What Are The Symptoms Of Eczema
Eczema causes skin flare-ups that occur periodically and can last for long periods. Some of the most common signs and symptoms of eczema include:
- Overly dry skin
- Thickened, scaly skin
- Raw, severely sensitive skin
Eczema can develop anywhere on your body. But its most common to have eczema flare-ups on your upper chest, hands and feet, neck, and inside bends of your knees and elbows. In infants, eczema tends to surface on the face and scalp.
Seattle Children’s Urgent Care Locations
If your childâs illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
Living With Atopic Dermatitis
The following steps can help manage atopic dermatitis:
- Avoid triggers
- Take brief baths or showers using lukewarm water.
- Practice good skin care.
- Dont use harsh soaps. Ask your healthcare provider to recommend a brand.
- Dress in light clothes. Sweating can make atopic dermatitis worse.
- Use a good moisturizer at least once a day. Ask your healthcare provider to recommend a brand.
- Avoid scratching the affected area.
- Minimize stress.
- Make lifestyle changes that prevent flare-ups.
- Avoid skin products that have fragrances and dyes
Also Check: What To Do When Your Eczema Flares Up
Weeping Eczema After Stopping Steroid Creams
While primary and secondary weeping eczema are well-known in the medical world, some people can still experience weeping eczema when they first stop using steroid creams. Why is this?
One doctor found that the steroids in the cream itself, indirectly kills Staph A, making it near to impossible for Staph A to colonize the area where you put your steroid cream.
In other words, when you use a steroid cream, the bacteria doesnt like it and leaves the area alone. So when you stop using it the bacteria comes back, sets up camp, and you experience weeping! This is especially the case if you have open eczema areas, where a higher concentration of Staph is likely to be found.
How Can I Reduce My Risk
There are steps you can take that may prevent ear eczema outbreaks:
- Establish a skin care routine, and follow your healthcare professionals recommendations for keeping your skin healthy.
- Avoid wool and silk, which can dry out your skin.
- Use a mild soap for your bath or shower, and pat your skin dry instead of rubbing it. Apply a moisturizing cream or ointment immediately after drying your skin to help seal in the moisture. Reapply cream or ointment two to three times a day.
- Take baths or showers with lukewarm water, not hot water.
- Drink at least eight glasses of water each day. Water helps keep your skin moist.
- Avoid sudden changes in temperature and humidity.
- Limit your exposure to known irritants and allergens.
- Avoid scratching or rubbing your irritated skin.
Also Check: Eczema And Food Allergy The Hidden Cause
Tips For Preventing Infections
Keeping eczema symptoms under control may help lower your chances of developing an infection. You can help prevent weeping eczema by doing the following:
- Avoid scratching. No matter how much your skin itches, try not to scratch it. Scratching carries with it a major risk for infection. Keep your fingernails short, and if the itching becomes bothersome, try using a cold compress.
- Use a humidifier. Dry indoor air can trigger itching and flaking of the skin. A humidifier adds moisture to the air in your home and protects your skin from drying up.
- Moisturize skin. Cracks and open areas in the skin can provide an easy entry for bacteria. Its important to moisturize your skin at least twice a day. The best time to apply a moisturizer is when your skin is still damp after getting out of the shower or bath.
- Take baths. Taking frequent baths or showers can reduce bacteria and remove dead skin. Use warm not hot water when bathing. Instead of rubbing, pat your skin dry.
- Avoid harsh soaps. Stay away from soaps that are made with harsh perfumes or dyes. If you do use these products, rinse them completely from your body when showering.
- Wear proper clothing. Choose clothing thats cool, smooth, and made of cotton. This will lower your chance of experiencing skin irritation.
How Is Atopic Dermatitis Treated
Factors such as your age, overall health, and health history will help your healthcare provider find the best treatment for you.
There is no cure for atopic dermatitis. The goals of treatment are to reduce itching and inflammation of the skin, to keep the skin moist, and to prevent infection.
Your healthcare provider may also prescribe medicines in severe cases. The following are commonly used to treat atopic dermatitis:
Don’t Miss: Are You Born With Eczema
Home Remedies For Weeping Eczema
Certain methods, like using bandages to wrap skin and keep it moisturized and protected, should not be used if you have an infection unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
Some people report improved symptoms with other approaches, such as:
- Antiseptic emollients. Your doctor may recommend these products to help hydrate your skin and protect it from bacteria.
- Stress management exercises.
When Should I See The Doctor
If the eczema is getting worse, is not responding to treatment or looks infected you should return to see your doctor. If flu-like symptoms develop with a raised temperature and the eczema worsens, then seek medical advice.
Wet wrapping should not be used on infected eczema as the moist conditions provide an ideal breeding ground for further bacterial growth. If you are using the wet wrapping technique and suspect that the skin is becoming infected, seek the advice of your doctor.
Information contained in this article was obtained from the Eczema & Infection Sheet published by the NES
It is not the policy of the Eczema Association of Australasia Inc to recommend or endorse any product or treatment.It is part of the role of the Association to provide information on a wide range of products and treatments to keep those involved with eczema as fully informed as possible as to all options available. For medical advice, consult your health professional.
Don’t Miss: Can Eczema Look Like A Rash
Articles On Atopic Dermatitis
It can be hard to tell for sure if you have atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema. Youâll want to see a dermatologist or other doctor to find out.
At your appointment, your doctor will check your skin and talk with you about your symptoms, your health history in general, and any rashes or allergies that run in your family.
Based on that information, they’ll decide if itâs eczema or something else.
Treatment For Eczema And Dermatitis
The goal of treatment for eczema and dermatitis is to alleviate the signs and symptoms of the skin ailment using the least amount of medication. Our dermatologists recommend at-home therapies to prevent and treat mild rashes, and offer phototherapy and medication for people whose symptoms persist despite nonprescription treatment.
You May Like: Aveeno Eczema Cream For Diaper Rash
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider About Eczema
- How can you tell that I have eczema?
- If I dont have eczema, what other skin condition might I have?
- Is there a specific brand of moisturizer that you recommend?
- Is there a prescription cream that you can prescribe?
- How often should I see a dermatologist regarding my eczema?
- What soaps, lotions, makeup, etc. should I avoid?
- What medications do you recommend?
- What at-home treatments do you recommend?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Eczema is very normal, very common, and very, very uncomfortable. It can affect your quality of life. At its worse it can keep you from sleeping, distract you and make you feel self-conscious in public. See your dermatologist or other healthcare provider as soon as you start to see signs of it. Explore at-home remedies and prescribed treatments.
Youre not alone! 15% to 20% of people experience eczema or another type of dermatitis at some point in their lives.
How Can I Tell If Eczema Is Infected
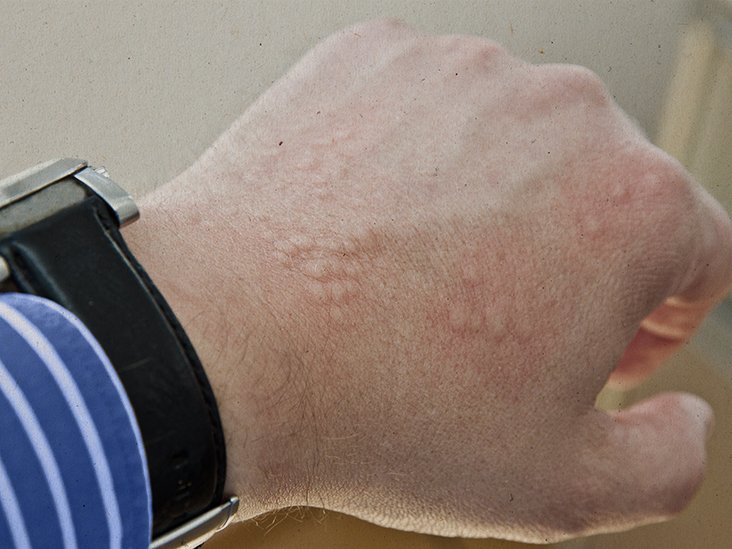
Infected atopic eczema looks red and angry, and is usually weepy with a yellowish crust. Yellow pus filled spots may also be present and small red spots around the body hairs . The skin feels hot, itchy and sore, which leads to more scratching. This in turn damages the outer layers of the skin, and creates cracks and moisture which allows more bacteria to grow. This can set up a vicious circle. If the eczema
If repeated attacks of infected eczema are suffered, your doctor may take a swab from the skin to be sent to the microbiology laboratory. This is a quick, painless procedure, and can help confirm what organism is causing the infection. It can also show which antibiotics should be effective as treatment.
The possibility of infection should always be considered in eczema which is getting worse or not responding to emollient or steroid treatment.
You May Like: Oatmeal Soap Recipe For Eczema
Building Your Own Eczema Care Team
Since eczema and atopic dermatitis are skin conditions, it makes sense that any care team would include a dermatologist. A dermatologist can help you develop a skin-care plan to prevent flares and reduce symptoms when they do appear, according to the AAD. This plan may include recommendations for skin-care and household products that are eczema-friendly, prescription or over-the-counter treatments for severe eczema and atopic dermatitis, and tips for avoiding triggers.
Your dermatologist may also refer you to other specialists if needed, or work alongside other doctors and healthcare providers to help you manage your symptoms. Allergists, primary care physicians, and pediatricians often coordinate care with dermatologists in the treatment of atopic dermatitis, says Lauren Ploch, MD, a board-certified dermatologist in Augusta, Georgia.
Allergists, for example, are trained to treat inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and atopic dermatitis, which are often tied to allergies, according to the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Your allergist can help you identify possible irritants to avoid, and recommend effective treatments to find relief from symptoms.
RELATED: 8 Ways to Avoid Eczema Flare-Ups in the Summer
What Causes Infection In Eczema
The commonest cause of infection in eczema is a bacterium known as Staphylococcus aureus. It thrives on the weepy, broken skin of eczema. When infected, there may be over 100 million bacteria on a patch of eczema just the size of a finger nail.
It is now known that Staphylococcus aureus is found on the skin of virtually everyone with atopic eczema, even when there are no obvious signs of infection or eczema, whereas it occurs on the skin of less than 1% of people who do not have eczema. Recent studies have shown that Staphylococcus aureus can trigger off eczema in areas of the body away from the bacteria. For example if the bacteria are found on the forearm, it can cause a flare up of eczema in the crease of the elbow joint.
There is growing scientific evidence that infection with Staphylococcus aureus makes atopic eczema worse and hinders healing. The number of bacteria on the skin has been found to multiply with the increasing severity of the eczema. Staphylococcus aureus has been shown to produce toxins which trigger an exaggerated reaction from the bodys defence system. It is thought that this over-reaction itself causes part of the problem.
This process is rather like a large, over-enthusiastic army fighting against a few invaders, and trampling the ground to pieces in the process!
You May Like: What’s The Best Remedy For Eczema
What Is Pediatric Eczema And When Should We See A Doctor
May 7, 2021
Watching your child suffer from pediatric eczema can be stressful and difficult, but it is a common and treatable skin problem. As a pediatric dermatologist at the University of Chicago Medicine Comer Childrens Hospital, I’m here to answer your questions about treating this itchy skin condition and explain how a physician can help.
What is pediatric eczema?
Pediatric eczema usually refers to atopic dermatitis. Atopic dermatitis is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition that leads to dry, scaly patches of skin that are often red, inflamed and very itchy. The first lesions may appear before an infant is 6 months old, but it most commonly occurs before a child turns 5. However, eczema can affect almost anyone at any age, and the condition can come and go throughout a persons life.
Atopic dermatitis often flares after exposure to certain triggers that irritate the skin. Common triggers include dry cold weather, outdoor allergens , fragrance , pets , and chemicals from smoking. Many organic or all natural products can be irritating to the skin since they contain botanical ingredients, which are common allergens. Contrary to popular belief, foods are rarely triggers for eczema.
What pediatric eczema symptoms should a parent look for?
The primary symptoms associated with eczema are red, dry, scaly patches of skin. Often, they are extremely itchy.
Here are some symptoms of pediatric eczema at different ages:
How do I know if my child is at risk?
How Did You Get Eczema
Medical experts dont yet know exactly what causes eczema or why the symptoms and triggers vary so widely between people who suffer from it. However, common triggers for eczema include:
- Cold or dry weather
- Temperature changes
- A cold or respiratory illness
Eczema occurs most often in families with a history of the condition, as well as asthma or seasonal allergies.
Read Also: Best Thing For Toddler Eczema
Home Treatment For Atopic Dermatitis
Good skin care is key. If your eczema is mild, that might be all you need, along with some changes in your daily habits.
If you have severe eczema, you may need to take medicine for it, too.
The basics:
Soap and moisturizer. Use a mild soap or soap substitute that won’t dry your skin. Youâll also want a good moisturizer in cream, lotion, or ointment form. Smooth it on right after a shower or bath, as well as at least one other time each day.
If your eczema is severe, you may find that it helps to take baths once a week with a small amount of bleach added to the water. That kills bacteria that live on the skin of people with eczema.
Short, warm showers. Donât take very hot or very long showers or baths. They can dry out your skin.
Stress management. Get regular exercise, and set aside time to relax. Need a few ideas? You could get together with friends, laugh, listen to music, meditate or pray, or enjoy a hobby.
Get a humidifier. Dry air can be stressful for your skin.
Should I See A Dermatologist For Eczema
Whether or not you should see a dermatologist for eczema largely depends on the severity of your problem. If the condition is fairly mild, you may want to try to handle it yourself. For more severe problems, it is likely in your best interest to have professional assistance managing and monitoring the condition.
Eczema is a skin condition whose cause is unknown. A person can live for decades before the problem suddenly arises, and individuals can suffer from eczema in varying degrees. For some people, the problem is fairly mild and may be contained in a limited area. For others, the itching, swelling, and burning associated with this condition may be severe, and it may occur in multiple sites on the body. Where your problem is located and the severity of it should factor into your decision to see a dermatologist for eczema.
If you feel that your condition is mild, you may want to try over-the-counter remedies before seeking medical attention. As there is no cure, there is generally no reason to go to a dermatologist if you can manage the problem yourself. If you decide later that it may be better for to get professional help, it will not be too late.
You May Like: Is Epsom Salt Good For Eczema
What Is Eczema What Does It Look And Feel Like
Eczema is a condition that causes your skin to become dry, red, itchy and bumpy. Its one of many types of dermatitis. Eczema damages the skin barrier function . This loss of barrier function makes your skin more sensitive and more prone to infection and dryness.
Eczema doesnt harm your body. It doesnt mean that your skin is dirty or infected, and its not contagious. There are treatments that can help manage your symptoms.
In the word dermatitis, derm means skin and itis means inflammation. The word as a whole means inflammation of the skin. Eczema originates from the Greek word ekzein which means to boil over or break out.