How Can A Dermatologist Help
A dermatologist specializes in skin diseases, including CSU. Your visit with a dermatologist will start off with a thorough medical history, followed by an exam, but dont expect a battery of tests.
For the most part, when it comes to chronic hives, we never identify why someone has it, which is why the current recommendation is not to do a crazy, expensive workuponly if the story pushes you in the direction of an underlying illness or condition, says Dr. Freidman.
The first order of business, then, is typically to confirm that you are in fact getting hives and not another skin condition, like a rash. Hives move around, and theyre typically inducible by scratching, so your dermatologist may lightly scratch the surface of your skin with an end of a tongue suppressor to bring one out. This diagnostic is aptly named a scratch test.
If your doctor suspects your hives are really a symptom of another condition or infection, such as Helicobacter pylori , a bacterial infection, he or she will do blood tests. There is limited data about how commonly H. pylori causes CSU, but one small study in Advances in Dermatology and Allergology showed 36 of 100 patients with CSU also had H. pylori, suggesting it should be part of a CSU workup.
Questions The Doctor May Have
Be prepared to tell the allergist about your symptoms and your lifestyle. They may want to know:
- What kinds of symptoms do you have?
- How long have you had them?
- When your symptoms happen, how long do they last?
- Do your symptoms come and go throughout the year, or do they last year-round?
- Do your symptoms hit when youâre outdoors, or indoors — like when you clean your home?
- Do they get worse when youâre around pets? Do you have any pets?
- Do you smoke? Does anyone in your family smoke?
- Do your symptoms keep you from doing things or from sleeping at night?
- What makes your symptoms better? What types of treatments have you tried?
- What allergy drugs are you taking now? Do they help?
- What other medications are you taking, including prescription and over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal supplements?
- What kind of heating system do you have? Do you have central air conditioning?
- Do you have any other health conditions, like asthma or high blood pressure?
- Do you have problems with your sense of smell or taste?
- Do you get better on the weekend and worse when you go back to work?
What Is Eczema And Who Gets It
Eczema is the term for a few different skin conditions. But most of the time, it refers to a common skin disease called atopic dermatitis, which causes a dry, itchy, red rash. If you scratch it, it can start to ooze and crust over. Do it over time, and your skin can get thick and dark.
Most people with eczema get it as children. Symptoms often improve by age 5 or 6, and flare-ups stop for more than half of kids by their teenage years. But many people still have the disease as adults, though their symptoms tend to be milder. Itâs less common to get eczema for the first time as an adult.
Also Check: Can Eczema Only Be In One Spot
Test For Dozens Of Allergens
The list of substances known to cause allergies is very long. Such substances are commonly used in cosmetics and cleansers, jewelry, bandages, colorants and even musical instruments! The standard routine test battery covers about twenty of the common allergens.
Are you exposed to less common allergens through your work or activities? The specialist will have noted this through the questionnaire and may carry out additional tests.
In case of a negative result, a ROAT may be recommended
If an allergy is strongly suspected but is not confirmed by the patch test, a ROAT may be carried out. You will be asked to apply the product to a small area of the forearm over the course of several days to see if a repeated application triggers redness.
Q : How Does Eczema Affect People Of Different Ages

Eczema is a chronic health problem that affects people of all ages, but is most common in babies :
- Infantile eczema occurs in around 20% of children under two years of age, and usually starts in the first six months of life. Infantile eczema usually improves significantly between the ages of two to five years.
- Childhood eczema may follow infantile eczema, or start from two to four years of age. Rashes and dryness are usually found in the creases of the elbows, behind the knees, across the ankles and may also involve the face, ears and neck. This form of eczema usually improves with age.
- Adult eczema is similar to that of older children with areas of very dry, itchy, reddened skin at the elbow creases, wrists, neck, ankles and behind the knees. It can cause rough, hard and thickened skin, which may also have weeping areas. Although eczema tends to improve in midlife, and is unusual in elderly people, it can occur at any age.
Read Also: Best Moisturizer With Spf For Eczema
Eczema Treatment From St Louis Allergists
Eczema is the most common skin condition diagnosed in our St. Louis allergy clinic, especially in children. Eczema affects one in five infants but only around one in fifty adults. We offer diagnosis and complete allergy treatment services to people of all ages who are suffering from eczema in the St. Louis area.
Eczema is a skin condition that may or may not be related to an allergy our St. Louis allergist will determine the exact cause of your skin irritation in order to determine the appropriate treatment. Eczema is now thought to be due to leakiness of the skin barrier, which causes the skin to dry out and become prone to irritation and inflammation by many environmental factors. Some people in St. Louis have a food sensitivity which can make eczema symptoms worse. In about half of patients with severe atopic dermatitis, the disease is due to inheritance of a faulty gene in their skin called filaggrin.
Unlike with urticaria , the itch of eczema is not caused by histamine so antihistamines are not prescribed as an allergy treatment because they do not control the symptoms. Eczema is often linked with asthma, allergic rhinitis or food allergy. This order of progression is called the atopic march. A large percentage of St. Louis residents suffer from asthma and may not be aware their skin condition is linked to asthma until it is diagnosed by an asthma doctor.
Can Certain Foods Cause Eczema
We do not yet properly understand the role of diet in eczema. There is no clinical evidence that there is any connection between diet and eczema getting better or worse in adults. Many carers believe that their childs eczema is caused by something in their diet, but only a small number of children with eczema are helped by changes to their diet .
Even those for whom changes to their diet have helped will still need to employ a good skincare routine to protect against other triggers. It is rarely diet alone that triggers eczema.
Keeping an accurate diary of what your child eats and the condition of the eczema can be useful when discussing concerns with your GP. If you are planning to make changes to a major nutritional source such as milk in young children, you must consult your GP so that the best supplement is identified. The most common food triggers are eggs, nuts, cows milk and sesame, but many other foods including soya, wheat, fish and nuts are common. Allergy testing is a specific area of medicine that requires expert interpretation of the results. Our factsheet on Diet and eczema in children contains further information.
You May Like: What Helps Eczema On Hands
Do I Have Eczema A Patient Story
Sometimes its hard to tell if you have eczema for both patients and doctors. Angela is a 35-year-old African American woman. She has a history of allergies but is otherwise healthy. Several months ago, she started having patches of itchy skin. At first, Angela thought it might be a new laundry soap she used, so she switched back to her old one, but the itching got worse. She tried several over-the-counter lotions, which provided limited relief. Angela made an appointment with her primary care doctor, who listened to her symptoms, did a physical exam, but didnt observe anything obvious. The doctor thought it might be a new allergy and suggested Angela start taking over-the-counter allergy medication.
Several months go by and Angela is miserable. The allergy medicine did nothing to help her symptoms. She developed several patches of thick, itchy skin. The constant itching is causing her to lose sleep.Angela finally decided to make an appointment with a dermatologist who had experience treating African American patients. The dermatologist listened to Angelas story, evaluated her skin, and noted thickened patches of darker skin where she complained of itching. He diagnosed her with eczema and started treatment.After nearly a year of symptoms, Angela finally had a diagnosis and was hopeful the treatment would provide relief.
Best Eye Drops: Alcon Naphcon Eye Drops
-
Non-oral solution for itchy, red eyes
-
Great size for on-the-go relief
-
Clears the eyes quickly
-
Can cause eye dryness if used excessively
Itchy, red eyes are a common reaction to allergies, but luckily, this problem can quickly be solved with proper eye drops. The highly recommended Alcon Naphcon-A Allergy Relief Eye Drops are a reliable option as the formula combines a redness reliever and an antihistamine ingredient to bring your eyes back to normal.
Dont Miss: Best Treatment For Infant Eczema
Recommended Reading: Colloidal Oatmeal For Baby Eczema
Key Points About Contact Dermatitis In Children
-
Contact dermatitis is a skin reaction from contact with certain substances.
-
It can be caused by irritants or allergens.
-
It causes many symptoms including skin redness, blistering, and itching.
-
Its important to not have any contact with irritants or allergens that have caused dermatitis.
-
Treatment may include cool cloths, dressings, skin creams or lotions, or prescription medicines.
Q: When Should People Of Color See A Specialist For Treatment
Kelly Maples, MD: When basic skin care and topical anti-inflammatory medications are not effective, or eczema is impacting quality of life, thats when you should consider going to a specialist such as an allergist or dermatologist.
Allergists can help when:
- your skin is not responding to mild to moderate topical corticosteroids or topical calcineurin inhibitors
- youre having trouble sleeping due to eczema
- youre concerned about the appearance of your skin
Allergists can also help identify eczema triggers and set up a plan to prevent symptoms before they develop.
Kelly Maples, MD, FACAAI, is a board-certified allergist and immunologist at Childrens Hospital of The Kings Daughters in Norfolk, Virginia. She is also Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Internal Medicine at Eastern Virginia Medical School. She is on the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology Board of Regents and is Chair of the ACAAI Dermatology Committee.
Have a medical question? Email or write to Ask the Allergist, Allergy & Asthma Network, 8229 Boone Blvd., Suite 260, Vienna, VA 22182.
8229 Boone Blvd, Suite 260, Vienna, VA 22182
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Acute Eczema
An Allergic Reaction Not Always
Eczema, complete with itching and its all-too-familiar red patches, can be divided into two main types. They have different causes, they progress differently, and they require slightly different treatments. One is an inflammatory contact reaction, most often due to an allergy, and the other is hereditary. So how can you tell if your eczema is caused by a contact allergy?
Why Is Eczema Harder To Diagnose On Black Skin Or Brown Skin
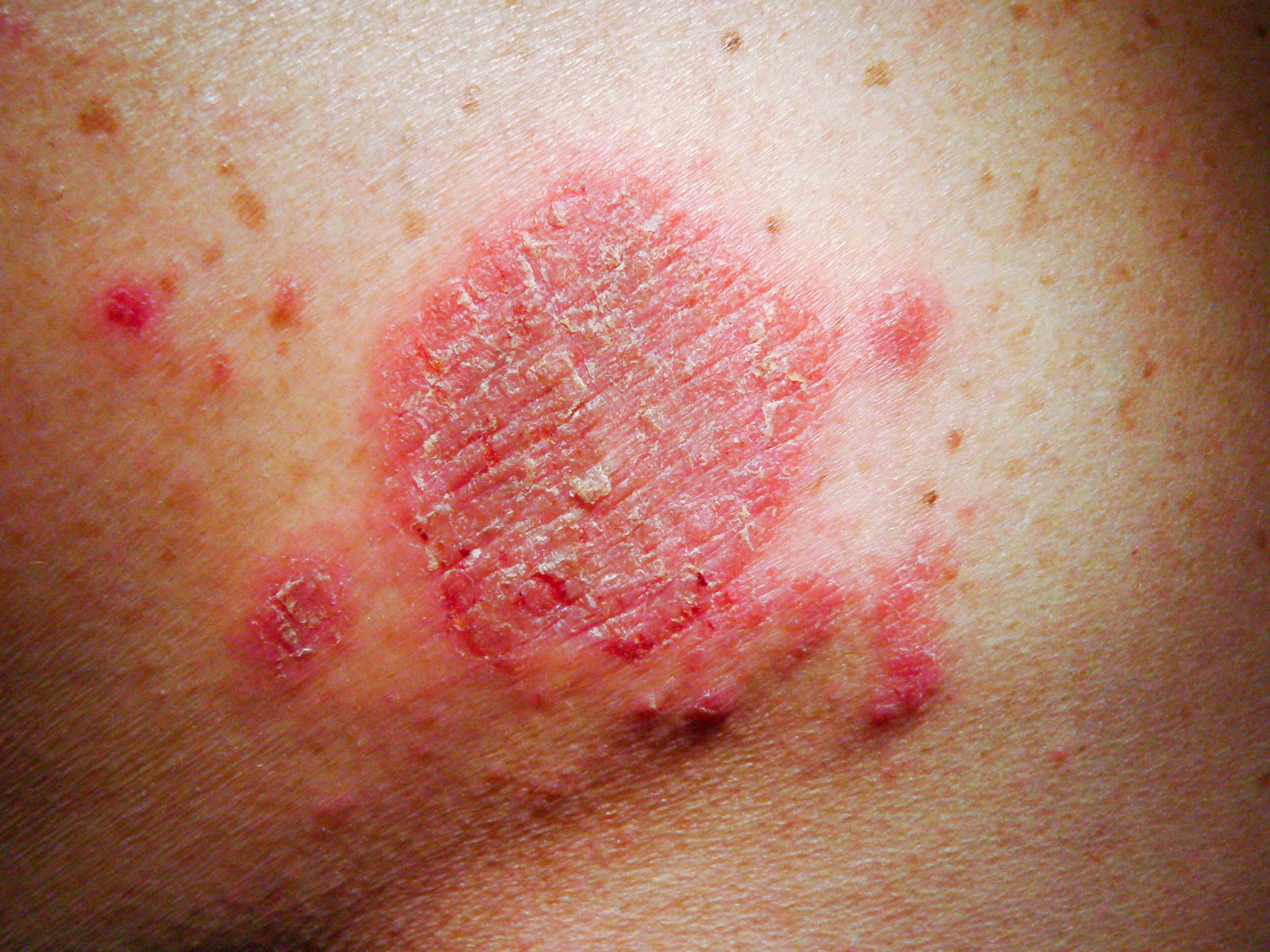
Perhaps more than any other medical specialty, doctors need to look at the skin to make an accurate diagnosis. And though it shouldnt be surprising, skin conditions often appear differently on different skin colors.
Like most areas of medicine, non-white skin types are underrepresented in the literature. Medical textbooks and journals might be chock-full of pictures, but often the majority show white people. Doctors in training may have limited resources to help them learn to identify skin conditions in non-white people though that has begun to change in recent years.
Imagine a doctor in a rural part of the country with limited diversity. An African American arrives at the office with itchy skin. The doctor may have limited experience treating Black patients, so they reference a textbook only to find out that what they are seeing is not found in a textbook. They may then do an online search,only to find similar limitations. This could lead to a misdiagnosis or a delay in diagnosis and treatment.
The Eczema in Skin of Color websiteoffers doctors and patients information and an image gallery to identify symptoms on different skin colors. This resource is designed to help people of color get an accurate and quicker diagnosis of eczema.
Also Check: What Causes Eczema Under Eyes
How To Use Emollients
Use your emollient all the time, even if youre not experiencing symptoms.
Many people find it helpful to keep separate supplies of emollients at work or school, or a tub in the bathroom and one in a living area.
To apply the emollient:
- use a large amount
- do not rub it in smooth it into the skin in the same direction the hair grows
- after a bath or shower, gently pat the skin dry and apply the emollient while the skin is still moist to keep the moisture in
You should use an emollient at least twice a day if you can, or more often if you have very dry skin.
During a flare-up, apply generous amounts of emollient more frequently, but remember to treat inflamed skin with a topical corticosteroid as emollients used on their own are not enough to control it.
Do not put your fingers into an emollient pot use a spoon or pump dispenser instead, as this reduces the risk of infection. And never share your emollient with other people.
What Foods Should I Eat Or Avoid To Reduce My Risk Of Eczema
The connection between eczema and food allergies is unclear. If you have food allergies, then one of the reasons why you must avoid that food is that it may cause or worsen dermatitis. Examples of common allergies include peanuts, dairy, eggs, sugar, alcohol and gluten. Pay attention to what you eat. If your eczema flares up after you eat a certain food, then you might have an allergy to it.
If you dont have a food allergy then there are no foods, including chicken, that will cause or worsen your eczema.
Read Also: Causes Of Eczema On Feet
How Can Good Eczema Control Help Prevent Food Allergy
Since healthy skin acts as a barrier, it also helps prevent substances like food allergens from getting into the body through the skin. Healthy skin helps protect the immune system from being exposed to food allergens. When your child’s eczema is under good control, your child’s skin is better at preventing food allergens from getting in.
New research suggests that when your child’s skin is scratched open, food allergens can get into the body more easily to make contact with the immune system. Direct contact between open skin and food, such as peanuts, may increase the chance that an allergy will develop to that food. The immune system may be more prone to developing a food allergy if the first exposures to the food are through scratched open skin.
The opposite may be true if the immune system is first introduced to the food by eating it. If the first exposure to a food is through the digestive tract, the immune system may more likely tolerate the food.
For more information about controlling eczema, please refer to the section on the next page called: How can I help control my child’s eczema?
What Are The Complications Of Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis is a Type IV hypersensitivity reaction, caused by a different immunologic mechanism than hives, angioedema, or anaphylaxis. However, very rarely, patients may have immunologic dysfunction which results in multiple types of concurrent hypersensitivity reactions. Thus, it is possible that people with contact dermatitis can develop hives and swelling after coming into contact with an allergen. Hives are red, raised, itchy skin welts. Angioedema is swelling deep under the skin.
Extremely rare, allergic contact dermatitis can overlap with a severe, life-threatening allergic reaction called anaphylaxis that can swell airways and close them. If you think you are experiencing anaphylaxis, call 911. Youll need an immediate epinephrine injection to counteract this allergic response. People with known allergies can carry an EpiPen®, a brand of injectable epinephrine.
Read Also: How To Tell If A Rash Is Eczema
Allergic Contact Eczema Versus Atopic Eczema
When costume jewelry earrings cause eczema to break out on the ear, this is a sign of an allergic reaction to the nickel in the earring. This is a classic example of allergic contact eczema.
This type of eczema differs from the other main type, atopic eczema. The latter is linked to atopy, a genetic condition, rather than a contact allergy. Atopy causes a hypersensitivity to the environment which may manifest in the skin, as eczema, or elsewhere in the body, as asthma for example.
In short, certain types of eczema are clearly linked to an allergy following direct contact with a product or object. Others are associated with a genetic hypersensitivity.
How Can An Allergist Help Eczema
An allergist may be able to help you identify triggers and recommend treatments to help manage your eczema.
Your allergist may perform a skin prick test or blood testing to help discover the allergens that are triggering your eczema. These tests can be used to help identify food, seasonal, or year-round allergies that may be contributing to your symptoms.
After identifying possible triggers, an allergist can prescribe medications to help manage symptoms.
Allergists can also offer immunotherapy, which is used to help build up the immune systems response to allergens.
There are seven types of eczema, and each has its own types of symptoms and triggers.
The different types of eczema include:
Recommended Reading: Does Zyrtec Help With Eczema