Treating Eczema In Teens And Adults
As with young children, keeping the skin well moisturized is key to controlling eczema in teens and adults. Apply emollients often throughout the day. Ointments are very effective at sealing in moisture, but because they’re heavier and leave your skin a bit greasy, you may want to save the application of these for nighttime.
Treatments for teens and adults with eczema include many of the same options used for children, namely topical corticosteroids, topical calcineurin inhibitors, and dupilumab. Antihistamines are sometimes used for their sedating properties if itch is impairing sleep, but they are not generally helpful in controlling the itch that comes with eczema.
Remember, too, that good personal care is important to allowing eczema to heal and preventing flareups. For instance, make sure your shower or bath water isn’t too hot. Very hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils. Aim for lukewarm water temperatures for your shower.
And don’t overlook things that may be contributing to skin irritation like perfumes and body sprays, makeup, laundry detergent, or fabric softeners.
Favorite Resource For Becoming An Advocate
We love that the NEA has made it so easy to advocate for better healthcare policies. Their Advocacy Action Center enables people to browse legislation related to eczema in various states. If you wish to take action, you can click on a button and fill out an online form to send a message to your local lawmaker.
Is Eczema Different For Infants Toddlers And Older Children
A painful, itchy rash on a babys face, torso or body may be eczema
Eczema looks and acts differently in infants and toddlers than it does in older children. The location and appearance of eczema changes as they grow, so its important to know what to look for during every stage of your infant or toddlers life.
Don’t Miss: Does Honey Help With Eczema
Whats In Your Eczema Toolkit
It bears repeating that anxiety and depression are prevalent among people with AD, and young patients are especially vulnerable. Its obvious that AD takes an emotional toll, but stress also appears to exacerbate the condition, says LeBovidge. If a child is feeling down, she strongly urges you to bring it to the attention of your family physician.
Wellness takes practice, and while practice doesnt always make perfect, it will get easier over time. Start by putting together your own wellness toolkit. Build the quality of life you want and need, one day at a time.
How To Prevent Eczema Outbreaks
Since eczema is a skin condition that is worsened by dry, damaged skin, many flare-ups can be prevented simply by keeping the skin hydrated, moisturized, and damage-free. Additionally, many eczema sufferers notice that they have certain triggers, like skin products, excess sunlight, or even detergents and soaps. It can be helpful to keep track of everything your skin comes in contact with this can help you avoid your personal triggers and, therefore, avoid painful flare-ups.
Also Check: What To Eat To Get Rid Of Eczema
Why Did My Toddler Develop Eczema
Similar to when babies develop eczema, children who develop eczema do so because of a combination of genes and environmental triggers, but researchers dont know a lot more about why eczema manifests on a childs skin. When something outside the body switches on the immune system, skin cells dont behave as they should causing eczema flare ups.
We also know that children who come from families with a history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to developatopic dermatitis.
Common eczema symptoms in children include itchiness, rashes and the breaking down of skin barriers that protect children from skin infections.
Prevention and treatment are often similar for toddlers and babies. No matter what age your child is, consult with a pediatrician or pediatricdermatologist before deciding on a treatment plan.
What Doesnt Cause Eczema
Eczema is not contagious. You canât catch eczema by coming in contact with someone who has it.
Eczema is not an allergic reaction. Even so, a large number of children who have eczema also have food allergies. That doesnât mean that certain foods such as dairy, eggs, and nuts â common food allergy triggers in children with eczema â cause it or make it worse. Before removing particular foods from your childâs diet, talk with your doctor to be sure your childâs nutritional needs will be met.
Don’t Miss: What To Do For Bad Eczema Breakout
What Are The Symptoms Of Eczema In Older Children
In toddlers under age 5, eczema usually affects the face. It can look red and bumpy. It can look also scaly and dry, or you may notice deep lines on their skin.
Children over 5 years old may have eczema that is red and itchy or rash-looking. It may also look like permanent goosebumps and be thicker. On dark skin, the thickening may be hyperpigmented.
Skin concerns may be a symptom of a different condition, so seeing a dermatologist can help determine whether the cause is eczema or something else.
Certain areas of the body are more likely to be affected by eczema than others. This can change, depending on your age.
Millions Live With Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is common worldwide. People of all ages from newborns to adults 65 years of age and older live with this condition. Symptoms range from excessively dry, itchy skin to painful, itchy rashes that cause sleepless nights and interfere with everyday life.
Atopic dermatitis is common
1 in 10 Americans has atopic dermatitis.
In the United States, research indicates that African American and Asian American children develop AD more often than white children.
When a child has deeply pigmented skin, AD tends to be diagnosed later in life. Sometimes, the condition is missed altogether because its less noticeable. In brown or black skin, you tend to see gray to violet-brown skin discoloration rather than red rashes.
Donât Miss: What Is The Reason For Eczema
Recommended Reading: What Can I Put On Eczema On My Eyelids
Living With Atopic Dermatitis
The following steps can help manage atopic dermatitis:
- Take brief baths or showers using lukewarm water.
- Practice good skin care.
- Dont use harsh soaps. Ask your healthcare provider to recommend a brand.
- Dress in light clothes. Sweating can make atopic dermatitis worse.
- Use a good moisturizer at least once a day. Ask your healthcare provider to recommend a brand.
- Avoid scratching the affected area.
- Minimize stress.
- Make lifestyle changes that prevent flare-ups.
- Avoid skin products that have fragrances and dyes
Importance Of Eczema Treatment
There is growing evidence that allergens introduced into the body through the skin can lead to the later development of food allergy, asthma and hay fever. Aggressively treating eczema in children and taking steps to restore normal skin barrier function may lower the risk of future development of these conditions.
Don’t Miss: What To Eat If You Have Eczema
Eczema Coping Tips Diet
In most cases, eczema isnt caused or made worse by diet. If you notice that your eczema seems to get worse after eating a particular food, you may be an exception to this. See your doctor or dietitian for proper allergy testing and dietary advice.Never self-diagnose or you risk depriving yourself of enjoyable and nutritious foods for no good reason. Unnecessarily avoiding certain foods can lead to nutritional deficiencies.
Causes Of The Diseases
Eczema and psoriasis, while two distinct conditions, have something key in common. Both diseases, says Dr. Amy Paller, Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics at the Northwestern Feinberg School of Medicine, involve the human immune system, just in different ways.
With psoriasis, the immune system is overactive in a manner that leads to the growth of too many new skin cells, too fast. These cells pile up on the surface of the skin, causing thick scales or plaques that can be dry, flaky and painful. Psoriasis can be triggered or worsened by stress, skin injury, cold/dry weather, medications or infections. Genetics also seem to play a role with psoriasis risks running in families.
While experts dont completely know what causes eczema, a combination of genes, immune system tendencies and triggers are believed to be involved. People with eczema tend to have overly-reactive immune systems that, when triggered by a substance outside or inside the body, respond by causing inflammation. Researchers have also found that some people with eczema have a mutation in a gene that plays an important role in the skin barrier leaving the skin more vulnerable to dryness, irritants and allergens . Similar to psoriasis, stress can also trigger eczema and family history can increase eczema risks.
Read Also: Can You Join The Military With Eczema
Where Is Eczema On Babies
In babies, eczema is often found on the scalp and face, particularly the cheeks. Itâs most often found on the head, but it can be found anywhere. It is not typically in the diaper area.
A baby may rub their face or head on the carpet or their sheets to scratch the itchy skin. This can further irritate the skin and lead to infection.
As they start to crawl, eczema may be more frequently seen on their elbows or knees. This is because these are areas that are prone to rubbing as they crawl.
In toddlers, eczema may often be seen on their face, around their mouth, or on their eyelids. It may also be on wrists, elbow creases, and knees.
How Is Eczema Diagnosed
There is no specific test used to diagnose eczema. The doctor will look at the rash and ask about symptoms, the child’s past health, and the family’s health. If family members have any atopic conditions, that’s an important clue.
The doctor will rule out other conditions that can cause skin inflammation, and might recommend that your child see a dermatologist or an allergist.
The doctor may ask you to ban some foods from your child’s diet, switch detergents or soaps, or make other changes for a time to see if your child is reacting to something.
Also Check: Is Yogurt Bad For Eczema
What Causes Atopic Dermatitis
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not known. It runs in families, which suggests a genetic link. Its also linked to asthma and allergies. There is likely an alteration of the proteins in the skin that leads to atopic dermatitis.
Certain triggers can make atopic dermatitis worse. For example, stress, hot or cold temperature, dry conditions, certain fabrics, or detergents can cause a flare-up.
What Foods Should I Eat Or Avoid To Reduce My Risk Of Eczema
The connection between eczema and food allergies is unclear. If you have food allergies, then one of the reasons why you must avoid that food is that it may cause or worsen dermatitis. Examples of common allergies include peanuts, dairy, eggs, sugar, alcohol and gluten. Pay attention to what you eat. If your eczema flares up after you eat a certain food, then you might have an allergy to it.
If you dont have a food allergy then there are no foods, including chicken, that will cause or worsen your eczema.
Don’t Miss: Is Eczema Itchy At Night
What Can I Expect If Ive Been Diagnosed With Eczema
Nearly half of children with eczema will outgrow the condition or experience great improvement by the time they reach puberty. Others will continue to have some form of the disease. For adults with eczema, the disease can be generally well-managed with good skin care and treatment, although flare-ups of symptoms can occur throughout life.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider About Eczema
- How can you tell that I have eczema?
- If I dont have eczema, what other skin condition might I have?
- Is there a specific brand of moisturizer that you recommend?
- Is there a prescription cream that you can prescribe?
- How often should I see a dermatologist regarding my eczema?
- What soaps, lotions, makeup, etc. should I avoid?
- What medications do you recommend?
- What at-home treatments do you recommend?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Eczema is very normal, very common, and very, very uncomfortable. It can affect your quality of life. At its worse it can keep you from sleeping, distract you and make you feel self-conscious in public. See your dermatologist or other healthcare provider as soon as you start to see signs of it. Explore at-home remedies and prescribed treatments.
Youre not alone! 15% to 20% of people experience eczema or another type of dermatitis at some point in their lives.
Also Check: How To Treat Eczema At Home For Babies
Tips For Reducing Outbreaks
- Apply cool compresses to your skin, or take a colloidal oatmeal or baking soda bath to relieve the itch.
- Moisturize your skin daily with a rich, oil-based cream or ointment to form a protective barrier against the elements. Apply the cream right after you get out of the shower or bath to seal in moisture.
- After you bathe, gently pat your skin with a soft towel. Never rub.
- Avoid scratching. You could cause an infection.
- Use fragrance-free detergents, cleansers, makeup, and other skin care products.
- Wear gloves and protective clothing whenever you handle chemicals.
- Wear loose-fitting clothes made from soft fibers, like cotton.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is often called the itch that rashes because it begins with itchy skin. Scratching the itchy skin causes a rash to appear.
This rash also tends to be very itchy.
AD causes itchy skin
No matter your age or where the AD appears on your skin, AD tends to itch.
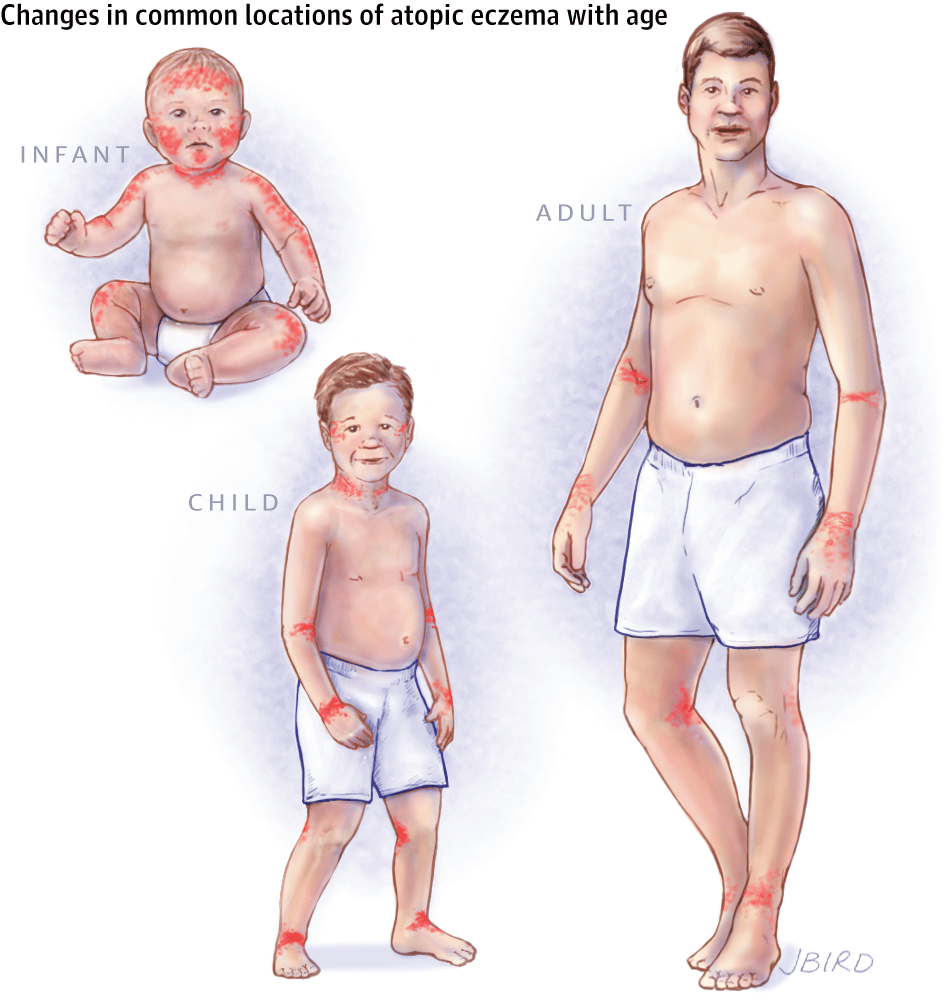
AD can develop on any area of your skin at any age. However, at certain ages, its more likely to appear on certain areas of your body and have a unique appearance.
Heres whats most common during each stage of life.
Also Check: What Causes Eczema To Get Worse
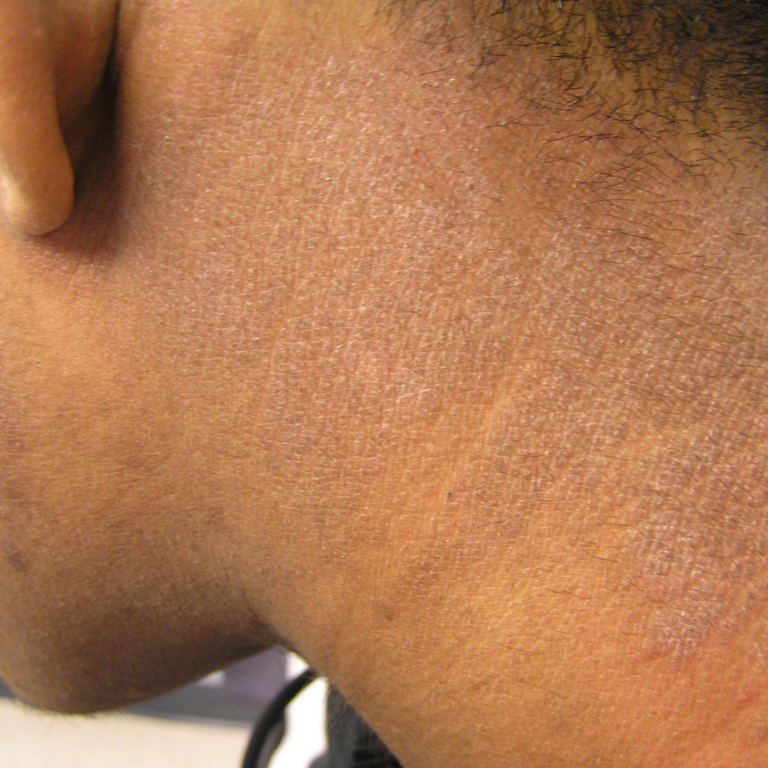
When Adults Get It
You might notice itchy patches on the hands, elbows, and in the “bending” areas of the body, such as the inside of the elbows and back of the knees. But eczema can appear anywhere, including the neck, chest, and eyelids. People who had atopic dermatitis as a child may see drier, scaly rashes as adults. The skin may be discolored or thickened.
Red Skin Syndrome Is Not Eczema
I joined the Eczema Association of Australasia after becoming desperate for an end to my itchy, red skin. I was first diagnosed with eczema around the age of 20 and prescribed a mild steroid cream for the rash on my chest. The rash cleared and the unfinished tube of cream sat idle in my bathroom cupboard for years. In my late twenties and thirties, I occasionally developed a small patch of dry skin, which I sometimes treated with a topical steroid cream or with a nonsteroidal emollient. It wasnt until my early forties that my skin rash become problematic.
You May Like: Dyshidrotic Eczema On Bottom Of Feet
Recommended Reading: Can Heat Flare Up Eczema
Use A Moisturizer On Your Skin Every Day
Moisturizers help keep your skin soft and flexible. They prevent skin cracks. A plain moisturizer is best. Avoid moisturizers with fragrances and a lot of extra ingredients. A good, cheap moisturizer is plain petroleum jelly . Use moisturizers that are more greasy than creamy because creams usually have more preservatives in them.
Regular use of a moisturizer can help prevent the dry skin that is common in winter.
Where Does Eczema Appear In Adults
Many children with AD have their condition go into remission, but about 10-30% of people continue to have recurrences of AD throughout adulthood. Only about 5% of cases of AD begin in adulthood.3,4 In adults, AD affects the inside creases of the elbows or knees, the nape of the neck, face, hands, upper arms, back, wrists, the fingers, feet, and toes. In some people with AD, the rash may cover much of the body, with it being especially noticeable on the face and neck. Other adults only experience AD as hand or foot atopic eczema. Adults with AD have a scalier rash than younger patients with the condition. Areas of chronic AD appear thickened, while areas of acute AD appear with redness, bumps, and broken skin.1-3
Recommended Reading: Does Eczema Cause White Patches
What Is It Like Living With Eczema
Many people live with eczema . As many as 15 million Americans may have this skin condition. Living with it can be challenging.
There may be times when your eczema disappears. This is known as a remission period. Other times you may have a flare-up, which is when it gets worse. The goal of treatment is to prevent such flare-ups, preventing your symptoms from getting worse. Be sure to avoid triggers, moisturize, take your medicine and do anything else your healthcare provider recommends.
What Is Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin disorder. It causes dry, itchy, scaly patches on the skin, often on the face and scalp in babies. Its most common in infants or very young children. Most will show signs of the condition in the first year of life. Symptoms may last until the teens or adulthood. It rarely starts in adulthood. Atopic dermatitis is not contagious.
Atopic dermatitis tends to run in families. This suggests a genetic link. Its also associated with asthma and allergies. These are immune hypersensitivity disorders.
Treatment for this condition is aimed at calming the skin inflammation, decreasing the itching, and preventing infections. Good skin care and medicine to control itching and infection are used.
Atopic dermatitis is often called eczema.
Also Check: Calamine Lotion For Babies Eczema
> > > Best Psoriasis Cure Available
3. To help safeguard the skin, the immune system release chemicals that can cause nerves to itch and blood vessels to dilate to prepare the skin for a sudden rush of immune cells
4. When the immune cells arrive at the scene, most work to kill off the pathogens causing the distress, but a few capture some of the invaders and take them back to the heart of the immune system, where other soldier cells are produced in a way to recognize and attack the invading cells on contact
5. Inflammation is the bodys way of opening blood vessels to allow more soldier cells to rush to the battlefield.
While this entire process is completely normal, people with psoriasis tend to overproduce these soldier cells when the body feels threatened. This overabundance of killer immune cells can actually be dangerous to the skin since they begin to attack good cells along with the bad ones.
While it is great to finally understand the impact an improperly working immune system can have on your skin and cause psoriasis more research is needed to pinpoint the exact cause for the over-firing of the cell messages. Most Common Places Pf Eczema Most Common Places Pf Psoriasis