Is Eczema Different For Infants Or Toddlers Than It Is For Older Children
A painful, itchy rash on a babys face, torso or body may be eczema
Eczema looks and acts differently in infants and toddlers than it does in older children. The location and appearance of eczema changes as they grow, so its important to know what to look for during every stage of your infant or toddlers life.
Key Points About Atopic Dermatitis In Children
-
Atopic dermatitis is a long-term skin condition. It’s common in babies and children.
-
A child with allergies or family members with atopic dermatitis has a higher chance of having atopic dermatitis.
-
Itching, dryness, and redness are common symptoms.
-
The goals of treatment are to ease itching and inflammation of the skin, increase moisture, and prevent infection.
-
Staying away from triggers is important to manage the condition.
-
It usually gets better or goes away as a child gets older.
What You Can Do
You can help reduce your child’s discomfort by:
- keeping their fingernails short to reduce the damage to their skin from scratching
- washing them with aqueous cream instead of soap – ask your pharmacist about aqueous creams and always follow the instructions on the product
- using non-biological detergent and a double rinse cycle when washing their clothes or bedding
- avoiding herbal, ‘natural’ or alternative creams – these can make eczema worse, as they may contain bacteria or high doses of steroids
- rinsing and drying them well after swimming
- dressing them in cool, breathable fabrics like cotton
- keeping them away from anyone with a cold sore – as the cold sore virus can cause eczema to become infected
- using extra moisturiser on areas your child scratches a lot
- avoiding anything you know that causes your childs eczema to get worse
Around 6 out of 10 children with eczema will grow out of it by the time they’re teenagers.
Read Also: How Do You Treat Eczema
These Are The Seven Types Of Eczema And Heres How To Tell Which One You Have
There are more than 31 million Americans with eczema, and yet no two patients experience the condition the exact same way. How is this possible? We know there are seven different types of eczema, but what makes each of them unique? We spoke with Dr. Peter Lio, assistant professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Northwestern University, and Dr. Jeff Yu, an expert in contact dermatitis at Massachusetts General Hospital, to get the details on the underlying similarities and differences between the seven different types of eczema.
Emollients And Fire Safety
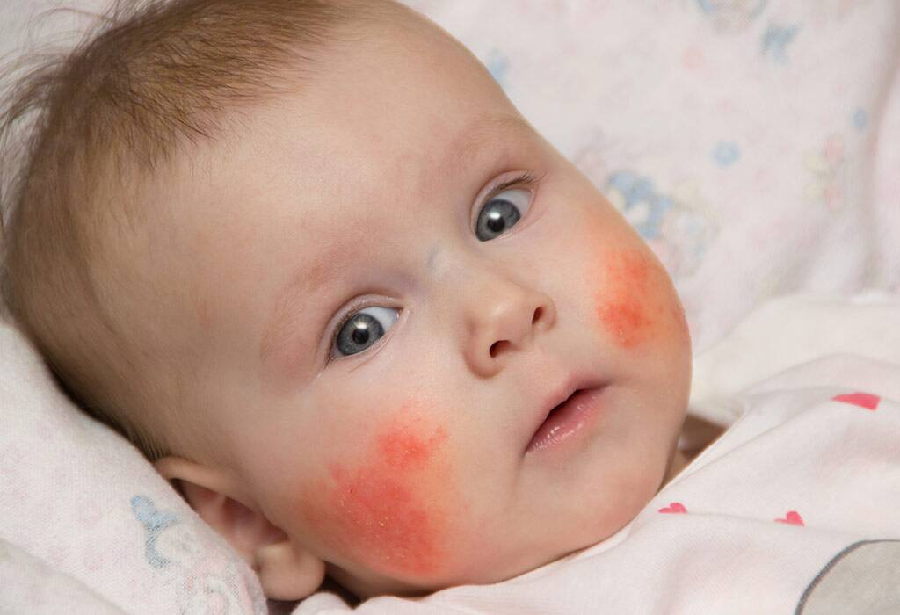

Lotions, creams or ointments used to moisturise your childs skin are also known as emollients.
Emollients are very effective at treating chronic dry skin conditions, such as eczema.
But it is important to be aware of the fire risk linked with them.
Emollients won’t cause a fire on their own. But if there is a build-up of emollient residue on clothing and bedding, this can quicken the speed of a fire.
Do not smoke near your baby or allow them near naked flames:
- while they are wearing emollient
- if they are wearing clothes or bandages that may have emollient on them
There is a fire risk with all paraffin-containing emollients. There may also even be a fire risk with paraffin-free emollients. There might also be a fire risk with other products that you put on skin over large body areas for more than a few days.
Washing clothing or fabric at a high temperature may reduce emollient build-up. But it might not totally remove it.
You May Like: Eczema On 4 Year Old
Natural Remedies For Baby Eczema
If you need some extra help soothing babys skin, these natural eczema treatments may make things better.
- Wet a washcloth. Drape cool, wet washcloths or gauze over your babys irritated skin for five to ten minutes at a time or however long you can get your squirmy worm to cooperate.
- Try an oatmeal bath. Sprinkle a bit of uncooked oatmeal, colloidal oatmeal or even baking soda into the tub when you wash your baby. All can naturally relieve eczema and irritation.
- Combat dry air. Running a cool-mist humidifier in your baby’s bedroom can help keep her skin super-hydrated. Clean it frequently to prevent bacteria and mold buildup.
- Dress your little one in layers. Sweating can reboot the eczema cycle, and thats the last thing you want. Layers let you customize babys outfit for toasty temps.
- Ask your pediatrician about probiotics. Studies are underway to see whether probiotics may ease eczema when added to dry baby formula or served as a dietary supplement. Get your doctor to weigh in before giving it a go.
Is There One Type Of Eczema That Is The Most Different From The Other Six Types
If the itchiness is universal, and if soap and detergents can trigger any type of eczema, we asked Dr. Lio if there were any subcategories of eczema that stood apart from the rest. The most different might be seborrheic dermatitis, he said. It is intimately connected to a yeast on the skin that does not seem to be playing the same role in other types of eczema. He added that contact dermatitis is different, as well, because a patient may have one key trigger for a flare and frequently when that flare is removed, the skin becomes 100% perfect and clear, unlike the other forms of eczema that have many potential triggers.
Read Also: Gold Bond Eczema Cream Ingredients
What Are The Symptoms Of Atopic Dermatitis In A Child
Symptoms may come and go, or occur most or all of the time. Any area of the body may be affected. In babies, symptoms usually affect the face, neck, scalp, elbows, and knees. In children, symptoms usually affect the skin inside the elbows, on the back of the knees, the sides of the neck, around the mouth, and on the wrists, ankles, and hands.
Symptoms can occur a bit differently in each child. They can include:
-
Dry, scaly skin
-
Pale skin on the face
-
Small, raised bumps that may become crusty and leak fluid if scratched
-
Rough bumps on the face, upper arms, and thighs
-
Darkened skin of eyelids or around the eyes
-
Skin changes around the mouth, eyes, or ears
-
Raised, red areas
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis can be like other health conditions. Make sure your child sees his or her healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Triggers Of Eczema Flare
- Soaps. Never use bubble bath. It can cause a major flare-up.
- Pollens. Keep your child from lying on the grass during grass pollen season.
- Animals. Avoid any animals that make the rash worse.
- Foods. If certain foods cause severe itching , avoid them.
- Wool. Avoid wool fibers and clothes made of other scratchy, rough materials.
- Dry Air. Use a humidifier if the air in your home is dry.
- Herpes Virus Infection . Keep your child away from anyone with fever blisters . The herpes virus can cause a serious skin infection in children with eczema.
- Eczema is not caused by laundry soap you use to wash clothing.
Read Also: The Best Soap To Use For Eczema
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Eczema
The signs of eczema :
- are mainly dry, itchy skin. Because it is so itchy, it is often called “the itch that rashes.”
- include redness, scales, and bumps that can leak fluid and then crust over
- tend to come and go. When they get worse, it is called a flare-up.
- may be more noticeable at night
Symptoms can vary:
- Infants younger than 1 year old usually have the eczema rash on their cheeks, forehead, or scalp. It may spread to the knees, elbows, and trunk .
- Older kids and teens usually get the rash in the bends of the elbows, behind the knees, on the neck, or on the inner wrists and ankles. Their skin is often scalier and drier than when the eczema first began. It also can be thicker, darker, or scarred from all the scratching .
Can My Baby Grow Out Of It
One of the most common questions parents have for pediatricians is whether their baby will outgrow their eczema. If you are wondering the same thing, rest assured. Most babies who develop eczema in the first few months of life outgrow it by the time they begin school at age 4 or 5. However, a small percentage of babies who develop eczema will not outgrow it. Unfortunately, there is no way to confirm whether a baby will or will not outgrow eczema in a few years but the chances of the condition staying increase if the condition runs in the family.
Read Also: Eczema In Elbow Crease Treatment
How Is Atopic Dermatitis Diagnosed In A Child
The healthcare provider will ask about your childs symptoms and health history. He or she may also ask if you or other family members have atopic dermatitis, asthma, or nasal allergies such as hay fever or allergic rhinitis. He or she will also ask about allergy symptoms in your child. The healthcare provider will examine your child, looking for signs of atopic dermatitis. There is no specific test for atopic dermatitis. Testing is usually not needed, but it may be done. Tests may include:
-
Blood tests. Your childs blood may be checked for levels of immunoglobulin E . IgE is released by the body’s immune system. Its high in most children with allergies and with atopic dermatitis. Other blood tests may also be done.
-
Skin tests. Skin tests may be done to check for allergies or other skin conditions.
Managing Eczema In Winter And Year Round: A Parents Guide
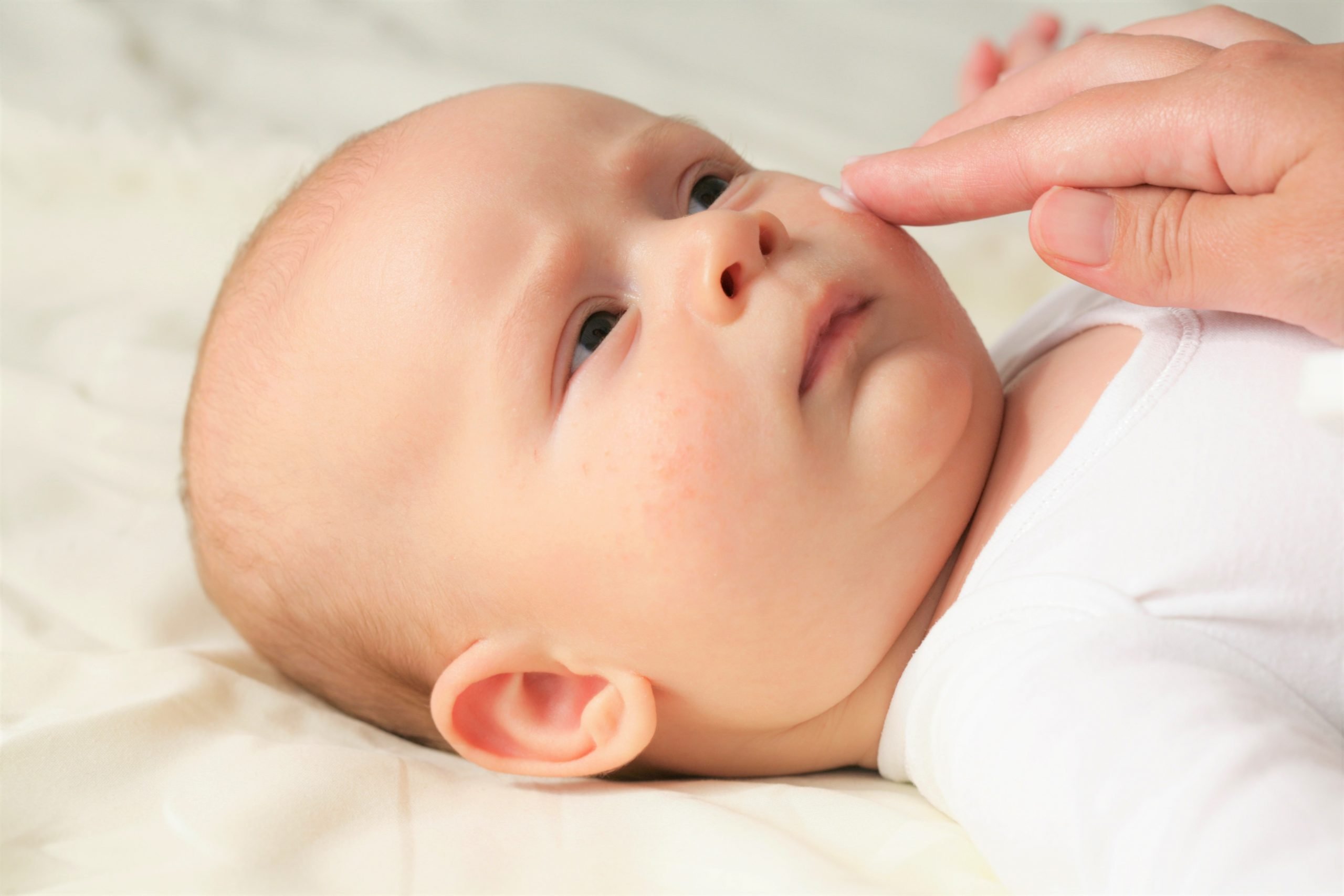

Cold, dry outdoor air and indoor heating can rob skin of its natural moisture in the winter. Red, crusty, dry patches can be common on a baby’s skin, particularly in winter, and cause concern for parents. Such symptoms can be treated, however, and many babies and children do outgrow the dry, itchy skin of atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema.
We spoke with pediatric dermatologist Katherine Puttgen to learn more.
Also Check: Dyshidrotic Eczema And Rheumatoid Arthritis
Can I Prevent New Skin Infections
If your child gets frequent skin infections, the following can be helpful:
You can avoid spreading bacteria and other germs by:
A bit of detective work may be necessary to find out whats causing the infections.
Acne Or Eczema Baby What Parents Should Know
Having an acne or eczema baby is a frustrating experience. Luckily, there are a few steps that parents can take to make sure their childs skin regains its normal appearance. Firstly, they should seek the advice of a pediatrician to get a diagnosis of the condition. If the doctors diagnosis is correct, the child may receive treatment that will help restore the babys skin.
A GP can help parents identify the cause of their childs eczema. They can recommend certain treatments and medication that are suitable for their childs case. However, they should not treat the babys eczema on its own. Besides these, the parent should not rub the affected area. If the eczema is too severe, a doctor will prescribe a treatment that will relieve the condition.
A pediatrician will also be able to provide the necessary treatments for eczema. A reputable eczema doctor can help parents treat their babys eczema. A childs eczema can be treated with medications. It is important to see a pediatrician as soon as the condition becomes chronic. There are some medications for eczema that are prescribed for the condition.
As a parent, you must follow the advice of a dermatologist. If your child has eczema or acne, it is important to follow all of the instructions provided by your pediatrician. This will help your child develop a healthy skin barrier. You should not treat an infants eczema with harsh soaps or lotions. Your childs eczema can cause scarring.
Recommended Reading: Best Chemical Peel For Eczema
How Can I Tell My Child Has A Skin Infection
A skin infection can look a lot like eczema. Both cause swollen, itchy skin that can ooze fluid and form crusts. By looking closely at your childs skin, you can find signs of a skin infection.
Youll want to look for:
-
Yellowish-orange or honey-colored crusts, often on top of eczema.
-
Pus-filled blisters, especially on top of eczema.
-
Sores that look like cold sores or fever blisters.
-
Reddish, swollen bumps on skin.
-
Streaks or redness spreading on skin.
Youll also want to check your child for:
-
A fever
-
Swollen tonsils and other lymph nodes
Infection or eczema?
A skin infection can look a lot like eczema. Looking for some common signs can help you spot a skin infection.
Diagnosing Food Allergy And Eczema Flare
- Your child’s doctor may suggest the steps listed below:
- Remove the suspected food or foods from your child’s diet for 2 weeks. The eczema should greatly improve.
- Then give your child that food when the eczema is under good control. This is called a “challenge.”
- If the food is causing flare-ups, the eczema should become itchy and red. The flare-up should occur quickly within 2 hours of eating the food.
- If this occurs, avoid giving this food to your child. Talk to your child’s doctor about the need for any food substitutes.
- If the eczema does not flare-up, your child isn’t allergic to that food.
Recommended Reading: Good Baby Wash For Eczema
Will My Baby Outgrow Eczema
Many babies who develop eczema in their first year eventually outgrow eczema by the time they start elementary school. Other children outgrow it by their early teens. Still others dont completely outgrow eczema by these ages, but notice that their eczema is less severe as they get older.
But eczema, especially chronic eczema, can also be lifelong. Some babies never outgrow eczema, and have the condition for the rest of their lives. Unfortunately, theres no cure for eczema, and no way to tell whether your little one will outgrow it.
Does Your Child Need To See A Doctor About Eczema
Yes. Take your child to see your GP if your child:
- might have eczema for the first time
- is very itchy and uncomfortable
- has eczema thats weeping or bleeding
- has eczema that hasnt improved much after a few days, even though youve been treating it as usual
- is having trouble sleeping because the rash is so itchy
- has painful or eczema that has developed pus
- has eczema and is generally unwell for example, has a fever and/or is sweating, feeding poorly or tired.
You should also take your child to the GP if youre not sure whether the rash is eczema.
If your childs eczema doesnt improve with a combination of medical treatment and management at home, your GP might refer your child to a dermatologist. If the GP thinks your childs eczema might be from allergies, they might also refer you to an allergy and immunology specialist.
Recommended Reading: What Is Eczema And What Does It Look Like
What Else Is Happening At Johns Hopkins Today
We go out of our way to provide the comprehensive care our patients with eczema need. On a case-by-case basis, we communicate with one another whether in allergy, dermatology, psychology or infectious disease to put together the best course of treatment for each child.We are optimistic that future therapies and approaches to care for those with even severe eczema are going to be greatly improved with more research and that the creation of the Eczema Day Treatment Unit will help us conduct cutting edge research and answer questions we face every day seeing and treating patients.
Location Plays A Big Part
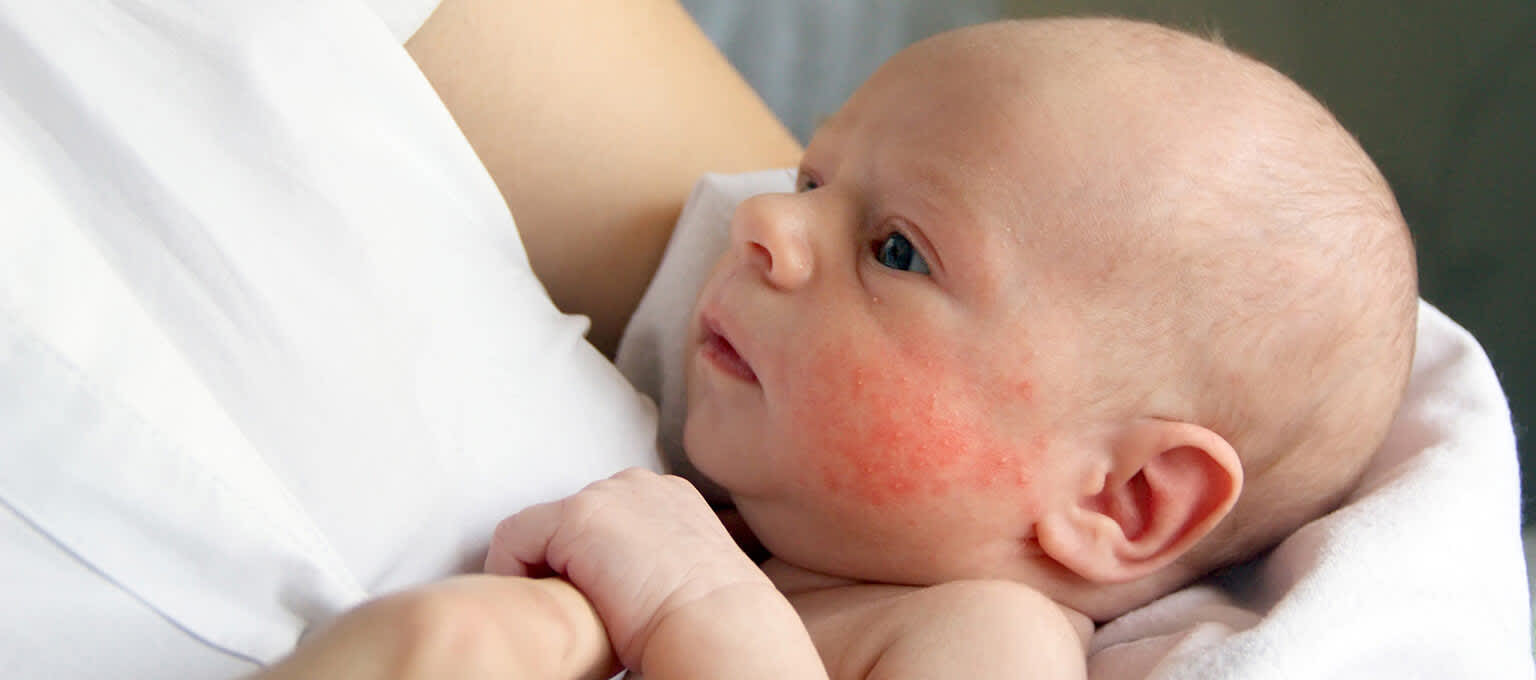
Babies from 1 month to 2 years old tend to get eczema on their cheeks and scalp. Older children will generally have it on the folds of their wrists, knees and ankles. If your child has a red, itchy and scaly rash that isnt in a classic location for eczema, it could be allergic contact dermatitis, meaning they might be allergic to something theyre coming into contact with such as soap, shampoo or lotion.
Read Also: How To Prevent Eczema Outbreaks
Managing Babys Eczema: Other Lifestyle Tips
Bathing and moisturizing are the cornerstones of baby eczema management, but they arent the only ways to manage baby eczema. Follow these other tips to help soothe your babys skin:
Moderate or severe eczema requires more in-depth care than mild eczema. The tips in the linked article may help you develop a detailed routine based on babys eczema severity.
How Does Baby Eczema Differ From Dry Skin
Dry skin is a symptom of eczema. Your pediatrician can diagnose eczema by examining your baby’s skin. He or she may send you to a pediatric dermatologist for confirmation and treatment if the condition is severe.
In general, dry skin can be handled at home with some moisturizer and isnt as bothersome as eczema. However, babies with darker skin tend to have drier skin than those with lighter skin making moisturization even more crucial.
Read Also: What To Do To Help Eczema