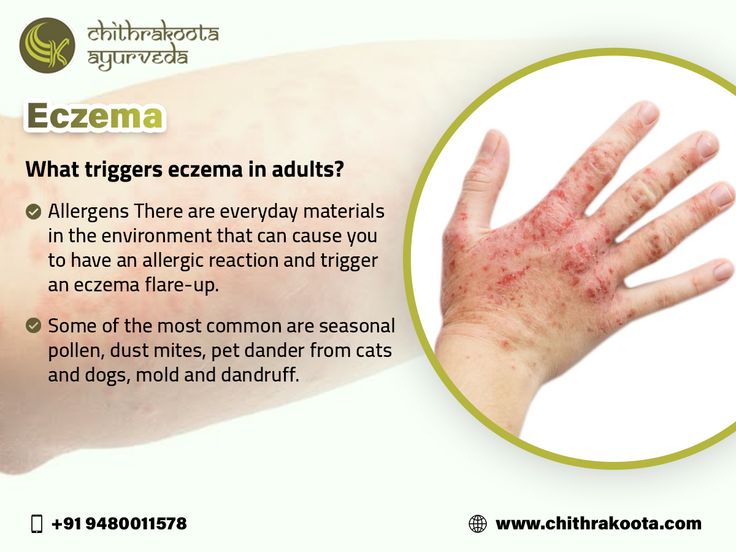
Can Allergies Cause Eczema To Flare Up
Allergies to foods as well as seasonal allergies can cause a flare-up of eczema for some people. Allergies to mold, dust mites, and pet dander can also cause eczema to flare up.
If you have any allergies to these substances, they may trigger the inflammatory response that can make your eczema symptoms worse.
Its important to know, however, that eczema is different for everyone. Just because you have an allergy to a particular food or substance doesnt necessarily mean that allergy will cause a flare-up of eczema.
Don’t Miss: Best Hand Cream For Severe Eczema
What Else Can I Do To Help Control My Child’s Eczema
- Keep your child’s finger nails short and clean. This can help prevent an infection if skin gets scratched
- Use unscented laundry products and avoid dryer sheets.
- Wash new clothes and remove tags before your child wears them.
- Dress your child in loose rather than tight clothes.
- If your child’s eczema is hard to keep well controlled, get help from health care providers who have expertise in eczema care.
Topical Application Of Edible Oils
Sometimes certain foods can be beneficial not as foods, but when used as topical treatments for eczema. The National Eczema Foundation suggests using virgin/cold pressed coconut oil on your skin to limit the staph bacteria on your skin, cutting the risk of an infection. Simply apply the oil to damp skin for best results. Another edible oil, sunflower oil, can also help the skin due to its anti-inflammatory properties. As with coconut oil, be sure youre using a pure form of the oil thats additive-free. Both oils can help retain the moisture in your skin by acting as a natural barrier between the air and your skin. This reduces dryness and helps cut the itchy feeling so typical of eczema. You can safely use these oils twice a day, but only if you arent allergic to them.10
You May Like: Can You Get Eczema On Your Neck
Common Allergens That Trigger Eczema Flares
While it is still not possible to cure eczema or prevent a flare, it is possible to manage the condition and reduce the number of uncomfortable red, rashy outbreaks. Research suggests that those living with eczema tend to have an overactive immune system response when substances, either inside or outside of the body, trigger an alert within the system.
Many people with eczema also have a history of allergies, like hay fever, asthma, or food allergies. Those who do not have allergies at the time their eczema surfaces have a 40 percent higher risk of developing allergic conditions later in life. When food allergies are suspected of causing skin reactions, the removal of suspected foods could improve skin symptoms.
How To Prevent Eczema From The Inside Out
Here are two ways to treat your eczema naturally:
12-week low chemical diet
The Eczema Detox is a healthy low chemical diet that is low in sugar and totally free of glutamates/MSG, preservatives/additives and dairy. It also has plenty of gluten-free and vegan options.
The Eczema Detox, which was published in 2018 and is the new version of The Eczema Diet, also shows you how to successfully diagnose food intolerances and chemical intolerances , so you know what to avoid and what to eat to become eczema free.
Skin friendly supplements
There are a range of nutrients to help prevent chemical sensitivity and repair eczema-prone skin, including magnesium, molybdenum, zinc, biotin, vitamin B6 and a range of vitamins to deactivate salicylates and other itch-promoting chemicals. Molybdenum deactivates sulphite preservatives and amines anti-histamine vitamin C and vitamin B6 to help reduce allergic reactions .
But it’s also what you avoid that can make a difference… Supplements usually contain hidden additives that can cause adverse reactions if you are a sensitive type of person that is prone to eczema.
Skin Friend AM is the supplement I created to prevent my daughter’s eczema more than fifteen years ago. It took years of testing before I felt confident that it could help others, and I worked with hundreds of eczema patients who tried the product and provided feedback for years before this product was manufactured in bulk and sold online.
Don’t Miss: Steroid Ear Drops For Eczema
Detergents Soaps And Shampoos
When you wash your body or your clothes, think gentle. Choose laundry detergent made for babies or sensitive skin, like fragrance-free types. Use only the amount suggested. If needed, rinse them twice. Skip fabric softeners and scented dryer sheets. For showers, pick a non-soap cleanser that is mild and fragrance-free. Shampoos are also available in clear, pH neutral, fragrance-free versions.
Scientists Identify Unique Subtype Of Eczema Linked To Food Allergy
Children with both conditions have abnormal skin near eczema lesions, NIH-funded research finds
Atopic dermatitis, a common inflammatory skin condition also known as allergic eczema, affects nearly 20 percent of children, 30 percent of whom also have food allergies. Scientists have now found that children with both atopic dermatitis and food allergy have structural and molecular differences in the top layers of healthy-looking skin near the eczema lesions, whereas children with atopic dermatitis alone do not. Defining these differences may help identify children at elevated risk for developing food allergies, according to research published online today in Science Translational Medicine. The research was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases , part of the National Institutes of Health.
Children and families affected by food allergies must constantly guard against an accidental exposure to foods that could cause life-threatening allergic reactions, said NIAID Director Anthony S. Fauci, M.D. Eczema is a risk factor for developing food allergies, and thus early intervention to protect the skin may be one key to preventing food allergy.
Children with atopic dermatitis develop patches of dry, itchy, scaly skin caused by allergic inflammation. Atopic dermatitis symptoms range from minor itchiness to extreme discomfort that can disrupt a childs sleep and can lead to recurrent infections in scratched, broken skin.
Read Also: Best Products For Baby Eczema
What Are Other Ways To Help Prevent Food Allergy
Many health professionals now think there are two steps parents can take to help prevent food allergy.
Health Canada recommends introducing solid foods to babies starting at six months of age. Babies with eczema should also be offered solid foods starting at six months.
You can introduce boneless fish, egg, peanuts, tree nuts, and sesame seeds in age appropriate forms starting at six months of age if you wish. Whole tree nuts and big globs of peanut butter are choking hazards. You can start by offering peanut, tree nut and sesame seed butters mixed into infant cereal.
When your baby is ready for finger foods, you can offer these foods spread thinly on small strips of toast. For more information about introducing solid foods to babies, see “Baby’s First Foods” and “Reducing Risk of Food Allergy in Your Baby“.
Since 2008, the American Academy of Pediatrics no longer recommends delaying the introduction of foods such as fish, eggs and foods that contain peanut protein beyond 4 to 6 months of age to babies at increased risk for allergy.
Can Food Allergies Cause Eczema
Its no secret that what we eat has a big impact on our overall health. And while there is a lot of debate about the role food allergies play in causingeczema, research suggests that certain foods may contribute to eczema flare ups and that people with eczema prone skin are more likely to also suffer from some type of food allergy or food intolerance.
Allergic reactions to food can also worsen skin problems, causing hives, itching, and redness.
You May Like: Robitussin Flu Medicine
You May Like: Why Is My Eczema Worse In The Morning
Food Allergic Reactions: What Triggers Them
Our immune systems protect our bodies from foreign invaders, like viruses and bacteria. But when someone eats a food they are allergic to, their immune system mistakes the proteins of that food for a foreign invader. The immune system signals their body to over-defend itself against those food proteins, and this triggers an allergic reaction.
Why Does My Skin Become Irritated
Itchy, irritated skin can be triggered by many factors, ranging from dry skin to certain fabrics, and even food allergies.
Eczema and food allergies often go together. In fact, food allergies may play a role in aggravating dermatitis. For others, eating or just touching a particular food may cause their skin to react .
When your skin is affected, symptoms may include redness alone or in combination with swelling, a rash or itchiness. Skin reactions to food can be immediate or take hours or even days to appear.
Some food allergies can be severe, causing life threatening reactions known as anaphylaxis.
Read Also: Vitamin E Oil For Eczema
How Is Allergic Eczema Treated
Treatment for allergic eczema depends on the severity of your symptoms. In all cases, though, its important to wash the affected skin with plenty of water to remove traces of the allergen.
You may not need additional treatment if your symptoms are mild and dont bother you. However, you might want to use a moisturizing cream to keep the skin hydrated and repair damage. Over-the-counter corticosteroid creams can help with itching and inflammation.
Your doctor may recommend prescription-strength ointments or creams if your symptoms are severe. They may also prescribe corticosteroid pills if needed.
Testing For Food Allergies
How do we look and test for food allergies? Through skin testing and blood testing which looks at the specific IgE for the allergen. Skin tests are beneficial in that they have greater accuracy and are available for many different allergens. They are also less expensive and deliver same-day results. However, to undergo skin tests, patients have to stop antihistamines.
Blood testing is a little more convenient they have a more quantitative result, and they are not affected by anti-histamines. Blood tests are particularly preferable to skin testing if the patient is very young or uncooperative, has had anaphylaxis to a food, or has extensive eczema and theres not a good place on the skin to test.
Read Also: Best Diapers For Babies With Eczema
Do Food Allergies Make Atopic Dermatitis Worse
We know food allergy and atopic dermatitis are highly associated. While not all atopic dermatitis patients have food allergy, up to 20 to 40 percent of children with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis will have an IgE-mediated food allergy. Which brings us to the controversial question: Can food allergies exacerbate atopic dermatitis?
We know that the two coexist, but we dont know whether food allergies make atopic dermatitis worse. There are some studies that suggest that patients with positive allergy testing to egg may get better if they eliminate eggs from their diet. This creates some cause for concern because taking the allergen out of a diet may prevent patients from developing an oral tolerance. We do try to be very careful with diagnosing food allergies.
A few years ago, I had the pleasure of participating on an expert panel that developed guidelines for food allergies. One of the most difficult guidelines to develop was the question of food allergies in atopic dermatitis.
I think the panel came to the conclusion based on the evidence and expertise that we had: The guidelines say that children less than 5 years old with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis may be considered for food allergy evaluation for milk, egg, peanut, wheat, and soy, if at least one of the following conditions is met:
Can Food Allergy Cause Eczema
Although food allergy is more common in children who have eczema, they are separate conditions.
Food allergy does not normally cause eczema, but having eczema may increase the chance that a food allergy develops. For a description of how eczema may increase the risk of food allergy, please refer to the section on the next page called: How can good eczema control help prevent food allergy?
You May Like: I Have Eczema On My Neck
Atopic Dermatitis And Food Allergy
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing, inflammatory skin condition that causes erythematous, pruritic skin lesions. While estimates vary, particularly according to geographic region, it has an estimated lifetime prevalence in children of 10 to 20 percent, and a prevalence in adults of 1 to 3 percent. A rising prevalence over the last several decades has been noted in particular in industrialized countries. Although clinical and family history are usually sufficient to make the diagnosis, the United Kingdom Working Partyâs minimum criteria for a diagnosis of AD include a history of dermatitis involving the flexural surfaces, history of dry skin, onset prior to two years of age, personal history of asthma, history of cutaneous pruritus, and visible flexural dermatitis. While the pathophysiology of AD is not fully understood, a genetic predisposition to skin barrier dysfunction in combination with environmental factors, such as irritants, microbes, extremes of temperature, psychological stress, and allergens, contribute to its multifactorial development.
Dont Miss: Is Cetirizine Non Drowsy
Tips For Relieving Eczema Symptoms
Since eczema tends to flare up periodically, its good to know how to find short-term symptom relief. The following tips can help soothe your skin and relieve some itching. Theyre not a substitute for seeing a dermatologist or allergist. A doctor can prescribe medication that interacts with your immune system, bringing more profound and long-term symptom relief.
Identify what triggers your eczema. Common triggers include dry heat, low humidity, harsh soaps, wool fabrics, and allergens.
Moisturize twice daily with a gentle, unscented moisturizer.
Use gentle soaps for hand washing and bathing. Look for unscented soaps as fragrance can cause irritation.
Limit your baths and showers to under 15 minutes. Bathing too long can overdry your skin.
Dry skin gently after bathing. Apply moisturizer while your skin is still wet.
Take a bleach bath. This sounds extreme, but its actually recommended by dermatology associations to reduce skin infections and calm flare-ups. Add ½ a cup of bleach to a 151 litre bathtub. Soak for no more than ten minutes, and dont dip your head underwater. Bleach baths should be taken no more than twice a week.
Take an allergy medication to calm your allergic immune response.
Wear smooth fabrics like silk or cotton. Avoid coarse fabrics like wool that can irritate and itch.
Practice relaxation and mindfulness techniques. This can help keep flare-ups at bay, and help you deal with the itching and mental distress of a current flare-up.
You May Like: What To Do To Help Eczema
Help Your Child Avoid Personal Irritants
Some substances can irritate skin and start the cycle of itching and scratching. If you notice that your child’s eczema gets worse after being exposed to something, help your child avoid it. Irritants are not the same for all children. If a common trigger does not bother your child, there is no reason to avoid it. Here are some examples of possible triggers that can cause eczema flare-ups in some children.
Perfumes and fragrances, including the skin care and bathing products that contain them
Harsh soaps
Bath salts or bubble baths
Rough clothing, including wool fabrics
Temperature extremes, including hot and cold, dry air
Skin Infections
Children with eczema often have more bacteria on their skin. Even when it does not cause an infection, the bacteria can make the skin more irritated and can make the eczema worse, so keeping clean is important.
Babies and children with eczema are also prone to skin infections. Infections make the eczema even worse and need to be treated by a doctor. An oral antibiotic, antibiotic cream or very small amount of bleach added to bath water might be prescribed. Bleach should not be added to bath water without guidance from your child’s doctor. Signs of possible infection include: increased pain, tenderness or swelling, hot skin, fever, pus, or red streaks extending from the affected skin.
Stress
Environmental allergens
Foods that are not allergens
What Are The Types Of Contact Dermatitis

The two main types of contact dermatitis are:
Allergic contact dermatitis: Your body has an allergic reaction to a substance that it doesnt like. Common allergens include jewelry metals , cosmetic products, fragrances and preservatives. It can take several days after exposure for an itchy, red rash to develop.
Irritant contact dermatitis: This painful rash tends to come on quickly in response to an irritating substance. Common irritants include detergents, soap, cleaners and acid.
You May Like: How To Help Face Eczema
What Causes Hives
Hives are often triggered by foods or medications. Among the most common foods that cause hives are peanuts, tree nuts and shellfish . Common medications associated with hives include penicillin, sulfa, phenobarbital, and aspirin.
Types of hives that are not triggered by an allergy:
- Cholinergic urticaria is the medical term for hives that appear after an activity that increases the body temperature like hot tub use, exercise, fever, or emotional stress. The hives usually occur as the skin cools after being warmed.
- Cold-induced hives occur after exposure to cold wind or water and often appear on the lips or mouth.
- Solar hives are caused by exposure to sunlight or a sunlamp, and a reaction can occur within one to three minutes.
- Exercise can trigger hives. With exercise-induced hives, some individuals may develop a lung obstruction and may lose consciousness. This severe reaction is called anaphylaxis and may be fatal.
- Chronic urticaria are hives that continue either daily or frequently for longer than four weeks.