What Causes Discoid Eczema
The cause of discoid eczema is unknown, although it is often accompanied by dry skin and is thought to be triggered by irritation of the skin.
Discoid eczema tends to affect adults and is rare in children. It is more common among men aged from 50 to 70 and women in their teens or twenties.
Some people with discoid eczema may also have other types of eczema, such as atopic eczema.
Read more about the causes of discoid eczema.
Heart Disease Risks Common In People With Eczema
Eczema, an itchy, scaly skin disease that usually starts early in life, may make people more prone to heart disease and stroke, according to a study in the Jan. 8, 2015, Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Researchers relied on data from more than 61,000 adults who took part in the 2010 and 2012 National Health Interview surveys. They found that people with eczema smoke and drink more and are less likely to exercise than people without the disease. Other factors that boost heart disease risksuch as severe obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterolwere also more prevalent among people with eczema. So were sleep disturbances, which were linked to even higher odds of having those risk factors.
To continue reading this article, you must log in.
- Research health conditions
- Prepare for a doctor’s visit or test
- Find the best treatments and procedures for you
- Explore options for better nutrition and exercise
What Questions Might My Healthcare Provider Ask To Diagnose Eczema
The conversation with your healthcare provider will need to cover a lot of information. Be sure to be specific about your symptoms.
- Where is your eczema located?
- What have you used to try to treat your eczema?
- What medical conditions do you have? Allergies? Asthma?
- Is there a history of eczema in your family?
- How long have you had symptoms of eczema?
- Do you take hot showers?
- Is there anything that makes your symptoms worse?
- Have you noticed that something triggers or worsens your eczema? Soaps? Detergents? Cigarette smoke?
- Is there so much itchiness that you have trouble sleeping? Working? Living your normal life?
Read Also: Best Treatment For Child Eczema
When To Seek Professional Help
Eczema that continues to worsen over time and does not improve with usual treatment like steroid medication can be an indicator of a bacterial or viral infection, especially when accompanied by pain, warmth, swelling, increased redness, blisters, and pus.
If any of these signs and symptoms are present, see your doctor immediately to determine if you have an infection. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent serious complications.
Eczema Resources We Love
The NEA is the most prominent U.S. organization devoted solely to education, research, patient support, and advocacy related to atopic dermatitis and other forms of eczema. We love their eczema fact sheets, glossary of skin-care terms, and informative webinars. Plus, they have a yearly family-friendly Eczema Expo each summer at a vacation destination.
This society is one of the most visible resources in the United Kingdom to educate people about eczema, provide help for people with the disease, and support research. Perhaps their most unique resource is a confidential telephone and email hotline that people in the United Kingdom can call Monday through Friday, 8 a.m. to 8 p.m. local time.
The AAD says it is the largest professional dermatologic association, with more than 20,500 physicians as members worldwide. They publish information about a variety of skin conditions, and we recommend checking out the robust resource center with information about childhood and adult eczema.
Because allergens can trigger eczema flareups, it makes sense to stay on top of information about managing allergies. The AAFAs site has a wealth of information about allergies, for both adults and kids.
Recommended Reading: Does Drinking Water Help With Eczema
How Is Eczema Treated What Medications Are Used
Treating eczema can be difficult if the cause is something you cant control, like genetics. Fortunately, you may have some influence over your environment and stress levels. Do your best to figure out what triggers or worsens your eczema, and then avoid it. The goal is to reduce itching and discomfort and prevent infection and additional flare-ups.
Consider these treatment tips:
If your child has skin problems, such as eczema, you can:
- Avoid long, hot baths, which can dry the skin. Use lukewarm water instead and give your child sponge baths.
- Apply lotion immediately after bathing while the skin is still moist. This will help trap moisture in the skin.
- Keep the room temperature as regular as possible. Changes in room temperature and humidity can dry the skin.
- Keep your child dressed in cotton. Wool, silk and manmade fabrics such as polyester can irritate the skin.
- Use mild laundry soap and make sure that clothes are well rinsed.
- Watch for skin infections. Contact your healthcare provider if you notice an infection.
- Help them avoid rubbing or scratching the rash.
- Use moisturizers several times daily. In infants with eczema, moisturizing on a regular basis is extremely helpful.
What Is It Like Living With Eczema
Many people live with eczema . As many as 15 million Americans may have this skin condition. Living with it can be challenging.
There may be times when your eczema disappears. This is known as a remission period. Other times you may have a flare-up, which is when it gets worse. The goal of treatment is to prevent such flare-ups, preventing your symptoms from getting worse. Be sure to avoid triggers, moisturize, take your medicine and do anything else your healthcare provider recommends.
Read Also: Can You Have Eczema Without A Rash
How To Use Emollients
Use your emollient all the time, even if you are not experiencing symptoms as they can help limit the return of your condition. Many people find it helpful to keep separate supplies of emollients at work or school.
To apply the emollient:
- use a large amount
- don’t rub it in, smooth it into the skin in the same direction that the hair grows instead
- for very dry skin, apply the emollient every two to three hours
- after a bath or shower, gently dry the skin and then immediately apply the emollient while the skin is still moist
If you are exposed to irritants at work, make sure you apply emollients regularly during and after work.
Don’t share emollients with other people.
Leaving Abbvie Web Site
You are leaving the RINVOQ site and connecting to a site that is not under the control of AbbVie. AbbVie is not responsible for the contents of any such site or any further links from such site. AbbVie is providing these links to you only as a convenience and the inclusion of any link does not imply the endorsement of the linked site by AbbVie. You should also be aware that the linked site may be governed by its own set of terms and conditions and privacy policy for which AbbVie has no responsibility. Conversely, the presence of this link does not imply the linked site’s endorsement of RINVOQ.com or AbbVie.
Do you wish to leave this site?
You May Like: Which Oil Best For Eczema
Living With Eczema And Atopic Dermatitis
Eczema can flare up when you are under stress. Learn how to recognize and cope with stress. Stress reduction techniques can help. Changing your activities to reduce daily stress can also be helpful.
The area where you had the eczema may easily get irritated again, so it needs special care. Continue to follow the tips provided here even after your skin has healed.
How To Use Topical Corticosteroids
When using corticosteroids, apply the treatment accurately to the affected areas. Unless instructed otherwise by your doctor, you should follow directions on the patient information leaflet that comes with the corticosteroid.
Do not apply the corticosteroid more than twice a day. Most people will only have to apply it once a day.
To apply the topical corticosteroid, take the following steps:
- apply your emollient first and ideally wait around 30 minutes before applying the topical corticosteroid, until the emollient has soaked into your skin
- apply a good amount of the topical corticosteroid to the affected area
- use the topical corticosteroid until the inflammation has cleared up, unless otherwise advised by your GP
Speak to your prescriber if you have been using a topical corticosteroid and your symptoms have not improved.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Itchy Skin Eczema
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Eczema
There are steps you can take that may prevent eczema outbreaks:
- Establish a skin care routine, and follow your healthcare professionals recommendations for keeping your skin healthy.
- Wear gloves for jobs where you have to put your hands in water. Wear cotton gloves under plastic gloves to absorb sweat, and wear gloves outside, especially during the winter months.
- Use mild soap for your bath or shower, and pat your skin dry instead of rubbing. Apply a moisturizing cream or ointment immediately after drying your skin to help seal in the moisture. Reapply cream or ointment two to three times a day.
- Take baths or showers with tepid rather than hot.
- Drink at least eight glasses of water each day. Water helps to keep your skin moist.
- Try to avoid getting too hot and sweaty.
- Wear loose clothes made of cotton and other natural materials. Wash new clothing before wearing. Avoid wool.
- Avoid sudden changes in temperature and humidity.
- Learn to recognize stress in your life and how to manage it. Regular aerobic exercise, hobbies and stress-management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, might help.
- Limit your exposure to known irritants and allergens.
- Avoid scratching or rubbing itchy areas of skin.
Importance Of Eczema Treatment
There is growing evidence that allergens introduced into the body through the skin can lead to the later development of food allergy, asthma and hay fever. Aggressively treating eczema in children and taking steps to restore normal skin barrier function may lower the risk of future development of these conditions.
Don’t Miss: What Does Eczema Look Like On Dark Skin
Eczema Coping Tips Avoid Changes In Temperature
Abrupt temperature and humidity changes can sometimes irritate the skin for example, going in and out of air-conditioned buildings on hot days or heated buildings on cold days.Hard physical activity or exercise that makes you sweat heavily can also trigger the itch of eczema.Suggestions include:
- In winter, dont overheat your house. Dress warmly when going outdoors and remove the extra layers as soon as you return.
- In summer, dont over cool your house. Air conditioners can dry out the air and irritate your skin.
- Avoid hard physical activity in hot weather. For example, do your gardening first thing in the morning, or in the evening when the sun is lower in the sky.
Living With Atopic Dermatitis
Like most medical conditions, early diagnosis is vital to getting AD under control. And while managing the physical symptoms is key, it’s also important to make sure you’re getting emotional support. Adults with AD are more likely to develop depression and anxiety, due to the chronic nature of the condition and sensitivity about visible symptoms.
Atopic dermatitis has been shown to be associated with cardiovascular diseases, likely because many with AD also have cardiovascular risk factors such as sleep disturbance and alcohol and cigarette use. 30319-9/fulltext” rel=”nofollow”> Source)
There is a potential connection between AD and other autoimmune conditions that are aggravated by inflammation, including celiac disease and Crohn’s Disease, as well as other atopic conditions, such as alopecia and vitiligo.
Also Check: Are Eggs Bad For Eczema
Eczema And Atopic Dermatitis Treatment
Your doctor may prescribe a corticosteroid cream or ointment to apply to your rash. This will help reduce itching and calm inflammation. Use it right after bathing. Follow your doctors directions for using this medicine or check the label for proper use. Call your doctor if your skin does not get better after 3 weeks of using the medicine.
Antihistamines like hydroxyzine reduce itching. They can help make it easier to not scratch. A new class of drugs, called immunomodulators, works well if you have a severe rash. Two drugs in this class are tacrolimus and pimecrolimus. These drugs keep your immune system from overreacting when stimulated by an allergen. However, they can affect your immune system. So the Food and Drug Administration recommends that these drugs be used only when other treatments wont work.
Try not to scratch the irritated area on your skin, even if it itches. Scratching can break the skin. Bacteria can enter these breaks and cause infection. Moisturizing your skin will help prevent itchiness.
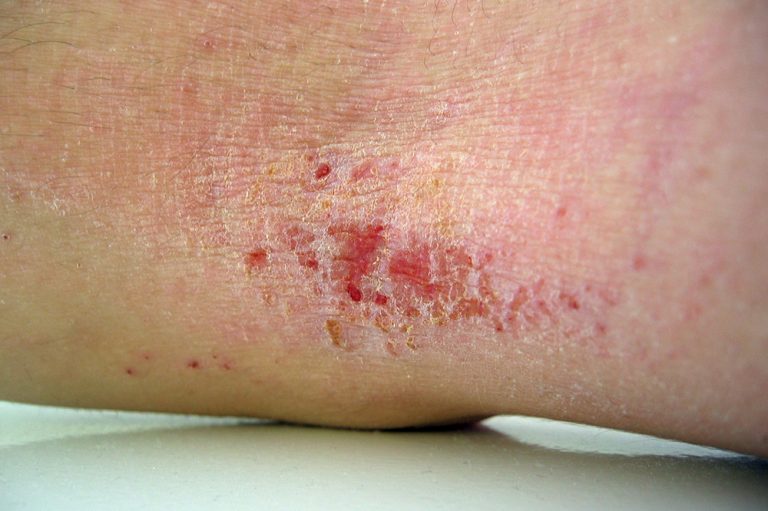
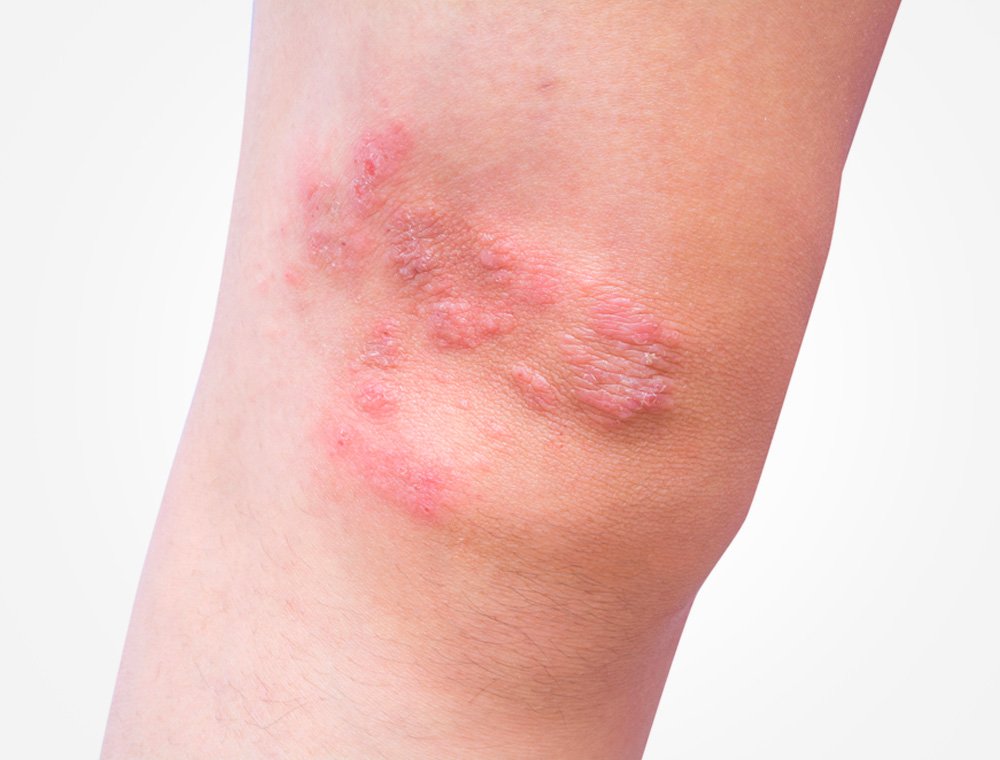
Symptoms Of Discoid Eczema
Discoid eczema causes distinctive circular or oval patches of eczema. It can affect any part of the body, although it does not usually affect the face or scalp.
The first sign of discoid eczema is usually a group of small spots or bumps on the skin. These then quickly join up to form larger patches that can range from a few millimetres to several centimetres in size.
On lighter skin these patches will be pink or red. On darker skin these patches can be a dark brown or they can be paler than the skin around them.
Initially, these patches are often swollen, blistered and ooze fluid. They also tend to be very itchy, particularly at night.
Over time, the patches may become dry, crusty, cracked and flaky. The centre of the patch also sometimes clears, leaving a ring of discoloured skin that can be mistaken for ringworm.
You may just have 1 patch of discoid eczema, but most people get several patches. The skin between the patches is often dry.
Patches of discoid eczema can sometimes become infected. Signs of an infection can include:
- the patches oozing a lot of fluid
- a yellow crust developing over the patches
- the skin around the patches becoming hot, swollen and tender or painful
- feeling sick
- feeling unwell
Don’t Miss: What Allergies Can Cause Eczema
Choice Of Topical Corticosteroid
There are different strengths of topical corticosteroids that can be prescribed depending on the severity of your eczema. Discoid eczema usually needs a stronger type of corticosteroid than other types of eczema.
You might be prescribed a cream to be used on visible areas, such as face and hands, and an ointment to be used at night or for more severe flare-ups.
Treating Atopic Eczema With Monoclonal Antibodies
In 2014 a team of researchers at Mt. Sinai in New York showed that dupilumab, a monoclonal antibody, helped resolve symptoms in people whose AD did not get better when they applied topical medications or avoided triggers. Dupilumab blocks specific cytokines involved in allergic inflammation and in 2017 was approved by the FDA for treatment of moderate to severe AD. By 2020, however, reports began popping up of patients developing joint and tendon pain and tenderness after being treated with dupilumab. Study of this and other monoclonal antibodies for treatment of atopic eczema continues.
Also Check: Does Neosporin Work On Eczema
Diagnosing Food Allergy And Eczema Flare
- Your child’s doctor may suggest the steps listed below:
- Remove the suspected food or foods from your child’s diet for 2 weeks. The eczema should greatly improve.
- Then give your child that food when the eczema is under good control. This is called a “challenge.”
- If the food is causing flare-ups, the eczema should become itchy and red. The flare-up should occur quickly within 2 hours of eating the food.
- If this occurs, avoid giving this food to your child. Talk to your child’s doctor about the need for any food substitutes.
- If the eczema does not flare-up, your child isn’t allergic to that food.
What Doesnt Cause Eczema
Eczema is not contagious. You can’t catch eczema by coming in contact with someone who has it.
Eczema is not an allergic reaction. Even so, a large number of children who have eczema also have food allergies. That doesn’t mean that certain foods such as dairy, eggs, and nuts — common food allergy triggers in children with eczema — cause it or make it worse. Before removing particular foods from your child’s diet, talk with your doctor to be sure your child’s nutritional needs will be met.
Recommended Reading: Cream For Eczema On Feet
Heart Disease And Eczema: Is There A Connection
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis a chronic inflammatory skin condition is associated with an increased risk of several other conditions. In particular, research suggests that severe eczema in adults is associated with cardiovascular disease.
Evidence of the association comes from a large study published in the BMJ, which found that relative to the general population, people with severe eczema had:
- A 20 percent higher risk of a stroke
- A 40 percent to 50 percent greater risk of heart attack , atrial fibrillation , and sudden cardiac death
- A 70 percent higher risk of heart failure
Another meta-analysis review showed that adults with predominantly active and severe eczema have a higher risk of heart disease, hypertension , and stroke. As someones eczema increased in severity, their risk of heart disease also increased.
This article explains the connection between heart disease and eczema, as well as ways to prevent or manage these conditions.
Favorite Annual Meetings For Eczema Patients
The NEAs annual expo provides a vacation retreat for people and families affected by eczema. The four-day event includes activities educational seminars camps for infants, children, and teens and hotel accommodations that are as free of potential allergens as possible. The next Eczema Expo is June 25 through 28, 2020, in Orlando, Florida. The organization offers a limited amount of needs-based scholarships to help people attend.
Recommended Reading: Does Stress Cause Eczema To Flare Up
The Inherited Barrier Defect
There is emerging evidence that inflammation in atopic dermatitis is associated with immune-mediated and inherited abnormalities in the skin barrier. This barrier failure causes increased permeability of the skin and reduces its antimicrobial function.
The main inherited abnormality causing disordered barrier function is filaggrin expression. Filaggrins are filament-associated proteins which bind to keratin fibres in the epidermal cells. The gene for filaggrin resides on chromosome 1 . This gene was first identified as the gene involved in ichthyosis vulgaris. Abnormal filaggrin is associated with early-onset, severe and persistent atopic dermatitis.
It is postulated that the loss of filaggrin results in:
- Corneocyte deformation , which disrupts the organisation of the extracellular lipid the lamellar bilayers.
- A reduction in natural moisturising factors, which include metabolites of pro-filaggrin.
- An increase in skin pH which encourages serine proteaseactivity these are enzymes which digest lipid-processing enzymes and the proteins that hold epidermal cells together. Serine proteases also generate active cytokines like IL-1a and Il-1beta and promote skin inflammation.
Proteins under investigation in atopic eczema include structural compounds, such as hornerin, cornulin, claudin 1/23 and ceramides, enzymes, such as kallikrein and serine peptidases.