Food Allergy And Eczema Flare
- Food allergies are a factor in 30% of young children with severe eczema. This factor is mainly seen in babies.
- The main allergic foods are cow’s milk and eggs.
- The main symptoms are increased skin redness and itching. Some parents report these symptoms start during or soon after the feeding.
- The eczema becomes easier to control if you avoid the allergic food.
Could It Be Cows Milk Protein Allergy
Babies with CMPA usually experience more than just one symptom and these symptoms can be very different from one another.
If you think that your baby has eczema, it could be CMPA.You may have even noticed other symptoms , which may affect other parts of your babys body.
For a simple and easy way to check common symptoms associated with CMPA, you can use our symptom checker.
How To Lessen The Burden Of Dry Skin:
- Bathing once a day or less often bathing frequently can lead to more dryness, counterintuitive.
- Limit baths to 10-15 minutes only. The longer the skin is wet, the more irritated it can become.
- Try adding oil to the bathwater. Coconut or baby oil, or a commercial bath oil product can help lubricate the skin. Please be careful about removing your child from the bath they may be slippery!
- After a bath or shower, gently pat the skin and do not rub. Avoid rubbing as friction can exacerbate eczema.
- Apply lotion or product that is lubricating. Essentially, anything greasy. Use either petroleum jelly, petroleum-free jelly, or oil-based products liberally on the areas of dryness.
- Consider a prescription ointment. Your physician may give you a steroid ointment to apply to affected areas 1-3 times a day. An ointment works better than cream.
- Keep the skin clean and lubricated
- Dry patches of skin respond well to lubrication. Use lubrication or moisturizer several times a day. The greasier the skin, the fewer flair ups.
If you notice the rash spreading or your child has other symptoms such as facial swelling, difficulty breathing, or gastrointestinal symptoms like vomiting, seek medical attention.
Also Check: What To Use For Bad Eczema
What Are The Symptoms Of Eczema
Eczema is a chronic condition which causes red, itchy areas on the skin. Sometimes the itching is very severe. When skin is scratched it can break open, ooze and then crust over. Symptoms of eczema can come and go. Babies with eczema often have it on their cheeks, forehead and scalp. Older children often have it on their hands, wrists, ankles, feet, and on the inside folds of their elbows and knees.
How Can I Help My Child Live With Atopic Dermatitis
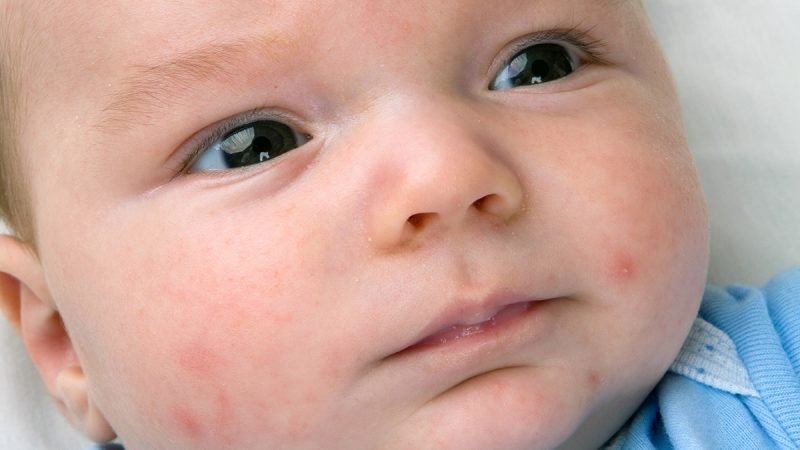
Atopic dermatitis has no cure. But it will usually get better or go away as your child gets older. There may be times when your child has few or no symptoms. And he or she may have times when symptoms get worse. This is called a flare-up. To help prevent flare-ups, make sure your child:
-
Stays away from triggers. Common triggers include irritants such as wool, soap, or chemicals. Other triggers include allergens such as eggs, dust mites, or pet dander. Stress is also a trigger.
-
Doesnt scratch the skin. Try to keep your child from scratching. It can cause symptoms to get worse. It can also cause infection.
-
Always has short fingernails. Trim or file your childs nails to keep them short and prevent scratching.
-
Takes baths or showers with warm, not hot, water. Air dry or gently dry the skin afterward.
-
Uses moisturizers. Put creams or ointments on after bathing.
-
Wears soft clothing. Dont dress your child in wool or other rough fabric.
-
Keeps cool. Try to keep your child as cool as possible. Getting hot and sweating can make him or her more uncomfortable.
-
Doesnt get the smallpox vaccine. Its not a common vaccine, but people with atopic dermatitis should not get the smallpox vaccine.
Talk with your child’s healthcare provider about other ways to help your childs skin condition.
Read Also: What Cream Can I Use For Eczema On My Face
Where On The Body Can Eczema Appear
Eczema can appear in any area where your child has come into contact with one of their triggers.
For example, if they have a grass allergy and rolled around in the backyard, they might have rashes anywhere there was exposed skin.
A child could get eczema around the outside of their mouth after eating acidic foods, like pineapple, or in the folds of their skin if they were sweating.
If your child had eczema as a baby, you might think youre a pro at identifying it. However, the symptoms of eczema in toddlers are actually different from the symptoms in babies. As kids get older, the location of their rashes can change.
Babies are prone to rashes on their faces and heads remember cradle cap? Thats a kind of eczema! Toddlers and older kids are more likely to get eczema in the following areas:
- creases of their elbows
What About Research
At Johns Hopkins, a lot of us in pediatric dermatology, pediatric infectious disease and pediatric allergy and immunology are looking at better ways to prevent or manage eczema. Were studying the optimal management of bacterial colonization and infection in atopic skin and the role of food allergy in eczema. Our specialties collaborate each brings a different approach to eczema management. Our goal is to work together to harness the best approaches to better understand eczema and, in doing so, to treat it more effectively.
Don’t Miss: Things To Help Baby Eczema
How Is It Treated
Because there is not yet a cure for eczema, our treatment goals are to reduce itching and skin inflammation, and to prevent infection. The best treatment for eczema is a proactive one, using gentle skin care and moisturizers to re-establish the skin barrier.
Infants and older childrens skin should be kept well moisturized, and washed with fragrance-free non-soap cleansers. We also recommend a fragrance-free ointment-based moisturizer, with petrolatum as either the only or the first ingredient. In young children and infants, it is reasonable to use an over-the-counter topical hydrocortisone ointment, which is a mild topical steroid, for up to a week.
But if the rash either persists or you find that you need to use the hydrocortisone more than one week out of the month, you should discuss further use with your childs pediatrician. You can apply the ointment, as prescribed, then a coat of petrolatum-based moisturizer, to help keep in the moisture.
If your childs skin does not respond well to any of these measures or becomes infected, contact your pediatrician, who can diagnose the condition and then prescribe another topical cream or antihistamine.
Prevention Of Toddler Eczema
If your child is genetically predisposed to eczema, theres not a lot you can do to prevent it from occurring. But you can try to minimize flare-ups when you can with these actions:
- Get to know your childs triggerswhether its cigarette smoke or scented detergentand avoid them when possible.
- Moisturize your childs skin regularly. One study conducted on babies found that those who were moisturized daily were less likely to develop eczema than those whose skin was not moisturized.
- Keep your childs fingernails short to reduce injury if they scratch their skin.
- Dress your child in soft, nonirritating clothing.
- Keep your child coolheat and sweat can cause eczema to flare.
- Get a dog. Research shows that children who have a dog in their household before they turn 1 have a lower risk of developing eczema by age 4 than those living in households without a dog.
Recommended Reading: Can Eczema Be Under The Skin
How Does Baby Eczema Affect My Childs Skin
Baby eczema makes your babys skin dry, itchy and sensitive. This happens because your babys protective barrier on the outermost layer of their skin is weak and doesnt work as expected. Their symptoms can last for a couple of weeks each time theres a flare-up of symptoms.
Baby eczema is a chronic condition, where it can come and go unexpectedly. Some children grow out of the condition when they reach adulthood but will still experience symptoms of dry skin or mild flare-ups throughout their life.
Tips: How To Stop Eczema Itching At Night
Now that we have an idea about what might be causing those irritating nighttime itches, we can combat them better. If you have a baby with eczema not sleeping, here are ten tips that should help your little one get a more peaceful nights rest.
1. Keep skin temperature regulated. Sweat is one of the most common eczema triggers, so keeping your little one cool at night is perhaps the most important thing you can do. Maintain a cool temperature in the nursery or bedroom. Always opt for air-permeable sleepwear that will allow the skin to breathe and absorb excess sweat. Westyn Baby sleepwear is made of modal, which does exactly that!
2. Avoid harsh fabrics.In most cases, lightweight, breathable fabrics are going to be better than warmer, heavier fabrics. Avoid things like Polyester and wool, which wreak havoc on sensitive skin. Instead, opt for super soft lightweight fabrics like the modal in Westyn Baby sleepwear.
3. Bathe baby at night. Bathtime is always fun for babies, but its also very important when battling eczema!A daily bath can actually help your babys skin retain moisture and prevent infections, but it must be done correctly. Keep bathtime brief , use lukewarm water, and moisturize within 3 minutes of bathtime . For more, heres a complete guide to Bathing Babies with Eczema.
Read Also: California Baby Eczema Body Wash
What Does Baby Eczema Look Like
Eczema doesn’t look the same on every baby. In babies with light skin, it usually shows up as patches of red skin. In darker-skinned babies, the rash might look purplish, brownish, or grayish. Eczema can be harder to see on babies with dark skin.
These patches are almost always dry, itchy, and rough.
Babies can get the condition just about anywhere on their body. Most often, it affects their cheeks and the joints of their arms and legs.
Itâs easy to confuse baby eczema with cradle cap. But there are some key differences.
Cradle cap is much less itchy and irritated. It generally clears up by age 8 months and usually appears on the scalp, sides of the nose, eyelids and eyebrows, and behind the ears. See a photo of what cradle cap looks like.
What Are The Symptoms Of Baby Eczema
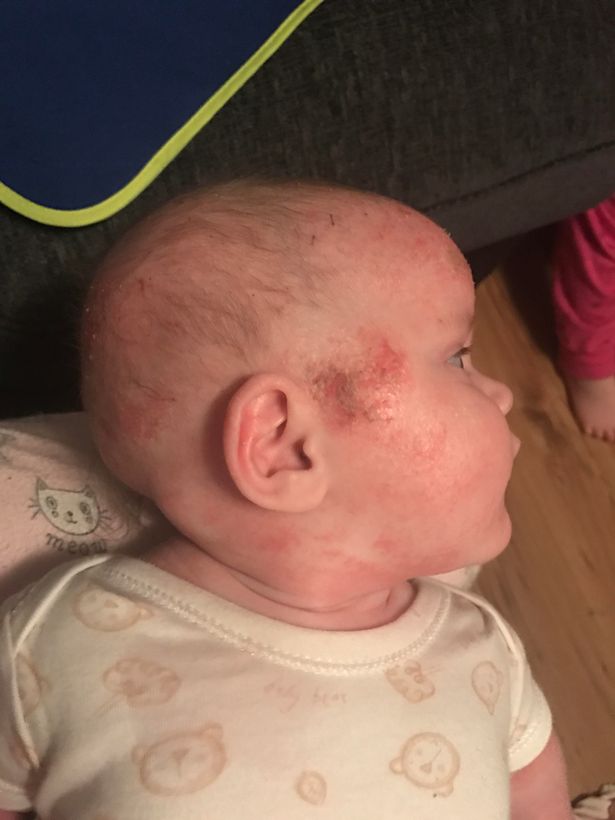
The symptoms of eczema baby vary for infants, toddlers and elder children. As the babies grow, the appearance and position of the skin condition starts to differ. According to each stage of the babys life, consider the following eczema symptoms in babies:
Eczema Symptoms in Babies during the initial 6 months
The following are the most commonly affected areas as a result of Atopic Dermatitis in babies:
- Face
- Forehead
- Scalp
However, the condition may not be limited only to these areas and can spread to other parts of the body. Most likely, the diaper area is the least possible to be affected by the skin disease due to moisture. During this period of time, the skin tends to appear red.
Eczema Symptoms in Babies during the 6 t0 12 months
During this phase, eczema usually affects the elbows and knees area. The locations are easily scratchable, hence, prevent the baby to itch-scratch the area. Scratching results in infection which ultimately leads to the formation of pus bumps on the affected dermis.
Eczema Symptoms in Toddlers during 2 to 5 years
At this stage, eczema has more commonly spread to the creases of elbows and knees, affected their hands, wrists and ankles. It may be even seen in the areas near the toddlers mouth and the eyelids. The eczema may cause the skin to become dry and scaly with deep thick lines.
Eczema Symptoms in children 5 years and above
Recommended Reading: What Helps Eczema Stop Itching
Does Your Baby Have Eczema
Our babies inherit a lot from us: our height, our hair color — and our tendency toward sensitive skin, including eczema.
If someone in your immediate family has allergic tendencies, eczema may be the first sign that your baby shares that tendency, too, says pediatrician Chris Tolcher, MD, clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Southern California School of Medicine.
Eczema can start as early as your baby’s second month. Symptoms can be mild and barely noticeable, or itchy and intense. Know the signs of baby eczema, how to treat it, and what eczema treatments to avoid.
What Does Eczema Look Like
In babies with paler skin, when eczema is flaring the skin is red and itchy. In babies with darker skin, the irritated, itchy areas may be red but are more likely to show as darker patches. They may also appear paler around the front or back of knees or elbows.
When an area of darker skin is treated for eczema, it may become lighter and may take several months to return to the babys normal skin tone.
Also Check: What Medication Is Used To Treat Eczema
Preventing Eczema In Babies With Dry Skin
Does your baby have flaky, irritated, cracked skin? About 1 in 5 kids gets eczema. For some, its the first symptom of a lifetime of allergies. Infants who have eczema are more likely to develop hay fever and asthma later. Doctors refer to this type of allergic disease progression as atopic march. How you treat your babys eczema could make all the difference.
We believe that cracked skin is the entry point for food allergens, such as peanuts and eggs. Food can get into the skin off the table or off people who eat these foods and then kiss or touch the baby. When the food comes through the skin, it causes an allergic reaction, says Donald Leung, MD, PhD, head of pediatric allergy and clinical immunology at National Jewish Health in Denver.
Doctors dont fully understand what causes eczema. They believe genetics and the childs environment each play a role. But parents can help repair their babys broken skin barrier and prevent allergens from getting in. This could stop development of future allergies.
In babies, eczema usually shows up as an itchy, red patch on the cheeks, chin, or scalp and the front of arms and legs. If you see these signs, Leung recommends the soak and seal method.
Gently bathe your baby in lukewarm water with a gentle cleanser free of soap. Dont scrub irritated skin. Allow your baby to soak for at least 5 minutes.
Which Foods May Trigger Eczema
When you have a food allergy, your body reacts to a harmless treat as if it’s a dangerous germ and attacks. Symptoms — like swelling — are side effects of your body’s defenses.
Eczema doesn’t seem to be an allergic condition, but reactions from food can make it worse in some kids. Itâs more likely in babies and young children.
Some foods are more likely to bring symptoms. The common offenders are:
- Milk
- Shellfish
- Soy
While trigger foods can make eczema worse, experts don’t think theyâre really the original cause. Instead, it seems to result from “leakiness” in the outer layer of skin that lets in irritants, germs, and allergens.
Recommended Reading: Colloidal Oatmeal Cream For Eczema
How Is Atopic Dermatitis Diagnosed In A Child
The healthcare provider will ask about your childs symptoms and health history. He or she may also ask if you or other family members have atopic dermatitis, asthma, or nasal allergies such as hay fever or allergic rhinitis. He or she will also ask about allergy symptoms in your child. The healthcare provider will examine your child, looking for signs of atopic dermatitis. There is no specific test for atopic dermatitis. Testing is usually not needed, but it may be done. Tests may include:
-
Blood tests. Your childs blood may be checked for levels of immunoglobulin E . IgE is released by the body’s immune system. Its high in most children with allergies and with atopic dermatitis. Other blood tests may also be done.
-
Skin tests. Skin tests may be done to check for allergies or other skin conditions.
Giving Your Baby Antiseptic Baths
Giving your baby an antiseptic bath twice a week can help improve eczema, decrease bacteria, and prevent skin infections. The best antiseptic to use is bleach. However, you need to dilute the bleach with water first. Bleaches come in different strengths and how much water you use depends on the strength of the bleach you are using.
Bleach is sold at the supermarket and will be in the cleaning aisle. You need bleach that has no added detergent or fragrance.
Always store the bleach where your baby or young children cant reach it.
Recommended Reading: What Can Cause Eczema On Hands
What Happens If My Baby’s Eczema Becomes Infected
skin infectionsBacterial infections
- ooze or weep fluid
- have a yellow, crusty appearance
- have small, yellow-white spots
Viral infections
- patches of eczema that are particularly painful for your baby, and get worse quickly
- fluid-filled blisters that burst, leaving small open sores on your baby’s skin
- a fever and seeming generally under the weather
Baby Eczema: Diagnosis And Treatment

Your childs doctor will diagnose eczema based on symptoms, the appearance of the rash, family and individual medical history, and evaluation for potential allergies.
There is no specific test to diagnose eczema, but a doctor might order blood tests and skin tests to look for allergies or rule out other skin conditions.
You May Like: Does Milk Cause Eczema In Toddlers