How To Follow An Anti
As eczema is an inflammatory skin condition, following an anti-inflammatory diet may help relieve symptoms.
This diet involves eating less of foods that may trigger inflammation in the body, and more of foods that help fight inflammation.
For this diet, its important to pay close attention to dietary fats, which can influence the overall amount of inflammation in the body.
In particular, trans fats, which include hydrogenated oils, some margarine brands, french fries, and other fried foods and saturated fats, which are found in red meats, full-fat dairy foods, butter, and poultry skin promote inflammation and therefore may potentially worsen eczema symptoms.
Large quantities of foods rich in omega-6 fatty acids, including vegetable oils, may also promote inflammation.
On the other hand, the three main omega-3 fatty acids alpha-linolenic acid , eicosapentaenoic acid , and docosahexaenoic acid also have anti-inflammatory properties. EPA and DHA are in fatty fish like salmon, sardines, mackerel, herring, and tuna. Meanwhile, ALA is in flaxseed, canola oil, and soybeans. Other sources of omega-3s include walnuts and green leafy vegetables, like kale, mustard greens, and spinach.
Monounsaturated fats, including olive oil and canola oil, may also be anti-inflammatory.
Aside from these dietary fats, other foods and drinks that may exert anti-inflammatory effects include:
A Final Word On Eating To Help Manage Symptoms Of Eczema
Theres no cure for eczema, but treatment can help you manage symptoms and reduce flares. While topical ointments and oral medications are effective, identifying and avoiding triggers that irritate your skin such as certain foods is also helpful for calming itching, redness, and rashes.
So if you havent already, talk to your dermatologist about an elimination diet. And if you suspect a food allergy, talk to your doctor about allergy testing.
Supplements For Relief Of Eczema Symptoms
Although more research is needed, a wide range of supplements may help reduce eczema symptoms, including:
- Sunflower Oil
While individual studies may suggest some of these supplements work for eczema, reviews of past research suggest there is no strong evidence to recommend people with eczema use these products.
Be sure to discuss with your doctor any supplements, vitamins, or home remedies before you try them.
Additionally, some of these supplements may have dangerous side effects or drug interactions, including vitamin D , evening primrose oil, borage oil, bromelain, and probiotics.
Also Check: Can Eczema Look Like A Rash
Can Elimination Diets Help Treat Eczema
An elimination diet involves removing certain foods from your diet to help identify the cause of an allergic reaction or other food-related symptoms. Youll avoid a particular food or ingredient for a few weeks, and then monitor your skin for any changes.
If symptoms improve, slowly reintroduce the food into your diet over a few days. If symptoms return, youve likely found a trigger.
An elimination diet isnt only effective for eczema. Its also helpful for identifying foods that may trigger other conditions, like celiac disease, a gluten intolerance, a lactose intolerance, and irritable bowel syndrome.
Research suggests that people with specific food allergies may find some eczema relief by avoiding those foods. But there isnt much evidence showing that so-called elimination diets those in which people completely stop eating certain food groups are effective for eczema relief in general.
In 2008, researchers from the Cochrane Collaboration conducted a literature review to see if elimination diets had any effect on eczema symptoms. In eight of the nine studies reviewed, people with eczema who followed elimination diets showed little to no improvement in symptoms but these people werent tested for food allergies beforehand.
In the last study, babies known to have an allergic reaction to eggs experienced fewer eczema rashes after going on an egg-free diet.
The Itchy Dozen Worst Foods For Eczema

People are often surprised to find the Itchy Dozen includes some of the so-called ‘good’ foods for eczema. I know the Itchy Dozen contradicts some popular beliefs published in online blogs. However, according to Australian research conducted over the past thirty years, these foods could be the reason your skin is dry, flaky and incredibly itchy .
I’ve seen this information help hundreds of so called ‘hopeless’ cases of eczema. People who have had eczema for 20, 30 or 40 years and more, who thought they were stuck with eczema for life, are seeing their eczema clear up for the first time. It can really change lives but it requires a change in beliefs about healthy eating. This quote sums it up:
“One man’s medicine is another man’s sleepless night itching.”
So a food that is good for an eczema-free person, such as avocado, could trigger a bout of maddening itching in another person.
Not counting allergy foods , here are the surprising foods and beverages most likely to give you itchy eczema …
1. Dairy products
Dairy products, including cows milk, yoghurt, butter and cheese, are the second most common allergy food seen in eczema sufferers .
- Yoghurt is particularly bad for eczema as it often contains added sugar, fruit flavourings, amines and a natural colour called Annatto which can trigger eczema.
Calcium deficiency can cause eczema
If you are itchy, one heaped scoop of Skin Friend PM mixed into water or food will quickly calm down the itch.
2. Grapes
You May Like: Eczema On Private Area Female
How Food Allergy Is Diagnosed
The symptoms may very from an individual to individual during allergic reaction. As soon as the trigger food is eaten a person may develop the symptoms that can affect their skin, respiratory tract, cardiovascular system and more.
Its sometimes impossible to predict how severe the next reaction will be and this should be kept in mind that each patient should be carefully counseled about the food triggers that causes fatal reactions.
These food allergies in adults, food allergies in babies may develop at any age but most probably will appear in the childhood. If in any case you feel a slight amount of allergy, you must visit an allergist as he/she can guide you for the medical tests, allergy examinations and will take care of your condition.
You will have a detailed list of questions about your eating habits, medical history and the symptoms so be prepared to answer the questions like:
- What you eat?
After knowing about your medical history, your allergist may ask for the allergy tests, skin tests or blood tests that will indicate whether the food-specific immunoglobulin antibodies are present in your body or not?
Read herein detail for both Allergy Testing
Your allergist will use these results to analyse, diagnose and manage the skin condition. In few cases, your allergist may ask for an oral food challenge, one of the most accurate way to diagnose food allergy.
Itchy Dozen Worst Foods For Eczema
Nutritionist Karen Fischer’s daughter had severe eczema and avoiding ‘the itchy dozen’ changed their lives. Now her daughter is eczema-free and Karen recently spoke about The Itchy Dozen Worst Foods for Eczema on prime time news .
This article includes the following:
- The itchy dozen worst foods for eczema
- Natural ways to treat eczema
- Further resources for people with eczema.
This article was written by Karen Fischer, and it is an edited extract from Karen’s eczema books:
Read Also: How Do You Get Hand Eczema
Link Between Eczema And Food Allergies
There is now a direct link between eczema and food allergies. While atopic dermatitis may be triggered or worsened by common food allergies such as those to eggs, milk, wheat, soy, and peanuts, eczema itself may be responsible for the development of food allergies in the first place.
Food allergies are considered official comorbidity of atopic dermatitis alongside asthma, allergic rhinitis and depression. As a result, they believe that if they could just cut certain foods from their diets, such as gluten or dairy, their eczema will go away.
Eczema is a serious skin condition that can cause itchy skin rashes, skin irritation and oozing blisters. It can also result in the flaky patches in severe condition. The cause of eczema is still not known but hereditary and environmental triggers usually play a major role in developing skin condition. The eczema symptoms may get worse as soon as a patient comes in the direct contact with the allergens/irritants.
Have you ever had eczema as a child and now usually develop hay fever, asthma or skin allergies as an adult? Is your child developing red, irritated, itchy, flaky patches on the skin? There may be few questions that you might have in your mind:
- Can eczema be caused by food allergies?
- What food to avoid when you have eczema?
- What are the most common food allergies?
- Are allergies and eczema related?
- Does food allergy cause eczema?
- What foods cause eczema to flare up?
Diet And Eczema In Adults
Thereâs no evidence that specific foods cause eczema or make symptoms flare. But some people say their symptoms get worse after they eat a particular food.
Keep in mind that itâs not always easy to figure out exactly whatâs making your skin condition flare. The link may seem clear, but because youâre around many triggers every day, itâs often hard to tell if the problem is food, or another trigger, like stress.
Some people with eczema try to completely cut out one or more foods from their diets, like eggs or cowâs milk. Itâs called an elimination diet. But thereâs not much good evidence that they help adults with the condition.
Unless you know you have a specific food allergy, be sure to talk to your doctor before you cut out entire food groups or make other major changes to what you eat.
You May Like: Is Polyester Bad For Eczema
Scientists Identify Unique Subtype Of Eczema Linked To Food Allergy
Children with both conditions have abnormal skin near eczema lesions, NIH-funded research finds
Atopic dermatitis, a common inflammatory skin condition also known as allergic eczema, affects nearly 20 percent of children, 30 percent of whom also have food allergies. Scientists have now found that children with both atopic dermatitis and food allergy have structural and molecular differences in the top layers of healthy-looking skin near the eczema lesions, whereas children with atopic dermatitis alone do not. Defining these differences may help identify children at elevated risk for developing food allergies, according to research published online today in Science Translational Medicine. The research was supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases , part of the National Institutes of Health.
Children and families affected by food allergies must constantly guard against an accidental exposure to foods that could cause life-threatening allergic reactions, said NIAID Director Anthony S. Fauci, M.D. Eczema is a risk factor for developing food allergies, and thus early intervention to protect the skin may be one key to preventing food allergy.
Children with atopic dermatitis develop patches of dry, itchy, scaly skin caused by allergic inflammation. Atopic dermatitis symptoms range from minor itchiness to extreme discomfort that can disrupt a childs sleep and can lead to recurrent infections in scratched, broken skin.
Eczema And Food Allergy By Jennifer Worth
Author: Jennifer Worth, SRN, SCMDate:
Asthma has always been part of my life, but never eczema. I was fifty seven when it started, just two little itchy patches on my legs. I thought nothing of it. They were so small – nothing could have told me of the horror that was to come.
Within about six months these two little patches had spread to cover my entire body, from my forehead to my feet. My skin was sloughing off all over, water poured out of my body, my legs were swollen up to look like elephant legs. With my hair and eyebrows coming out, and my face bright red and puffed up, my appearance changed beyond recognition. And the itching …!
“Used to” – these are the key words of this article, and the reason why I have been asked to write it.
One day we had a Chinese take-away for dinner. I bless the day as heaven-sent. I was violently sick after eating it, and could not eat for four or five days. During those days without food the eczema virtually cleared up. As soon as I started eating again, the eczema reappeared. This incident gave me the clue to the cause of my eczema. I told my doctor, told the hospital consultant, told the dietician. They all smiled condescendingly and said it was coincidence – there was no connection between food and eczema.
Many people have asked me what EPD is how does it work, where can you get it, and what does it cost? It is a very subtle and complex medical process, and I give below a brief summary of what it is about.
You May Like: What Can You Put On Eczema On Eyelids
Foods To Avoid If You Are A Breastfeeding Mother To A Baby With Eczema:
This is very well known that a mothers milk can help their babies grow a stronger immune system. But there may be cases when the foods eaten by the mother can affect their babys health. Proteins in many foods can usually pass into the breastmilk and cause various allergic reactions.
If you suspect that your baby is developing eczema due to an allergy of food protein passing through the breast milk, immediately consult your doctor about the elimination of those foods from your diet.
Also Read:Do You Know : U.S Children Are More Prone To Allergy Risks
If you are breastfeeding mother then you must avoid foods that include:
The Link Between Food Allergies And Eczema
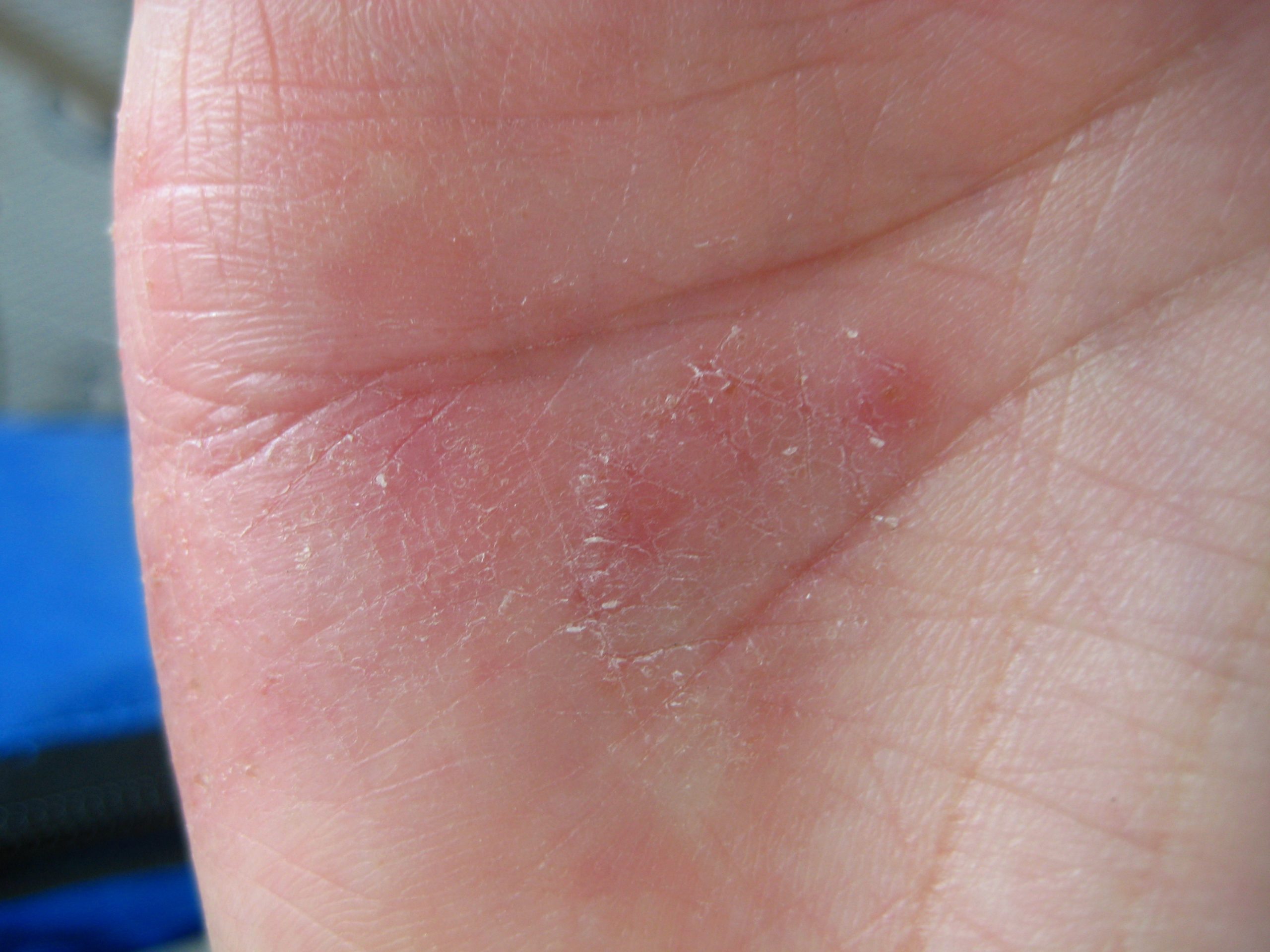
Though food allergies may not be at the top of the list of skin rash triggers, certain foods can cause eczema. These steps can help you decide if your child should get tested.
The list of irritants and allergens that can trigger an eczemarash includes everything from dry skin and scratchy clothes to cold weather. Since about one third of children with eczema may also have food allergies, you may be wondering if it could also play a role in your childs symptoms.
There is an increased association of food allergies in children with eczema, but the overwhelming majority of children with eczema do not have food allergies, says Daniela Kroshinsky, MD, director of pediatric dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. In general, children with more severe eczema are more at risk for developing food allergies, she says.
In addition, a July 2013 study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology found that infants with eczema had a higher risk of developing food allergies. Researchers theorize that the breakdown in the skin barrier may contribute to an allergic immune response in food.
Food Allergies as Potential Eczema Causes
According to Dr. Searing, these seven foods are most often linked with food allergies:
- Eggs
- Fish
- Peanuts
Food allergy reactions can range from mild to potentially life-threatening and usually happen a few hours after eating. Typical food allergy symptoms can include:
When Food Allergy Testing May Be Needed
You May Like: Best Hand Cream For Severe Eczema
Food Allergies And Eczema
Food allergies can sometimes cause eczema for young children. But after age 3 or 4, itâs rare. An allergic reaction to things like dairy products, eggs, nuts, soy, or wheat may cause hives or other skin problems that look like eczema, but they’re not the same.
If you think a food allergy is playing a role in your childâs skin disease, talk with their doctor. Ask if testing is likely to help get their condition under control.
Atopic Eczema Is Not A Food Allergy
Atopic dermatitis is not a food allergy, but there may be a connection between the two.
In exploring the topic of diet and eczema, we outline three main concepts: food allergies and forbidden foods, unhealthy foods and, in this chapter, a normal diet is sufficient. Also, in conclusion, we discuss helpful foods such as those with antioxidant or anti-inflammatory benefits.
Don’t Miss: Ways To Help Baby Eczema
What Is Food Allergy
Food allergies are the allergic reactions to different foods that acts as eczema triggers. It is an abnormal response to the foods triggered by your bodys immune system. In adults and children different foods like fish, peanuts, soy, wheat, eggs, tree nuts and milk can cause allergic reactions. As per the studies conducted 1 in 25 children is affected by food allergy. Food allergies can be divided into two types:
- Immediate : The symptoms begin too quickly after eating certain foods
- Delayed : The symptoms begin within 15-20 minutes after having certain foods
Also Read:Delayed Food Allergy Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
An allergic reaction to food can affect the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, skin and in severe cases cardiovascular system.These reactions may be unpredictable and can range from mild to severe including life threatening conditions. Keep in mind that children may communicate different symptoms than adults.
Food Allergies Diet And Different Eczema Types
In 2018, 6.5 percent of American children reported having food allergies in the previous 12 months, according to the National Center for Health Statistics at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention .
Food allergies are the result of an abnormal immune system response. The body reacts to a certain food as if it were harmful or dangerous, which triggers symptoms such as hives, itching, swelling, tingling in the mouth, coughing, and vomiting.
A severe food allergy can cause anaphylaxis, a life-threatening reaction in which the throat swells and blocks the airway.
Interestingly, food allergies are more common among people with eczema as many as 30 percent of children under age 5 with eczema may also have at least one food allergy.
Research published in February 2014 in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology suggested atopic dermatitis is a primary risk factor for the development of food allergies in young infants. Scientists dont know why.
But researchers evaluating the skin of children with both conditions have found structural and molecular differences in the top layers of otherwise healthy-looking skin near eczema lesions. The skin was also more prone to water loss and had a greater presence of staph bacteria. Researchers also found evidence that the skin barriers were immature.
More research is needed to fully understand these changes. But scientists believe that these differences could help identify children at risk for food allergies.
Don’t Miss: Best Cream For Baby Eczema Australia