Treating Eczema Rashes After Trigger Exposure
Anyone can get eczema, from newborn babies to elderly adults. While eczema may go away periodically, it is a chronic condition that can come back.
If you or a loved one has eczema, talk to your doctor. There is no cure for the condition, but as the AAAAI notes, there are over-the-counter and prescription treatments that may ease the symptoms, including:
- Emollients
What Are The Treatments For Severe Hand Eczema
If your hand eczema is severe, discuss the possibility of a dermatology referral with your GP. The referral may be for diagnosing contact allergy or for treatment, which may include a short course of oral steroids or immunosuppressants . Alternatively, dermatology departments may recommend alitretinoin or phototherapy, as described below.
Differences Between Ad In Adults And Children
Even if you had AD as a child, your skin can look and feel differently when you have AD as an adult. Thats actually one of the most striking differences between AD in adults and AD in children.
In adults, the skin tends to be extremely dry and scaly where the AD appears.
If youve had AD for years, patches of your skin may be thick, leathery, and darker than the surrounding skin. Years of scratching causes this. The thickened skin can itch all the time.
Adults also tend to get AD on different parts of their bodies than do children. When an adult has AD, its most likely to form in one or more of these areas:
-
Backs of the knees
-
Back of the neck
-
Face
Adults, unlike children, often have AD around their eyes. Youll often see thickened, darker skin circling the eyes, as shown in the picture on this page. The skin around the eyes also tends to be very itchy.
You May Like: Deodorant For Kids With Eczema
What Does It Look Like
The signs of eczema in infants include itchy, dry and scaly skin, redness and swelling of the skin and small bumps that open and weep when scratched. In infants and young children, eczema is usually found on the face, outside of the elbows, and on the knees.
In older children and adults, eczema tends to be on the hands and feet, the arms, and on the back of the knees.Keep in mind that all patches of dry skin are not eczema. The cold, dry outdoor air and indoor heating can dry all babies skin in winter, causing dry patches. In children prone to dry skin, so can the sun, air conditioning, and pool and salt water.
We dermatologists usually say if its not itchy, its not eczema you cant make a diagnosis of eczema unless there is an itchiness that goes with the rash. Babies with cradle cap, also known as seborrheic dermatitis, can also have a wide-spread rash, which is not eczema in itself. But it is common for cradle cap and eczema to co-exist in the first several months of life.
Dealing With Eczema Flares
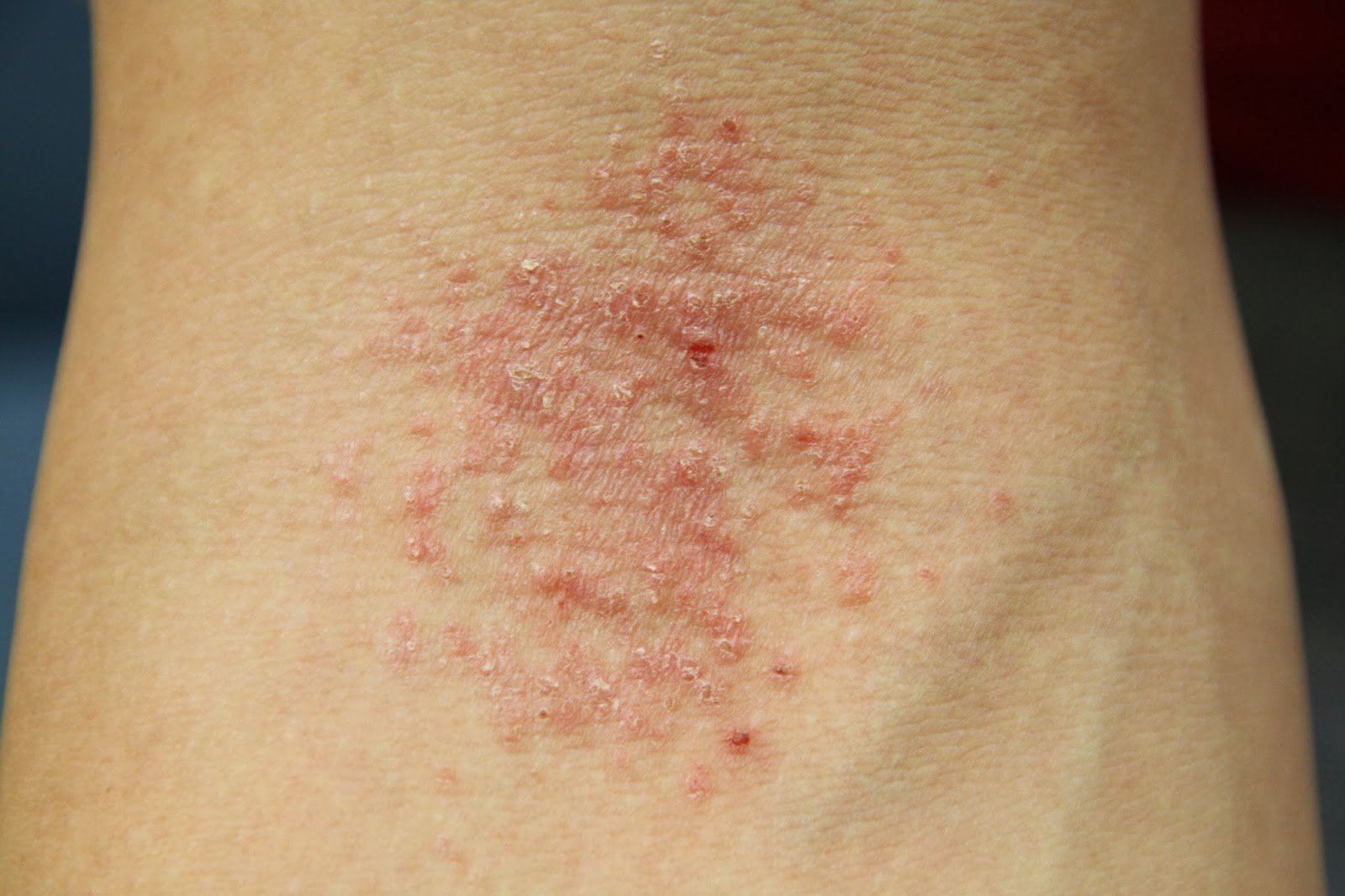
Eczema is a condition of the skin that erupts in the different parts of the body. As true as the phrase, “Prevention is better than cure” holds, once you have acquired the condition, dealing with it becomes the prime matter of concern. Sometimes, it is the little things in life that help us overcome an ailment. To begin with, you can prevent the flares from doubling up by avoiding friction or rough contact with the area. Try not to scratch or rub the patch of skin in and around the lesions. Avoid wearing clothes that prevent your skin from breathing. Instead, choose light and skin-friendly materials. Observe your cosmetic products and toiletries for a while. If you have recently switched to a new brand or is allergic to a particular skin care product or lotion, identify them and remove them from your cupboard immediately. This method rules out the first cause of most skin irritations.
Eczema is a relatively chronic skin condition that stays for a while until the visible symptoms subside. You may experience flare-ups at different points in time, but it takes a while to leave the body completely. Proper treatment using prescribed medications can help in curbing the ailment. Overall, a good approach to hygiene, skin care routine and a healthy diet can keep eczema at bay.
Hence, once you feel that you have this condition, medical attention is required to have a proper diagnosis.
Read Also: Mustela Baby Face Cream For Eczema
Eczema On Neck Pictures:
Eczema on Neck is a skin condition that cause the skin to become red, inflamed, dry and itchy. The dry patches can be seen all over the body but most prominently on the neck, elbows and thighs. The dry skin causes itching and gets the condition worse. Avoid triggers and allergens to get rid of the condition. Immediately seek for a medical help and try changing your daily regime. Include foods that are beneficial for itch control and manage the skin condition by the daily regimes prescribed by your doctor.
Also ReadEczema & Dry Skin Relief Causes, Natural Treatments & Remedies
General Tips For Coping With Eczema
Other tips to manage your eczema include:
- Keep your fingernails short longer nails are more likely to injure your skin when you scratch.
- If the water in your area is hard or alkaline, consider installing a water-softening device.
- Swim in the sea in warm weather whenever you can seawater is known to reduce the symptoms of eczema.
- Use sun exposure for limited periods for example, when swimming at the beach. This can help relieve eczema symptoms. But be aware that ultraviolet radiation is a risk factor for skin cancer and premature ageing of the skin. Also, if sun exposure causes overheating, this can also aggravate eczema.
Also Check: How To Calm Eczema On Face
What Else Is Happening At Johns Hopkins Today
We go out of our way to provide the comprehensive care our patients with eczema need. On a case-by-case basis, we communicate with one another whether in allergy, dermatology, psychology or infectious disease to put together the best course of treatment for each child.We are optimistic that future therapies and approaches to care for those with even severe eczema are going to be greatly improved with more research and that the creation of the Eczema Day Treatment Unit will help us conduct cutting edge research and answer questions we face every day seeing and treating patients.
Q : How Can Skin Be Maintained And Protected Every Day
It is important to keep skin that is prone to eczema well moisturised every day:
- Moisturisers add moisture and form a barrier that protects the skin, so that it retains moisture. If the protective barrier of skin is damaged eczema frequently develops.
- Apply non-perfumed moisturiser to the face and body twice every day.
- Avoid moisturisers containing food proteins such as goat milk, wheatgerm and nut oils.
- After a bath or shower in lukewarm water, pat the skin dry and apply moisturiser.
- Use non-soap based wash or oil and avoid soap and bubbly products which dry out the skin.
- After swimming , rinse and apply moisturiser.
Recommended Reading: Does Coffee Make Eczema Worse
What About Research
At Johns Hopkins, a lot of us in pediatric dermatology, pediatric infectious disease and pediatric allergy and immunology are looking at better ways to prevent or manage eczema. Were studying the optimal management of bacterial colonization and infection in atopic skin and the role of food allergy in eczema. Our specialties collaborate each brings a different approach to eczema management. Our goal is to work together to harness the best approaches to better understand eczema and, in doing so, to treat it more effectively.
When Adults Get It
You might notice itchy patches on the hands, elbows, and in the “bending” areas of the body, such as the inside of the elbows and back of the knees. But eczema can appear anywhere, including the neck, chest, and eyelids. People who had atopic dermatitis as a child may see drier, scaly rashes as adults. The skin may be discolored or thickened.
You May Like: Best Body Wash For Toddler Eczema
How Is Eczema Diagnosed What Tests Are Done
Your healthcare provider will take a close look at your skin. They will look for classic signs of eczema such as a redness and dryness. They will ask about the symptoms youre experiencing.
Usually your healthcare provider will be able to diagnose eczema based on examining your skin. However, when there is doubt, they may perform the following tests:
- An allergy skin test.
- Blood tests to check for causes of the rash that might be unrelated to dermatitis.
- A skin biopsy to distinguish one type of dermatitis from another.
Types Of Eczema That May Be Confused With Atopic Dermatitis
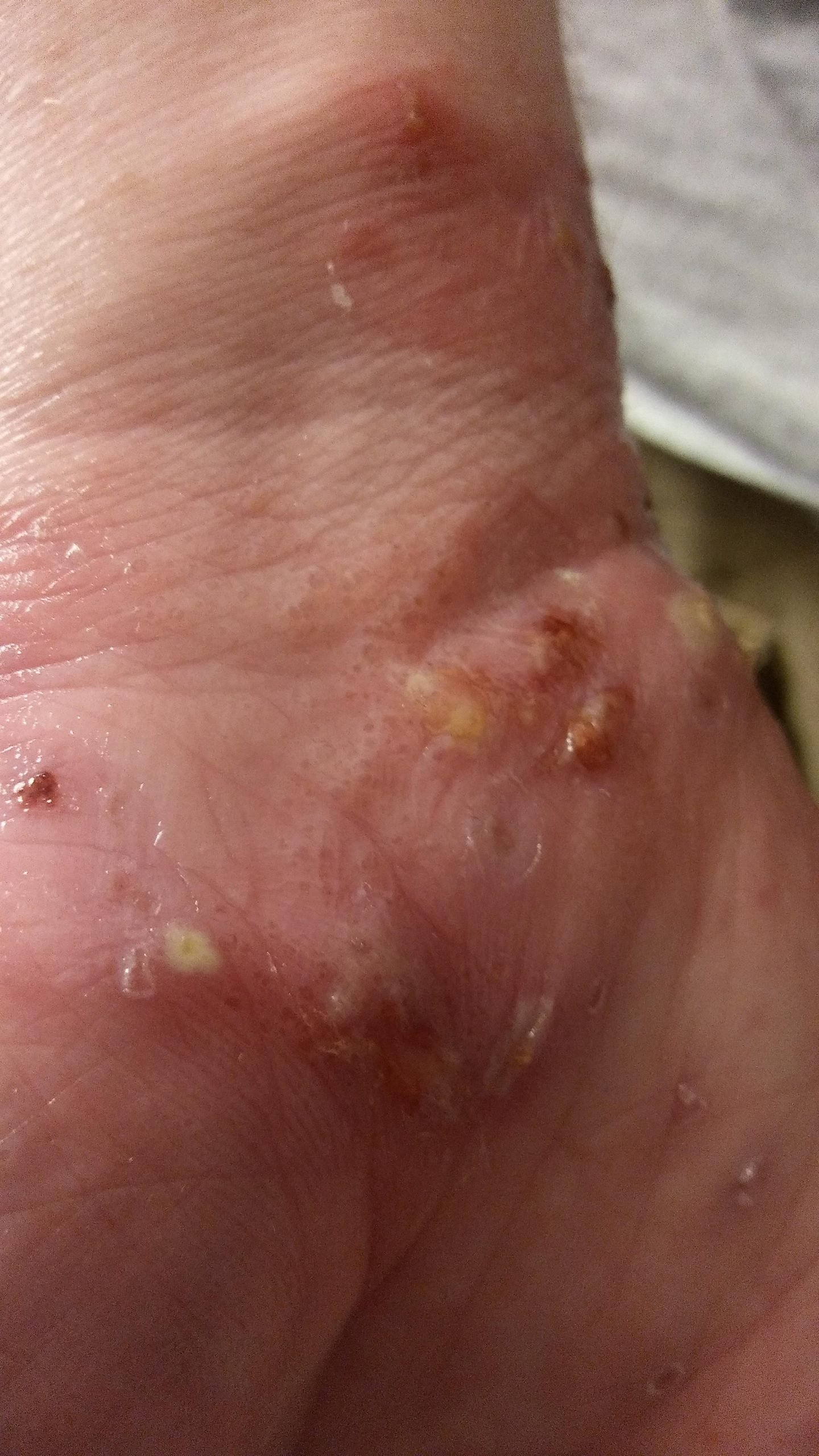
Its critical to receive an atopic dermatitis diagnosis from a dermatologist, who can tell you which of the many different types of eczema you have. The treatment you need will depend on the kind of eczema you have. Types of eczema include:
Contact eczema or contact dermatitis A localized skin reaction to a substance in the environment that causes skin to become inflamed and itchy. Most often, the skin immediately reacts to irritants, such as chemicals , abrasion, or heat, and is thus known as irritant contact eczema. Other times, the skin reacts slowly after contact with a substance that the immune system recognizes as foreign or allergenic, such as poison ivy, nickel, or latex this is called allergic contact eczema.
Hand eczema A form of eczema that is sometimes mistaken for simple dry skin, it produces dry, thick, scaly patches on the hands that may crack and bleed. Like contact eczema, hand eczema is triggered by various irritants and allergens. As such, it is most often found in people who work in cleaning, catering, hairdressing, healthcare, and mechanical jobs.
Seborrheic dermatitis A chronic condition in which white or yellow scaly patches of skin develop in oily areas, such as the scalp , face, and ears. Unlike many other forms of eczema, seborrheic dermatitis is not a type of allergic or irritant reaction, and microorganisms that live on the skin can contribute to the condition.
Recommended Reading: Eczema Around Eyes How To Treat
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Eczema
There are steps you can take that may prevent eczema outbreaks:
- Establish a skin care routine, and follow your healthcare professionals recommendations for keeping your skin healthy.
- Wear gloves for jobs where you have to put your hands in water. Wear cotton gloves under plastic gloves to absorb sweat, and wear gloves outside, especially during the winter months.
- Use mild soap for your bath or shower, and pat your skin dry instead of rubbing. Apply a moisturizing cream or ointment immediately after drying your skin to help seal in the moisture. Reapply cream or ointment two to three times a day.
- Take baths or showers with tepid rather than hot.
- Drink at least eight glasses of water each day. Water helps to keep your skin moist.
- Try to avoid getting too hot and sweaty.
- Wear loose clothes made of cotton and other natural materials. Wash new clothing before wearing. Avoid wool.
- Avoid sudden changes in temperature and humidity.
- Learn to recognize stress in your life and how to manage it. Regular aerobic exercise, hobbies and stress-management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, might help.
- Limit your exposure to known irritants and allergens.
- Avoid scratching or rubbing itchy areas of skin.
What Are The Symptoms Of Eczema
The most important thing to remember is that eczema and its symptoms are different for everyone. Your eczema may not look the same on you as it does on another adult or on your child. Different types of eczema may even appear in different areas of the body at different times.
Eczema is usually itchy. For many people, the itch can range from mild to moderate. But in some cases, it can become much worse and you might develop extremely inflamed skin. Sometimes the itch gets so bad that people scratch it until it bleeds, which can make your eczema worse. This is called the itch-scratch cycle.
What to look for:
Read Also: Stress Induced Eczema On Hands
Which Skin Type Are You
Skin type is described by the Fitzpatrick classification , which determines the colour of skin by phototype, which depends on the amount of melanin pigment in the skin.
In this article we describe skin as lighter or darker.
Skin types: Fitzpatrick classification, adapted from:
| Skin type | |
| VI | Skin black |
Skin changes are caused either by active eczema or by scratching as a result of eczema itch. These changes can result in two types of pigmentary skin changes in eczema:
- HYPO-PIGMENTATION Loss of skin pigment or colour, usually seen as patches of skin that are lighter than overall skin tone.
- HYPER-PIGMENTATION Patches of skin becoming darker than the normal skin tone.
Hypo- and hyper-pigmentation are more visible in darker skin types but can occur in any skin type and can be concerning and distressing for anyone with eczema.
The main way of improving skin pigmentation changes is to treat the underlying eczema and inflammation. But discoloration can last for months or years, even after the eczema is treated.
Natural Remedies For Eczema
If you search online, youll be flooded with natural remedies for eczema. Its important to note that complementary and alternative therapies for eczema are largely unproven. While the research is mixed, many eczema sufferers swear by their natural treatments.
If youre interested in natural remedies for eczema, its best to speak with a naturopathic doctor. A naturopathic doctor will help you pinpoint the cause of your eczema by looking at your vitamin D intake, your overall gut health and any food sensitivities you might have.
In a study discussing the benefits of various natural remedies for eczema, omega-3 supplements and probiotics were found to show great promise. The study concluded that a dietary intake of omega-3 supplements may have therapeutic effects on eczema symptoms. In addition, probiotics supplements may also help eczema by regulating the immune system and preventing the inflammation that comes with it.
Also Check: How To Treat Eczema On Breast
How Is Eczema Treated
There is no cure for eczema. But treatments can help with symptoms. The doctor will recommend different treatments based on how severe the symptoms are, the child’s age, and where the rash is. Some are “topical” and applied to the skin. Others are taken by mouth.
Topical moisturizers. Skin should be moisturized often . The best time to apply moisturizer is after a bath or shower, with the skin patted dry gently. Ointments and creams are best because they contain a lot of oil. Lotions have too much water to be helpful.
Topical corticosteroids, also called cortisone or steroid creams or ointments. These ease skin inflammation. It’s important not to use a topical steroid prescribed for someone else. These creams and ointments vary in strength, and using the wrong strength in sensitive areas can damage the skin, especially in infants.
Other topical anti-inflammatory medicines. These include medicines that change the way the skin’s immune system reacts.
Medicine taken by mouth. These can include antihistamines to help itchy kids sleep better at night, antibiotics if a rash gets infected by bacteria, and corticosteroid pills or other medicines that suppress the immune system.
Other types of treatment can include:
- wet wraps: damp cloths placed on irritated areas of skin
- bleach baths: bathing in very diluted bleach solution
How Common Is Eczema
Eczema affects up to 15 million Americans. Infants are prone to eczema and 10% to 20% will have it. However, nearly half outgrow the condition or have significant improvement as they get older.
Eczema affects males and females equally and is more common in people who have a personal or family history of asthma, environmental allergies and/or food allergies.
You May Like: What Hand Soap Is Good For Eczema
How Discoid Eczema Is Treated
Discoid eczema is usually a long-term problem, but medications are available to help relieve the symptoms and keep the condition under control.
Treatments used include:
- emollients moisturisers applied to the skin to stop it becoming dry
- topical corticosteroids ointments and creams applied to the skin that can help relieve severe symptoms
- antihistamines medications that can reduce itching and help you sleep better
There are also things you can do yourself to help, such as avoiding all the irritating chemicals in soaps, detergents, bubble baths and shower gels.
Additional medication can be prescribed if your eczema is infected or particularly severe.
- feet
The face and scalp are not normally affected.
The first sign of discoid eczema is usually a group of small red spots or bumps on the skin. These then quickly join up to form larger pink, red or brown patches that can range from a few millimetres to several centimetres in size.
Initially, these patches are often swollen, blistered and ooze fluid. They also tend to be very itchy, particularly at night.
Over time, the patches may become dry, crusty, cracked and flaky. The centre of the patch also sometimes clears, leaving a ring of discoloured skin that can be mistaken for ringworm.
You may just have one patch of discoid eczema, but most people have several patches. The skin between the patches is often dry.
Southern Cross Medical Library

The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
Recommended Reading: Best Body Wash For Eczema Australia