Slow Down During Flare
No matter how careful you are, your eczema may flare up sometimes. When it does, take steps to be kind to your skin so you donât make it worse.
Dial back the intensity of your workouts until your skin calms down. For example, walk instead of run. Once youâve healed, you can go back to your usual routine.
Not all of these tips will apply to you. If sweat and spandex donât bother you, great. Stick with strategies that work for you.
Establish A Skincare Routine
Keeping your skin hydrated is one of the most important steps you can take in minimizing eczema flare-ups. A gentle moisturizing routine with products that are safe for sensitive, eczema-prone skin can help to curb itchiness and irritation.
- Choose a gentle cleanser that wont disturb the skins microbiome and disrupt the skin barrier. La Roche-Posays Lipikar line offers a few cleanser options that are perfect for eczema-prone skin. Lipikar Syndet AP+ is a cream-based soap-free cleanser that can be used on the face or body for a non-irritating cleanse for adults and babies. Cleansing oil is another popular option for cleansing irritation-prone skin. Lipikar Oil AP+ is a lipid-replenishing oil cleanser that helps to nourish the skin barrier and protect the skin from the drying effects of hard water. Lipikar Surgras Bar Soap, a twist on the typical bar soap, provides a cleansing option that protects the skin barrier without leaving skin feeling dry.
- After cleansing, using a cream suitable for eczema-prone skin is essential to keep skin hydrated and happy. La Roche-Posay Lipikar Baume AP+M is a soothing balm that locks in moisture while helping to relieve itchiness. Another option for a cream suitable for eczema-prone skin on the face is Toleriane Ultra Overnight, a gentle, nourishing night cream that helps to repair skin while you sleep.
Where Does Facial Eczema Usually Show Up
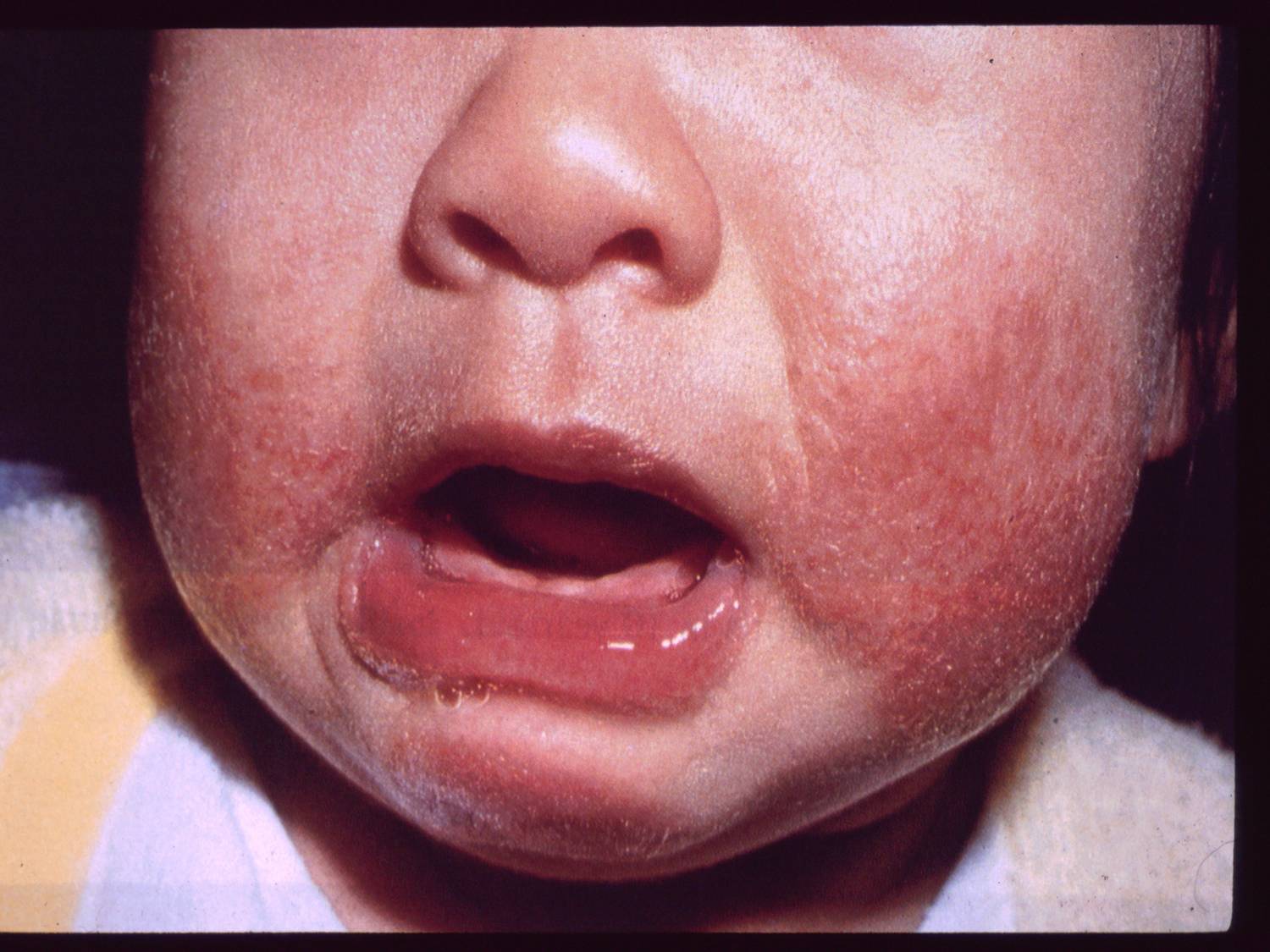
While eczema can occur anywhere, it is common to experience flare-ups on the scalp, the forehead, the eyelids and skin around the eyes , and behind the ears. Babies in particular can suffer from eczema on the cheeks. There is also a particular type named Hand Eczema which may lead to red, itchy and/or dry irritated hands with cracks or blisters.
Recommended Reading: Best Lotion For Eczema On Legs
Is Eczema Different For Infants Or Toddlers Than It Is For Older Children
A painful, itchy rash on a babys face, torso or body may be eczema
Eczema looks and acts differently in infants and toddlers than it does in older children. The location and appearance of eczema changes as they grow, so its important to know what to look for during every stage of your infant or toddlers life.
What Helps Eczema On The Body
When it comes to your body moisturiser, the same rules apply: you need a skincare product designed specifically to help look after your skin which may be more prone to sensitivity and of course dryness. The Lipikar Baume AP+ by La Roche-Posay is a soothing body balm for itchy skin and eczema-prone skin that helps replenish the skins natural lipids, reduce tightness and soothe itching. Apply morning and evening after using your Lipikar Syndet AP+ gentle body wash for faster and more effective results. Skin feels instantly soothed and comfortable.
Read Also: Best Diapers For Babies With Eczema
What Foods Should I Eat Or Avoid To Reduce My Risk Of Eczema
The connection between eczema and food allergies is unclear. If you have food allergies, then one of the reasons why you must avoid that food is that it may cause or worsen dermatitis. Examples of common allergies include peanuts, dairy, eggs, sugar, alcohol and gluten. Pay attention to what you eat. If your eczema flares up after you eat a certain food, then you might have an allergy to it.
If you dont have a food allergy then there are no foods, including chicken, that will cause or worsen your eczema.
Why Do We Get Eczema On The Face
Well, the skin on the face is far more sensitive than the rest of the body, and in some places is very thin and prone to faster absorption of toxin and allergen exposure.
There are a number of potential triggers that we can speculate over and test their effects by elimination. These include: Incorrect moisturizer Run off from shampoos, hair dye and styling products Incorrect makeup Allergic reaction to nickel in eyelash curlers, tweezers, mobile phones Transporting allergens from the hands to the face from touching and we touch our faces up to 136 times per day!
As you might already know, there are various types of eczema, so determining the actual type of eczema youre dealing with can help you work out how to tackle the task of getting rid of it.
If eliminating one of the above triggers improves the condition, then this is wonderful and you can enjoy a face with no eczema! Otherwise if the eczema is persistent, then your condition is potentially atopic, and may require a more holistic form of treatment.
When searching for the best cream for eczema on the face, its important to understand up front that it may take a while before you find a cream which works for you – especially if the condition is atopic.
While I understand that almost anyone can have a reaction to some ingredient, be that natural or otherwise. There are certain ingredients added to products that are known to cause irritation to even strong eczema-free skin.
You May Like: What Probiotics Are Good For Eczema
Signs Of An Infection
Areas of skin affected by eczema can become infected. Signs of an infection can include:
- your eczema getting a lot worse
- fluid oozing from the skin
- a yellow crust on the skin surface or small yellowish-white spots appearing in the eczema
- the skin becoming swollen and sore
- a high temperature and generally feeling unwell
See your GP as soon as possible if you think your or your child’s skin may have become infected.
Why Did My Child Develop Eczema
The exact cause of eczema is unknown. Researchers do know that children who develop eczema do so because of a combination of genes and environmental triggers. When something outside the body switches on the immune system, skin cells dont behave as they should causing flare ups.
We also know that children who come from families with a history of atopic dermatitis, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis.
Don’t Miss: Eucerin Eczema Relief Cream Walgreens
Eczema Causes And Risk Factors
Experts arenât sure what exactly causes eczema. Things that may make it more likely include:
- An immune system response to something irritating
- Problems in your skinâs barrier that let moisture out and germs in
- A family history of other allergies or asthma
Know more about the link between allergies and eczema.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Eczema
The signs of eczema :
- are mainly dry, itchy skin. Because it is so itchy, it is often called “the itch that rashes.”
- include redness, scales, and bumps that can leak fluid and then crust over
- tend to come and go. When they get worse, it is called a flare-up.
- may be more noticeable at night
Symptoms can vary:
- Infants younger than 1 year old usually have the eczema rash on their cheeks, forehead, or scalp. It may spread to the knees, elbows, and trunk .
- Older kids and teens usually get the rash in the bends of the elbows, behind the knees, on the neck, or on the inner wrists and ankles. Their skin is often scalier and drier than when the eczema first began. It also can be thicker, darker, or scarred from all the scratching .
Read Also: Eczema On Face During Pregnancy
Tips For Reducing Outbreaks
Here are a few ways to prevent eczema flare-ups and manage symptoms:
- Apply cool compresses to your skin, or take a colloidal oatmeal or baking soda bath to relieve the itch.
- Moisturize your skin daily with a rich, oil-based cream or ointment to form a protective barrier against the elements. Apply the cream right after you get out of the shower or bath to seal in moisture.
- After you bathe, gently blot your skin with a soft towel. Never rub.
- Avoid scratching. You could cause an infection.
- Use fragrance-free detergents, cleansers, makeup, and other skin care products.
- Wear gloves and protective clothing whenever you handle chemicals.
- Wear loose-fitting clothes made from soft fibers, like cotton.
You should also avoid any known triggers.
What Is It Like Living With Eczema
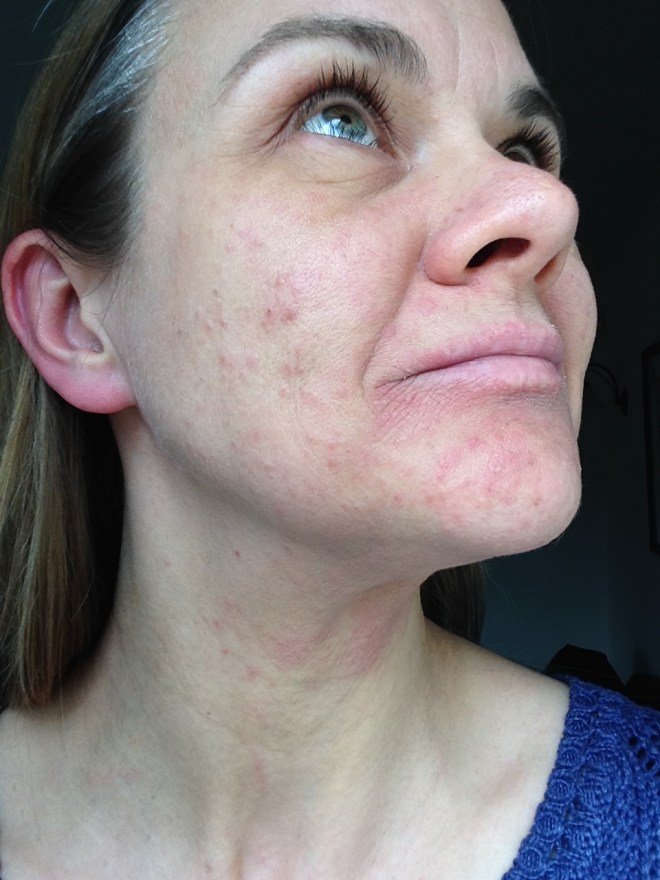
Many people live with eczema . As many as 15 million Americans may have this skin condition. Living with it can be challenging.
There may be times when your eczema disappears. This is known as a remission period. Other times you may have a flare-up, which is when it gets worse. The goal of treatment is to prevent such flare-ups, preventing your symptoms from getting worse. Be sure to avoid triggers, moisturize, take your medicine and do anything else your healthcare provider recommends.
Also Check: Is Cetaphil Lotion Good For Eczema
Can You Get Eczema As An Adult
Eczema or psoriasis? Managing eczema in summertimeNickel allergySevere atopic dermatitis
Adults can get any type of eczema, including atopic dermatitis , which many people consider a childhood disease.
When AD begins after your 18th birthday, dermatologists call it adult-onset atopic dermatitis. Youd receive this diagnosis if you never had AD before. A peak time for developing adult-onset AD is in your 50s.
AD and the eyes
In adults, atopic dermatitis often develops on skin around the eyes.
Some adults who have AD had it as a child. Its possible for AD to go away in childhood and return years later. When the AD returns, its often much milder.
For some children, the AD never goes away, so its a lifelong disease. This happened to Peter Moffat, the award-winning writer of the British TV series Criminal Justice. You can read about how AD affects his life by going to: Adults with eczema too often suffer in silence
Q 1: How Can Infections Due To Eczema Be Prevented And Treated
People with eczema that is not well managed can be more likely to have skin infections with bacteria such as Staph , and viruses such as the cold sore virus.
People with eczema who have infections need to treat these as they occur. They may also need long term prevention strategies, such as diluted bleach baths, which can help prevent future skin infections.
Long term oral antibiotics can be helpful for people who suffer from recurrent infected eczema.
Read Also: Best Formula To Give Baby With Eczema
Helping Your Child Feel Better
If your child has eczema, keep their fingernails short and their skin moisturized. Dress them in loose-fitting clothes and make sure they don’t get overheated. Depending on how severe their eczema is, your doctor may recommend wet wraps, a diluted bleach bath, over-the-counter or prescription medications, and/or light therapy to help.
Q : How Should Eczema Flares And Severe Eczema Be Treated
Skin damage can be prevented by applying creams or ointments prescribed by your doctor as soon as eczema is present. In contrast, not using enough of the treatments can cause skin damage due to itching, which can lead to scarring.
If prescribed, use topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors:
- These treatments actively treat inflammation .
- Ensure that adequate amounts are used. As a guide, one fingertip unit is the amount of ointment from the first bend in the finger to the fingertip, which will cover an area equal to two adult hands.
- Apply moisturiser after corticosteroid cream or ointment has been applied.
If prescribed, use an immune modulating treatment for severe eczema:
- People aged 12 years or older with severe eczema which has not responded to other prescribed topical treatments can now be prescribed an immune modulating treatment known as dupilumab on the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme in Australia.
- Immune modulating treatments modify the bodys immune response to prevent inflammation that plays a central role in eczema, but they are not immunosuppressants.
You May Like: Is Castor Oil Good For Eczema
Treatment Of Facial Eczema
Eczema on the face requires careful treatment as facial skin is more easily irritated by and vulnerable to the side effects of topical therapy. It is important to consider the possibility of an allergic contact dermatitis in anyone with a persistent facial eczema, even if they have a longstanding, in-built eczema tendency. It is helpful to make a diagnosis of which particular type of facial eczema someone has in order to know which treatment is likely to work best, and to help give an idea of the expected outcome usually, as eczema is a chronic condition, controlling facial eczema and preventing flares will be the main focus of treatment.
In general, treatment of facial eczema involves avoiding further irritation caused by cosmetics and toiletries, switching to a gentle regimen of skin cleansing, and actively treating the eczema with emollients and anti-inflammatory therapy .
Is It Cradle Cap
“Cradle cap” in babies is a condition that doctors call seborrheic eczema or seborrheic dermatitis. It appears as oily, scaly patches on the scalp. In contrast, atopic dermatitis is more often found on the cheeks, though it can also affect the scalp. Also unlike eczema, cradle cap typically isnât itchy. Usually cradle cap clears up without treatment in a few weeks or months.
Recommended Reading: Is Eczema A Sign Of Pregnancy
Q : How Is Eczema Related To Food Allergy
Whilst food allergy can trigger or worsen eczema symptoms in some people, food allergy is rarely the cause of eczema. Most food allergy causes hives , vomiting and irritability within 30 minutes of eating the offending food. Food allergy only occasionally triggers delayed eczema flare ups.
Many babies with moderate or severe eczema will also have a food allergy. In some babies with severe eczema, short term removal of certain food/s using a medically supervised elimination diet may result in better eczema control. An elimination diet should be supervised by a clinical immunology/allergy specialist , in association with a dietitian with specialised knowledge of food allergies.
If there is no improvement in two weeks on the elimination diet, it means that food is unlikely to be the cause of the eczema. If the skin improves, foods are introduced one at a time as a medically supervised food challenge, to confirm which food causes the eczema to flare.
If food allergy is not the cause of eczema, removal of the food/s will not reduce symptoms.
Children with eczema and/or food allergy can have false positive allergy tests, and this can lead to unnecessary removal of foods which may affect growth and development. Removal of foods may also increase the risk of developing allergy to those foods. Therefore, allergy test results should always be interpreted by a clinical immunology/allergy specialist.
Triggers Of Eczema Flare
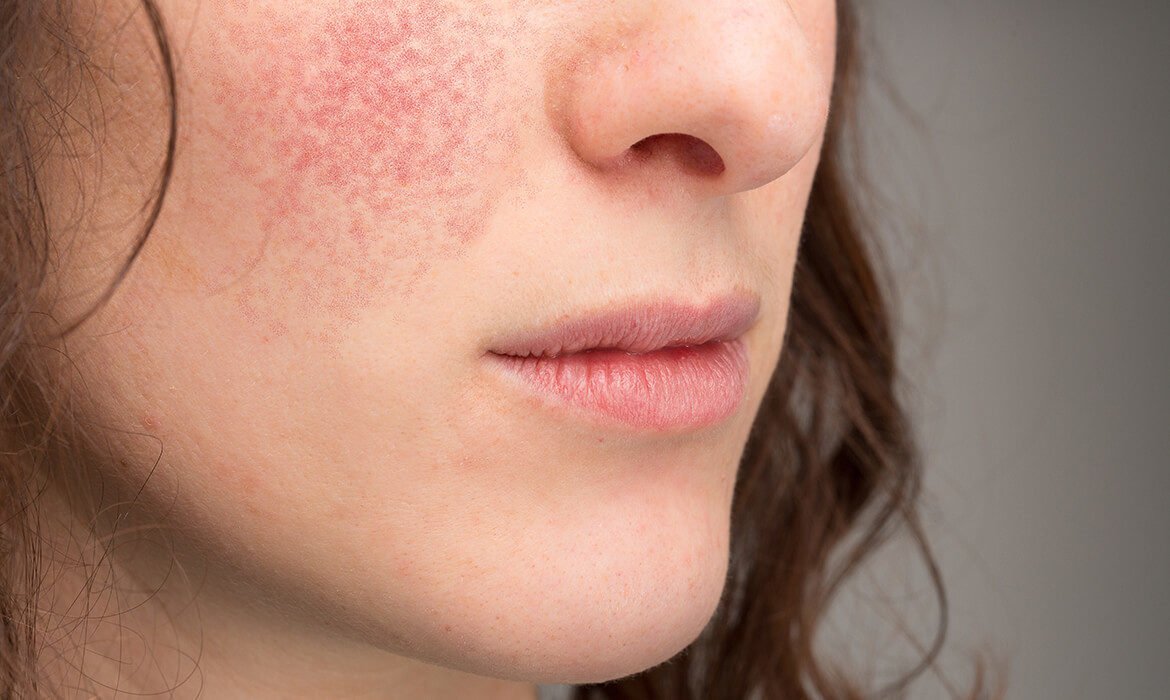
- Soaps. Never use bubble bath. It can cause a major flare-up.
- Pollens. Keep your child from lying on the grass during grass pollen season.
- Animals. Avoid any animals that make the rash worse.
- Foods. If certain foods cause severe itching , avoid them.
- Wool. Avoid wool fibers and clothes made of other scratchy, rough materials.
- Dry Air. Use a humidifier if the air in your home is dry.
- Herpes Virus Infection . Keep your child away from anyone with fever blisters . The herpes virus can cause a serious skin infection in children with eczema.
- Eczema is not caused by laundry soap you use to wash clothing.
Read Also: Best Moisturizer For Eyelid Eczema
When Adults Get It
You might notice itchy patches on the hands, elbows, and in the “bending” areas of the body, such as the inside of the elbows and back of the knees. But eczema can appear anywhere, including the neck, chest, and eyelids. People who had atopic dermatitis as a child may see drier, scaly rashes as adults. The skin may be discolored or thickened.
Diagnosis & Treatment Options
Eczema is not a contagious condition. There is also no cure for it.
There are many treatment options that can help to manage eczema breakouts, reducing their severity and frequency. Eczema treatment is focused on repairing damaged skin and alleviating uncomfortable symptoms.
Current treatment options include:
- Topical corticosteroid creams and ointments. Anti-inflammatory creams target skin itchiness and inflammation.
- Systemic corticosteroids. Prescription corticosteroids can be swallowed or injected when topical creams are not effective enough.
- Antibiotics. These are prescribed when a bacterial skin infection is also present.
- Antifungal/antiviral medications. These are used to treat fungal or viral infections related to eczema.
- Antihistamines. These reduce itchiness and improve sleep.
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors. These are used to decrease inflammation of the immune system that is causing flareups.
- Skin barrier-repairing moisturizers. These help to keep moisture in and repair the skin.
- . Ultraviolet A or B light waves can be used to treat moderate eczema.
- Wet wrap therapy. This treatment is used for severe eczema. Three lukewarm baths per day are given, followed by the application of topical medications and moisturizers. The skin is then wrapped in wet gauze.
Recommended Reading: What Can Make Eczema Flare Up
Prescription Creams And Ointments
If self-care measures dont prevent flare-ups, your doctor may suggest medicines you rub on your skin:
Corticosteroids have long been used to treat eczema. They come in a range of strengths. You usually stop using them once the flare-up is under control.
Calcineurin inhibitors affect how your immune system works. They can curb flare-ups but have serious side effects, so youd probably only use them if other treatments fail.
Apply A Cold Compress
Even with the best skin care, you may still end up with swollen, red, itchy patches of skin. For some immediate relief, apply a cold compress. This can simply be a cool, damp towel no need to get fancy.
Submerge the towel or washcloth in cold water and wring it out before placing it on the affected area.
Recommended Reading: How To Avoid Itching Eczema