What To Expect At Your First Dermatologist Appointment For Eczema
Going to your first appointment with a dermatologist is one of the first steps toward managing eczema symptoms. Knowing what to expect may put you at ease and help you feel prepared to share the information your doctor needs about your skin condition.
In your first visit, youll establish a relationship with your doctor and provide them with a basis for shaping your skin care plan. Be prepared to answer questions about your medical history. This information gives the doctor some insight into your eczema.
You should also keep the following in mind during your first visit to the dermatologist:
- They will check your skin for other conditions besides eczema.
- You should be treated with respect. If youre not comfortable, find a new doctor.
- Your doctor will likely recommend treatments or prescribe medications for your eczema.
- You will most likely come back for a subsequent visit to see how well your symptoms are being managed with your new treatment.
How Can Parents Help
Help prevent or treat eczema by keeping your child’s skin from getting dry or itchy and avoiding triggers that cause flare-ups. Try these suggestions:
- Kids should take short baths or showers in warm water. Use mild unscented soaps or non-soap cleansers and pat the skin dry before putting on cream or ointment. Teens should use unscented makeup and oil-free facial moisturizers.
- Ask your doctor if it’s OK to use oatmeal soaking products in the bath to help control itching.
- Kids should wear soft clothes that “breathe,” such as those made from cotton. Wool or polyester may be too harsh or irritating.
- Keep your child’s fingernails short to prevent skin damage from scratching. Try having your child wear comfortable, light gloves to bed if scratching at night is a problem.
- Kids should avoid becoming overheated, which can lead to flare-ups.
- Kids should drink plenty of water, which adds moisture to the skin.
- Get rid of known allergens in your household and help your child avoid others, like pollen, mold, and tobacco smoke.
- Stress can make eczema worse. Help your child find ways to deal with stress .
Food Allergy And Eczema Flare
- Food allergies are a factor in 30% of young children with severe eczema. This factor is mainly seen in babies.
- The main allergic foods are cow’s milk and eggs.
- The main symptoms are increased skin redness and itching. Some parents report these symptoms start during or soon after the feeding.
- The eczema becomes easier to control if you avoid the allergic food.
Don’t Miss: Best Organic Soap For Eczema
Medicines For Atopic Dermatitis
If your doctor decides you need meds to treat your eczema, those may include:
Hydrocortisone. Over-the-counter cream or ointment versions of it may help mild eczema. If yours is severe, you may need a prescription dose.
Antihistamines.Ones you take by mouth are available over-the-counter and may help relieve symptoms. Some of these make you drowsy, but others donât.
Corticosteroids. Your doctor may prescribe these if other treatments donât work. Always follow your doctors directions when taking steroids by mouth.
Drugs that work on your immune system. Your doctor may consider these medicines such as azathioprine, cyclosporine, or methotrexate if other treatments donât help. There are also prescription creams and ointments that treat eczema by controlling inflammation and reducing immune system reactions. Examples include pimecrolimus , which is a cream, and crisaborole and tacrolimus , which are ointments. You should only use these for a short time if other treatments dont work and you should never use them on kids younger than 2, according to the FDA.
Injectables. Dupilumab is an injectable medicine for moderate to severe eczema. It works by controlling the bodyâs inflammatory response. This medicine is given every 2 weeks as an injection and should only be used by people 12 and older.
Prescription-strength moisturizers. These support the skinâs barrier.
What Are Some Types Of Eczema
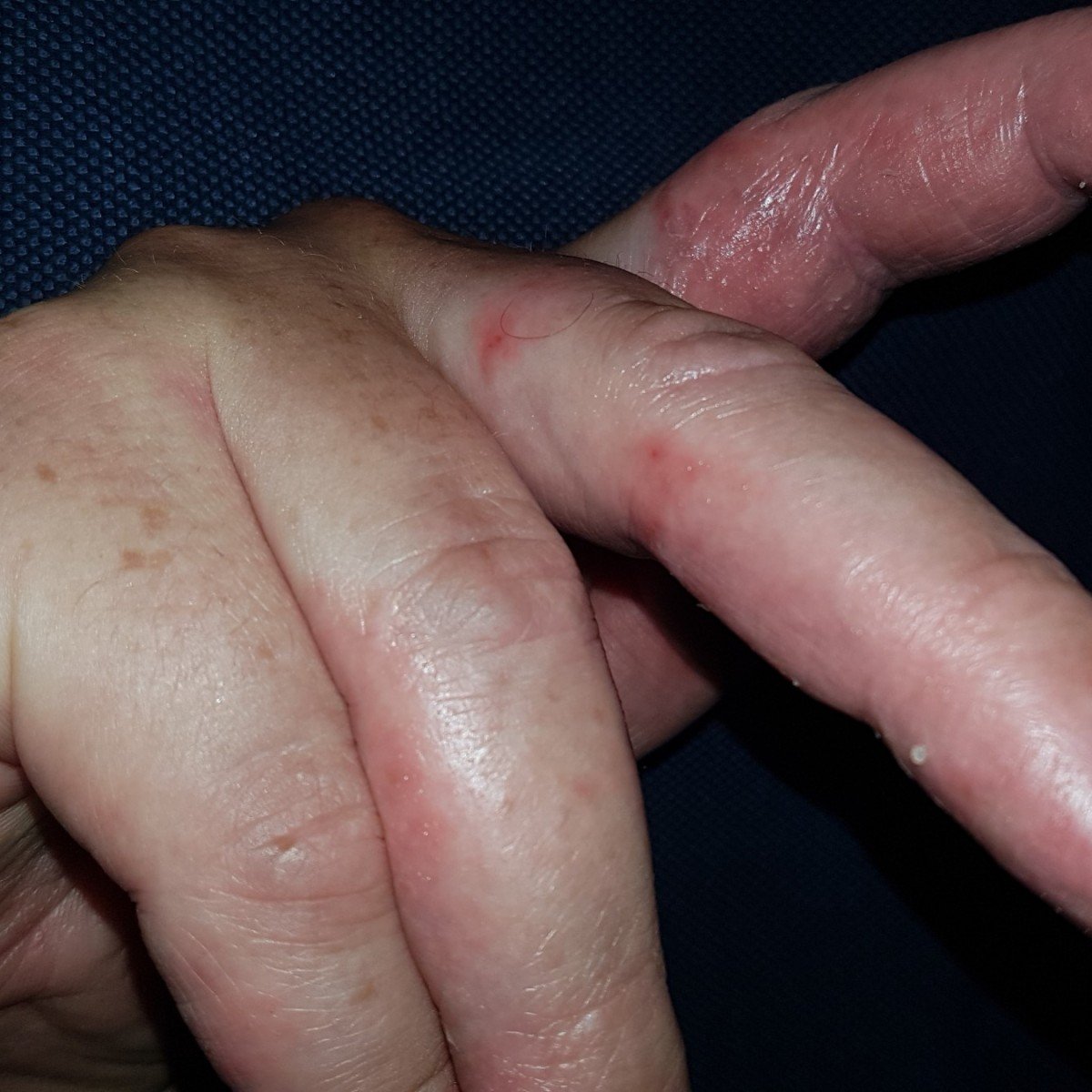
There are many kinds of eczema and each has its own particular set of causes, symptoms, and treatments. Some types of eczema include:
- Atopic dermatitis. A type of eczema characterized by dry, itchy, inflamed skin. It is the most common form of eczema and most frequently occurs in children, but can develop in adults. It is associated with certain allergies and asthma.
- Contact dermatitis. This develops due to skin exposure to allergens, chemicals, materials, or other irritants. Symptoms vary depending on the allergen or irritant involved, but can range from reddening to blistering to a burning sensation.
- Dyshidrotic eczema. Also known as pompholyx, this type of eczema is characterized by tiny itchy blisters that resemble tapioca pudding on the palms, fingers, and soles of the feet. It typically occurs in young adults.
- Nummular eczema. Also called discoid dermatitis, this produces itchy, circular patches of inflamed skin that measure 2 to 3 centimeters in diameter. It usually affects the arms and legs.
- Seborrheic dermatitis. A chronic form of eczema that causes inflamed, scaly skin in parts of the body with a high concentration of sebaceous glandsglands that produce a kind of oil called sebumincluding the face, scalp, and chest.
- Lichen simplex chronicus. Also called neurodermatitis, this form of eczema develops as a result of chronic scratching which results in thickened, or lichenified, skin that is usually itchy, dry, and darker than surrounding skin.
Don’t Miss: What Do You Do For Eczema
Questions To Ask Your Doctor About Atopic Dermatitis
Triggers, potential food allergies, stress, itch and other topics to discuss with your healthcare provider.
An estimated 27 million adults and children in the United States have atopic dermatitis, the most common form of eczema. Symptoms of atopic dermatitis include red, dry, itchy skin that can be flaky or scaly in appearance. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, and may improve for periods of time before flaring up and getting worse.
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is unknown, and there is no cure. However, there are a number of treatments available that can help ease and control symptoms. Because atopic dermatitis affects each person a little differently, treatment is typically individualized and it may take some time to understand what triggers symptoms, what eases symptoms and what treatments are effective. If you are diagnosed with atopic dermatitis, it is important to work with a healthcare provider who understands atopic dermatitis, as well as your needs as a patient.
The following are some topics you may want to discuss with a healthcare provider.
Ask about managing stress Stress can trigger and exacerbate atopic dermatitis symptoms, and the condition itself can be stressful to manage. If you are experiencing stress or anxiety, discuss these feelings with your healthcare provider, and discuss ways to manage stress and activities that may help lower stress. Lowering stress is an important part of overall health.
Dont Miss: Gold Bond Medicated Eczema Relief
How Do Dermatologists Treat Ad
This condition cannot be cured, but proper treatment can control it. A treatment plan created by a board-certified dermatologist can help:
-
Reduce flare-ups
-
Keep your skin moist
-
Lower your risk of infection
While a dermatologist tailors each AD treatment plan to a patients individual needs, most treatment plans include the following:
Skin care: A skin care plan for AD involves:
-
Being gentle with your skin
Your dermatologist will explain how to use baths and moisturizer to help heal your skin.
Trigger management: AD can make the skin very sensitive and very reactive. Things that you come into contact with every day can cause AD flare-ups. Anything that causes AD to flare is known as a trigger.
Everyone has unique eczema triggers, so its important to find your triggers and figure out how to avoid them. Common triggers include skin care products, weather , wool clothing, stress, and laundry detergents that contain fragrance.
Your dermatologist can help you figure out what triggers your AD. To learn more about eczema triggers, go to: Eczema triggers
Medication applied to the skin: Your treatment plan may include medication that you apply to your skin, light treatments, medication that works throughout the body, or some combination of these.
Most people can control AD with medication that they apply to their skin. When this is part of your treatment plan, you may apply one or more of the following:
Don’t Miss: Is Chocolate Bad For Eczema
Diagnosing Eczema & Dermatitis
The different types of eczema and dermatitis can look and feel very similar on the skin. Rashes are often red, scaly, and dry but can also be cracked, oozing, and blistered. Most rashes are very itchy and people find it difficult not to scratch.
NYU Langone dermatologists, with their extensive experience and expertise, may differentiate between atopic, contact, and nummular dermatitis simply by examining the distribution of the rash on your skin and asking questions about your family and medical history.
Our doctors have also been leaders in the diagnosis of contact dermatitis since the 1930s, when the patch test was brought to the United States and the technique was refined. This allergy test is uniquely designed to identify the cause of contact dermatitis without using needles. The patch test remains the only reliable method of determining which substances cause an allergic reaction when they come into contact with the skin.
How Do Dermatologists Diagnose Atopic Dermatitis
To diagnose atopic dermatitis , a board-certified dermatologist carefully examines your skin and asks questions.
To help ensure that your dermatologist has accurate information, its helpful to answer these questions before your appointment:
-
Do any of your blood relatives have AD, asthma, or hay fever?
-
What are your symptoms?
-
When did the symptoms begin?
-
Where do the rashes appear on the skin?
Providing your dermatologist with this information can be very helpful. AD tends to wax and wane, so you may have clear skin when you see your dermatologist.
A skin exam along with information about your health and symptoms may be all that are needed to diagnose AD. Some people also need a skin biopsy.
Your dermatologist can quickly and easily perform a skin biopsy during your appointment. To do this, your dermatologist will numb and remove a tiny amount of skin. When looked at under a microscope, this can provide valuable information.
Having a skin biopsy can also help your dermatologist select the best treatment.
Also Check: Eczema Relief Skin Protectant Cream
When To See The Doctor
Not sure whether you need to make an appointment? You may need to go to the doctor if:
- Your skin shows signs of infection .
- Your symptoms are affecting your sleep or other daily activities.
- Over-the-counter remedies are not helping.
- The treatments recommended or prescribed by your doctor are not working or have had unexpected or severe side effects.
You may also visit the doctor if you experience flare-ups times when your eczema symptoms worsen.
Treating Atopic Dermatitis In Infants
About 10% to 20% of infants develop eczema, with the rash usually on the face and scalp. In most cases, this condition improves after age 5 and may disappear for good.
Medical experts believe itâs a genetic condition or passed from parents to their kids. Symptoms can vary depending on the age of the child.
In more severe cases, infants can have eczema on uncommon areas like the torso, elbows, and knees. Children and teens will notice the rash in the inner elbows, behind the knees, on the neck, or on the wrists and ankles. The skin may appear drier and thicker, and develop a scaly texture.
There are some steps you can take to treat your childs eczema or prevent flare-ups:
- Avoid skin care products with fragrances and other possible irritants.
- Cut your childâs fingernails and encourage them to wear gloves to prevent skin damage from excessive scratching.
- Maintain a routine of bathing, moisturizing, and applying age-appropriate treatments recommended by a pediatrician. Ask your doctor about the âsoak and sealâ method.
- Talk to a pediatrician or dermatologist about the benefits of oatmeal baths or bleach baths to reduce inflammation and discourage bacterial growth.
- Boost the effectiveness of any topical medication and rehydrate the skin by using wet wrap therapy. This can also prevent your child from scratching their skin.
Also Check: Can Dog Dander Cause Eczema
Can You Prevent Eczema
Medical professionals do not know how to prevent eczema outbreaks in any age group. Avoiding triggers, once you identify them, should help keep the condition under control.
Apart from triggers, choose soft, comfortable clothing and gentle, nonirritating soaps as part of your skin care regimen. Use heaters, air conditioners, dehumidifiers and other devices that can regulate the ambient temperature.
Avoid any allergens that affect you. If you cannot avoid them, see your doctor for a prescription to help you manage your allergies.
What Is The Underlying Cause For Eczema
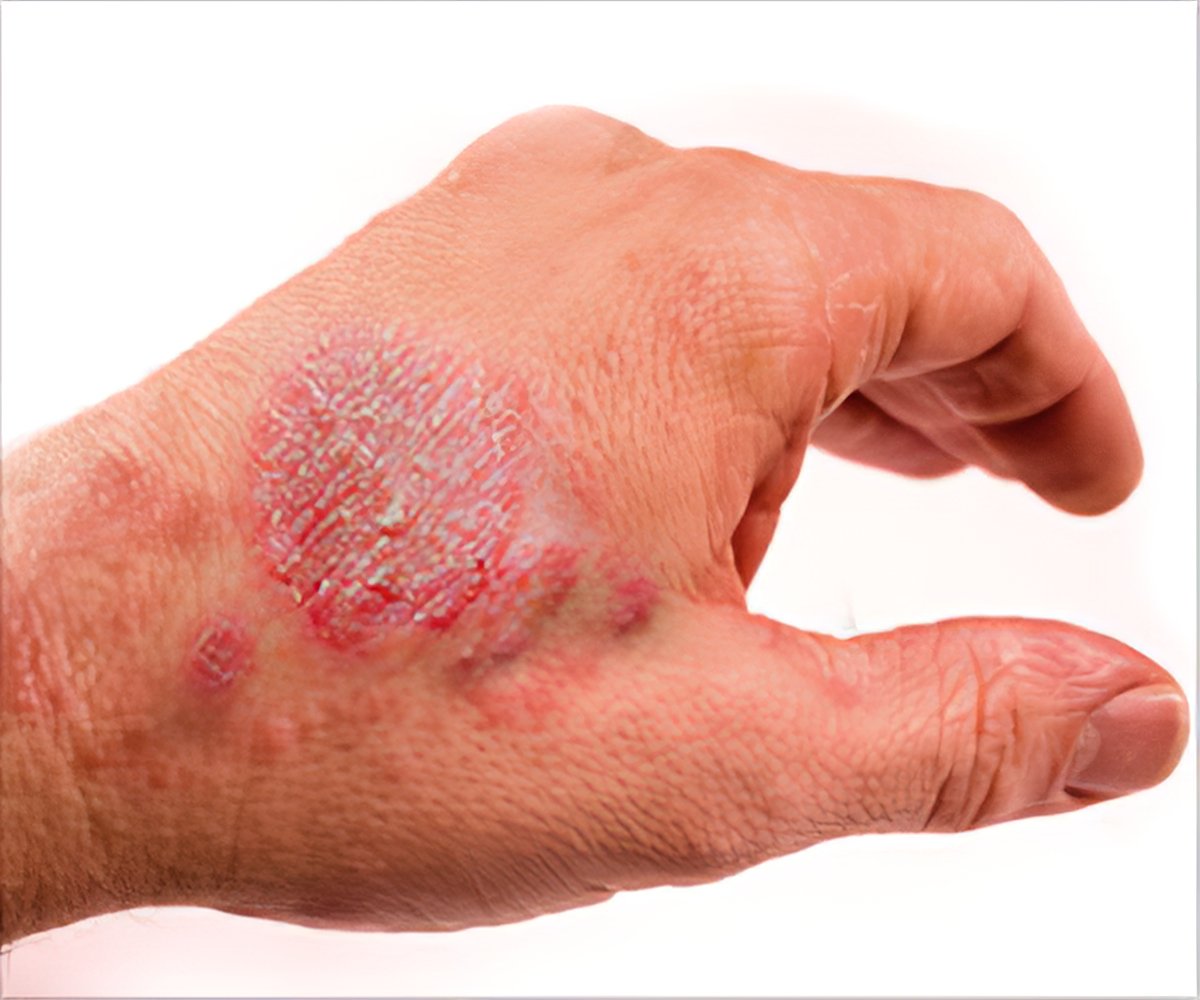
Medical researchers acknowledge the fact that there is no proven cause of eczema. However, most of them believe that a combination of genes and an external or internal trigger can lead to eczema.
Research shows that most of the patients who suffer from this condition tend to have an over-reactive immune system that produces the inflammation when triggered by either internal environment or external substances. It is this inflammation that causes the itchy and sometimes painful symptoms of eczema.
Research has also revealed that some patients with dermatitis have a gene mutation responsible for creating filaggrin a special protein which primary role is to help your body maintain a healthy and protective barrier on the top layer of your skin.
If your body fails to produce enough filaggrin to build the protective layer, you end up losing a lot of moisture, letting in bacteria and other viruses ultimately leading to chronic inflammation. This is the primary reason why many individuals with dermatitis have dry and infection-prone skin.
Dont Miss: Eczema Around Eyes And Mouth
You May Like: Eczema On Eyelids Treatment Uk
Physical Examination And Medical History
A dermatologist carefully examines your skin during a physical exam. The pattern, location, and appearance of a rash provide our doctors with important information about its causes.
Your doctor may ask questions about when symptoms appeared, what parts of the body they affect, and whether a rash is persistent or comes and goes. They also want to know if there are any noticeable patterns about when the rash appears, such as if there is a seasonal variation or if the rash appears when using certain perfumes or after exposure to certain metals or fabrics. Knowing whether anyone else in your family has been diagnosed with eczema or dermatitis may help doctors better understand your diagnosis.
Doctors may also ask about the personal hygiene products used in your household. Many cosmetics, moisturizers, and soaps contain irritating ingredients that may cause eczema and dermatitis. Our dermatologists can recommend nonirritating, fragrance-free products that have low levels of preservatives. Often, these are available at drugstores in a similar price range as the products you normally buy.
It can be hard to tell for sure if you have atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema. Youâll want to see a dermatologist or other doctor to find out.
At your appointment, your doctor will check your skin and talk with you about your symptoms, your health history in general, and any rashes or allergies that run in your family.
How Is Eczema Diagnosed
Your doctor will begin to make a diagnosis by asking you about your symptoms, when they began, and whether you have allergies or asthma. He or she will conduct a physical exam to look at your skin and assess your symptoms. In most cases, at this point your doctor will be able to make a diagnosis. Sometimes, though, your doctor will order additional diagnostic tests.
The most common diagnostic tests for eczema are patch tests and skin biopsy.
- Patch test: A physician will place one or several adhesive patches on your back. Each of these patches contains a small dose of an allergen. The patches remain in place for two days, at which point the physician examines the skin to determine which, if any, particular allergens cause skin irritation.
- Skin biopsy: In this procedure, a physician removes a small piece of skin tissue. Once collected, a pathologist will examine the tissue sample under a microscope to confirm diagnosis.
Read Also: Best Face Wash For Eczema On Face
What Should I Expect With Phototherapy
During your visit, you will apply a moisturizing oil to the skin and stand in a large cabinet undressed except for underwear and goggles to protect the eyes. The light-emitting machine will be activated for a short time usually just seconds to minutes and it will either treat the entire body or just certain exposed areas. It may take one or two months of steady treatment with phototherapy to start to see improvement in eczema symptoms, and at that point, the frequency of the visits can sometimes be reduced or stopped for a period to see if the eczema is in remission.
Potential side effects of phototherapy include:
- Sunburn and skin tenderness
- Premature skin aging
Treatment For Eczema And Dermatitis
The goal of treatment for eczema and dermatitis is to alleviate the signs and symptoms of the skin ailment using the least amount of medication. Our dermatologists recommend at-home therapies to prevent and treat mild rashes, and offer phototherapy and medication for people whose symptoms persist despite nonprescription treatment.
Don’t Miss: Cradle Cap Vs Eczema On Scalp
How Is Contact Dermatitis Treated
Treatment involves working out what allergen or irritant is causing the contact dermatitis and then avoiding it. The rash should clear slowly once you avoid the trigger.
It is possible to have different types of contact dermatitis at the same time. You may need to avoid several different allergens or irritants.
Your doctor may recommend a moisturiser, steroid creams or tablets, or therapy such as ultraviolet light. In severe cases, immunosuppressant medication may be needed.
Try not to scratch the affected skin and keep your nails short so you dont accidentally scratch yourself and break the skin. Your pharmacist or doctor may be able to recommend some products which can help with dry, sore or itchy skin.