How Long Does Baby Eczema Last
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, while some babies may continue to experience eczema through adulthood, many will outgrow it around age 4.
Baby eczema may also evolve as your little one gets older. According to the National Eczema Association, it might appear on babys face in early infanthood but pop up in key areas like the knees, elbows and hands as they get older. As they approach big-kid territory, eczema often hides in knee folds or elbow creases and other sweat-prone spots.
Whether eczema is an acute or perpetual problem for your child, its reassuring to know that there are many baby eczema treatments and preventive measures you can take to reduce the symptoms and alleviate the itch.
No one likes to see their baby in discomfortand the appearance of any rash can be disconcerting. But if you recognize eczema, you can rest assured that its common and treatable.
About the experts:
Anna Bender, MD, is a pediatric dermatologist at Weill Cornell Medicine and New York-Presbyterian in New York City. She received her medical degree at the Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons.
Latanya Benjamin, MD, FAAD, FAAP, is a Florida-based pediatric dermatologist and dermatologic surgeon and Society for Pediatric Dermatology board member. She earned her medical degree at Drexel University College of Medicine in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Plus, more from The Bump:
Is Eczema Different For Infants Or Toddlers Than It Is For Older Children
A painful, itchy rash on a babys face, torso or body may be eczema
Eczema looks and acts differently in infants and toddlers than it does in older children. The location and appearance of eczema changes as they grow, so its important to know what to look for during every stage of your infant or toddlers life.
Are There Likely To Be Any Complications Of Eczema
It’s important to control your child’s eczema – uncontrolled eczema can lead to poor sleep which can have long-term effects on learning and behaviour.
Children with eczema are more likely to get skin infections.
Eczema makes the skin dry and cracked and increases the chance of infection by bacteria and viruses . Infected eczema may be wet, crusted or painful. See your doctor for treatment.
If your child’s eczema gets worse or becomes infected, you will need to take them to your doctor. Sometimes, a hospital stay may be necessary.
It’s important to control your child’s eczema. Uncontrolled eczema can lead to poor sleep which can have long-term effects on learning and behaviour.
Read Also: Eczema White Patches On Skin Treatment
Natural Remedies For Baby Eczema
If you need some extra help soothing babys skin, these natural eczema treatments may make things better.
- Wet a washcloth. Drape cool, wet washcloths or gauze over your babys irritated skin for five to ten minutes at a time or however long you can get your squirmy worm to cooperate.
- Try an oatmeal bath. Sprinkle a bit of uncooked oatmeal, colloidal oatmeal or even baking soda into the tub when you wash your baby. All can naturally relieve eczema and irritation.
- Combat dry air. Running a cool-mist humidifier in your baby’s bedroom can help keep her skin super-hydrated. Clean it frequently to prevent bacteria and mold buildup.
- Dress your little one in layers. Sweating can reboot the eczema cycle, and thats the last thing you want. Layers let you customize babys outfit for toasty temps.
- Ask your pediatrician about probiotics. Studies are underway to see whether probiotics may ease eczema when added to dry baby formula or served as a dietary supplement. Get your doctor to weigh in before giving it a go.
Eczema Around The Eye
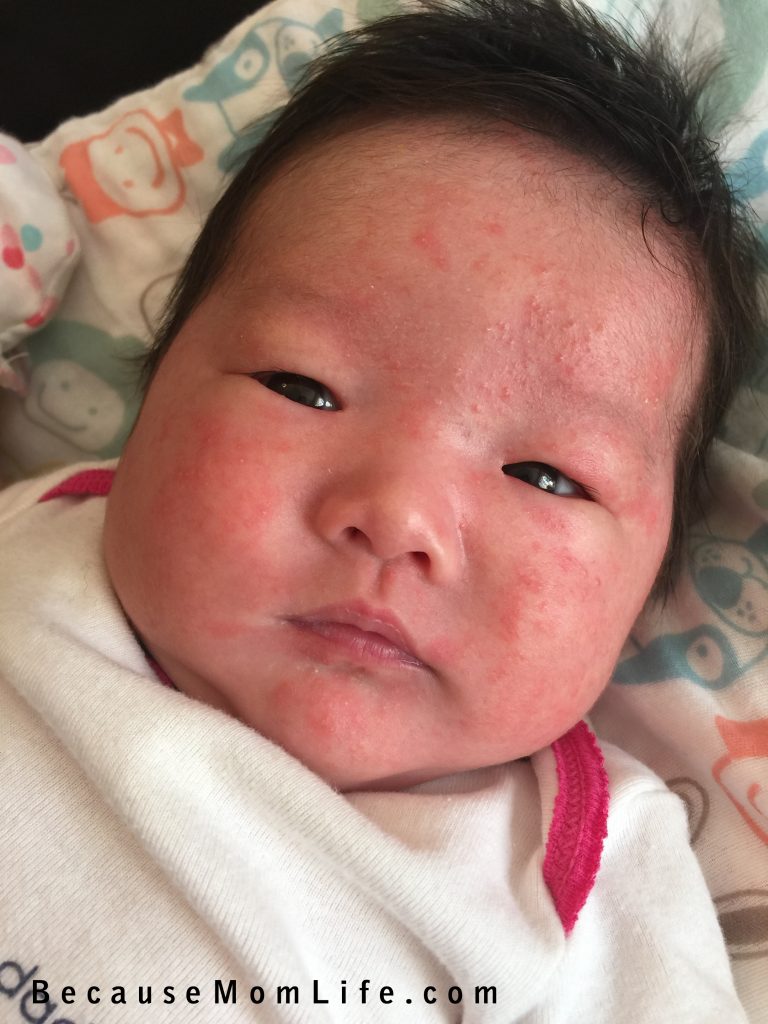
When eczema occurs on the face, it often affects the skin around the eyes or eyelids . Eczema that develops near the eyes needs special attention because the eyes themselves can be affected.
Those with eczema around the eyes are more susceptible to certain eye problems such as conjunctivitis , inflamed cornea, and changes in the shape of the cornea .
Also Check: Best Shampoo For Eczema Itchy Scalp
What Caused My Babys Eczema
There is no single cause of atopic eczema. Eczema is a complex condition it is genetic but also involves an overactive immune response to environmental factors, which cause eczema flares. Because the atopic gene is hereditary, it runs in families, and is responsible for three conditions: eczema, asthma and hay fever.
Fifty per cent of people with eczema have an additional genetic element a difference in a skin protein called filaggrin which leads to further problems in the skin barrier. All atopic conditions can be linked to allergies in some people, but there are also many universal irritants, such as soap and heat.
Avoid Triggers And Treat Infection
Stay cool
Getting too hot from clothing or heating can make eczema worse – stay cool.
Avoid soap and fragrances
Soap and fragrances are the most common triggers of eczema. Only use skin care products designed for eczema. Many are available on prescription from your doctor or nurse prescriber.
Eczema is made worse by infection such as from:
- school sores
- the cold sore virus which can cause severe painful infection of eczema
Avoid contact with cold sores. See your family doctor urgently if your child gets an infection from cold sores.
Find out more about school sores.
Removing foods from your child’s diet does not usually help eczema
Removing foods from your child’s diet does not usually help eczema and can be dangerous, leading to anaphylaxis.Please talk with your doctor about this.
Also Check: Gloves In A Bottle Eczema
What Causes Eczema In Children
Researchers dont know exactly what causes baby eczema, but they believe its most likely due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Eczema is not contagious.
Infants are more likely to develop eczema if family members have a history of eczema, hay fever, or asthma.
While these conditions dont cause one another, infants are more likely to develop hay fever or asthma if they already have baby eczema.
Scientists believe eczema results from an immune-system dysfunction that affects the skin barrier and its ability to hold in moisture.
What Does Baby Eczema Look Like
Eczema often appears on the face and scalp in infants under 6 months old. The rash will usually be red and it may bubble up, ooze fluid, then crust over. Older babies may develop eczema on their elbows and knees.
Eczema usually does not occur in the diaper area because the skin stays too moist. Rashes in this area are more likely diaper rash.
The itchiness of eczema can make an infant very uncomfortable. A baby cannot tell a caregiver what is wrong, but their behavior may hint that eczema is causing them discomfort.
Signs to look for include:
- Trouble sleeping
Don’t Miss: Eczema Rash On Baby Back
Ways To Prevent Baby Eczema
Eczema itself cannot be prevented, but knowing and avoiding triggers can help prevent flare-ups of the condition.
Some ways to reduce triggers include:
- Keep your child out of cold, dry air.
- If they are 6 months or older, make sure your child gets an annual flu shot.
- Read labels on products to help your family avoid common irritants.
- Double-rinse your laundry to remove detergent residue.
How To Impede The Scratching
My oldest child still deals with eczema flare ups from time to time, so I know first hand the difficulty associated with trying to keep a baby from incessantly scratching at those itchy patches. Baby eczema and sleep dont have to cancel each other out!
The best solution Ive found to deal with this issue is to sew the ends shut on your babys long-sleeved shirt/pajama/onesie. This may not stop the scratching, but will keep the nails from breaking the skin.
If like me youre not very crafty, then consider purchasing something from Bamboo Bubby. They have specially designed sleeves and sleep sacks in natural fabrics that can keep the itching to a minimum.
Also Check: Dyshidrotic Eczema Over The Counter Treatment
Baby Eczema And Cradle Cap Symptoms
- Thickened skin
- Darkened skin on the eyelids and around the eyes
- Changes to the skin around the mouth, eyes, or ears
Cradle cap causes symptoms not commonly seen in other types of infantile eczema, such as greasy yellow scales on the scalp that sometimes appear in a thick layer covering the entire top of the head. Over time, the scales become flaky and rub off.
What Causes Infant And Toddler Eczema
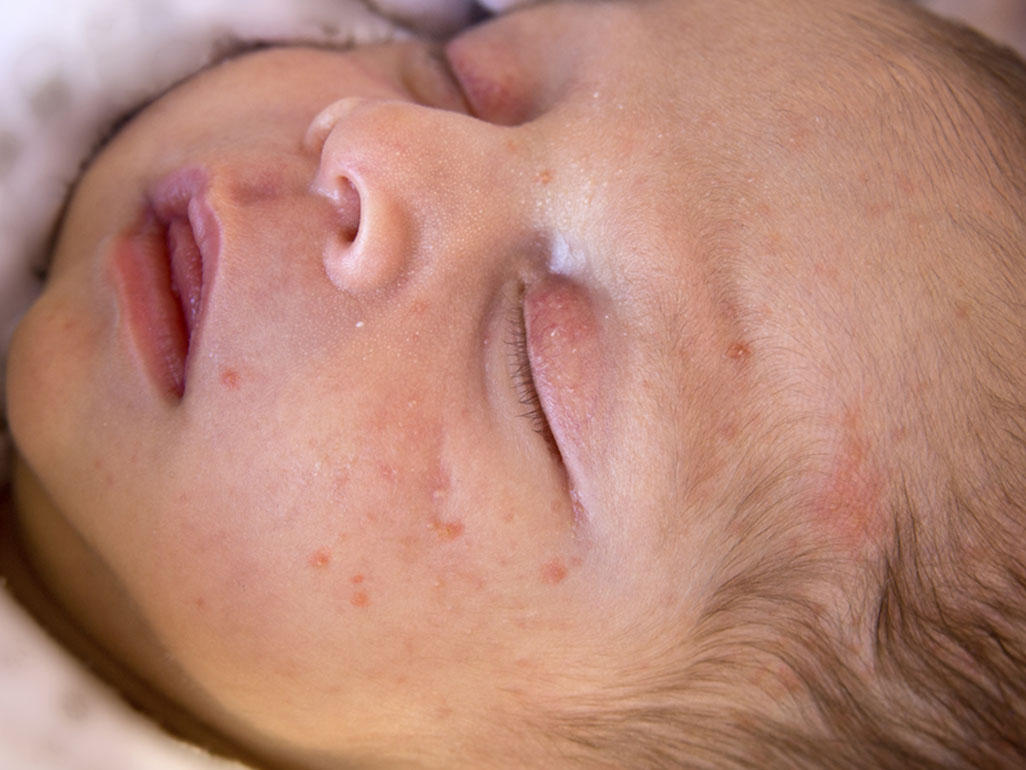
As stated above, eczema is a mixture of dry skin and allergies. The cause is mainly genetic an inborn tendency toward dry skin and allergies. There is no way to change these genetics. The important issue is not what causes eczema in the first place, but what allergens and skin irritants your child is exposed to that are triggering the flare-ups.
Also Check: Eczema On Top Of Feet
Seattle Children’s Urgent Care Locations
If your childâs illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
Medical Treatment For Eczema
Eczema cant be cured. But it can be managed by preventing and treating flare-ups as soon as they appear.
If your childs skin is inflamed and itchy, theyll probably need some corticosteroid ointment or cream. For mild eczema, you can buy mild corticosteroids over the counter at your pharmacy. The most common is hydrocortisone 1% cream. For more serious eczema or if the over-the-counter products arent working, youll need to see your GP to get a prescription for a stronger corticosteroid.
Other eczema treatments include pimecrolimus, a non-steroidal cream. Doctors might prescribe this cream for children with mild to moderate eczema on the face and in body folds.
If your child is scratching at a rash, you could ask your pharmacist or GP about using an antihistamine medication for a few days. Together with a corticosteroid cream, this might give your child some rest and help the flare-up to settle.
If your childs eczema rash gets infected, your doctor will prescribe a course of oral antibiotics.
You May Like: What To Do To Help Eczema
How Is Eczema Diagnosed
There is no specific test used to diagnose eczema. The doctor will look at the rash and ask about symptoms, the child’s past health, and the family’s health. If family members have any atopic conditions, that’s an important clue.
The doctor will rule out other conditions that can cause skin inflammation, and might recommend that your child see a dermatologist or an allergist.
The doctor may ask you to ban some foods from your child’s diet, switch detergents or soaps, or make other changes for a time to see if your child is reacting to something.
When To See A Doctor
While you can do a lot to control your babys eczema, sometimes you have to seek medical attention. Look out for the following signs and see a doctor if any of these occur.
- Unresponsiveness to over-the-counter medications. There are a lot of over-the-counter creams available that can sooth eczema. These ointments are very good at treating eczema for your baby. If they arent working, however, you should see a doctor to get prescription medicine instead.
- Changes in responsiveness to prescription medicine. Just because one medicine is working today doesnt mean it will always work. If you have prescription medication for your babys eczema and you see it doesnt work as well as it previously did to control symptoms, its time to reevaluate the medicine. Your doctor will be able to examine your baby and see if another medicine will be better.
- Appearance of yellow crust on the eczema patches. Yellow crust indicates that there may be a bacterial infection. This needs to be checked out immediately by a doctor because if it goes untreated, it will get worse. Your doctor will be able to determine if antibiotics should be prescribed to stop the infection.
- Development of pus-filled blisters on the eczema patches. Blisters are also a sign that there may be an infection. They are also very painful and a sign that the eczema isnt being managed adequately. A doctor can evaluate your management plan and make adjustments, so you can better control your childs eczema symptoms.
Also Check: Is Zinc Oxide Good For Eczema
What Else Is Happening At Johns Hopkins Today
We go out of our way to provide the comprehensive care our patients with eczema need. On a case-by-case basis, we communicate with one another whether in allergy, dermatology, psychology or infectious disease to put together the best course of treatment for each child.We are optimistic that future therapies and approaches to care for those with even severe eczema are going to be greatly improved with more research and that the creation of the Eczema Day Treatment Unit will help us conduct cutting edge research and answer questions we face every day seeing and treating patients.
Will My Baby Grow Out Of Eczema
Sadly, it is impossible to predict whether your baby will have eczema for life or for just a short time. So far, there is no cure for eczema. Eczema is a chronic condition with periods of flare and periods of remission, and most people with a history of eczema still have problems with dry and itchy skin. If your child has a difference in their filaggrin gene, they will not grow out of it. Even if your baby appears to grow out of their eczema, it may return during the teenage years or in adulthood.
Also Check: How To Get Eczema Off Your Face
Which Is The Best Emollient For My Baby
Emollients treat dry skin by providing a surface film of oils. This increases water in the upper layer of the skin, restoring and providing a robust skin barrier, to prevent the entry of environmental agents or triggers.
Emollients soften the skin and reduce itch. If they are used regularly to maintain skin hydration, they can reduce the frequency of eczema flares. Leave-on emollients include lotions, creams,ointments and gels.
The emollient advised or prescribed for your baby should prevent dry skin and not cause irritation. You might need to try several products until you find the right one. Apply leave-on emollients regularly, throughout the day for example, at every nappy change and after bathing.
Use the product liberally . To apply the product, dot it all over the skin, and then smooth it in, using a gentle, downward, stroking motion rather than rubbing in.
What Does Eczema Look Like
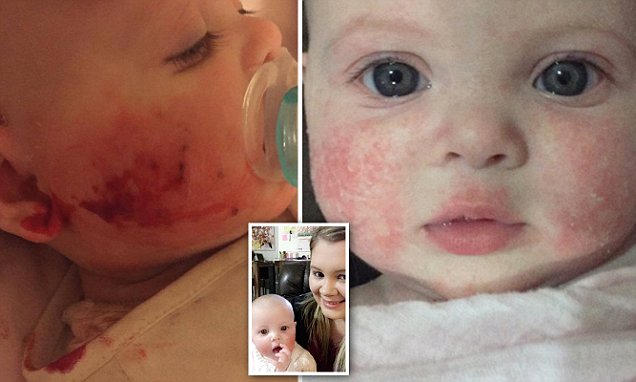
In babies with paler skin, when eczema is flaring the skin is red and itchy. In babies with darker skin, the irritated, itchy areas may be red but are more likely to show as darker patches. They may also appear paler around the front or back of knees or elbows.
When an area of darker skin is treated for eczema, it may become lighter and may take several months to return to the babys normal skin tone.
Recommended Reading: How To Heal Baby Eczema
What Is The Best Eczema Cream For Babies
To soothe itchiness even more, you could try adding oatmeal soaking products to your babys tub. Use mild, unscented body and laundry soaps. Perfumed, deodorant, and antibacterial soaps can be rough on a babys sensitive skin. Clean carefully. Use soap only where your baby may be dirty, such as the genitals, hands, and feet.
How Can I Prevent Baby Eczema
Since several factors can cause eczema in your baby, theres no way to completely prevent the condition. You can help your baby reduce their risk of developing a flare-up of symptoms by:
- Avoiding triggers, irritants and allergens.
- Using moisturizer on your babys skin daily.
- Giving your baby baths with warm, not hot, water that is between five to 10 minutes long.
- Choosing moisturizers or ointments without fragrance, designed for babies.
Also Check: How To Treat Eczema On Scalp Naturally
How Is Atopic Dermatitis Diagnosed In A Child
The healthcare provider will ask about your childs symptoms and health history. He or she may also ask if you or other family members have atopic dermatitis, asthma, or nasal allergies such as hay fever or allergic rhinitis. He or she will also ask about allergy symptoms in your child. The healthcare provider will examine your child, looking for signs of atopic dermatitis. There is no specific test for atopic dermatitis. Testing is usually not needed, but it may be done. Tests may include:
-
Blood tests. Your childs blood may be checked for levels of immunoglobulin E . IgE is released by the body’s immune system. Its high in most children with allergies and with atopic dermatitis. Other blood tests may also be done.
-
Skin tests. Skin tests may be done to check for allergies or other skin conditions.