What Can Caregivers Do
When treating eczema, caregivers need to follow the treatment plan and try to reduce symptoms in the child. Equally, they should remain vigilant for any skin infections, monitor the childs condition, and schedule doctors appointments as necessary.
However, this can be stressful for caregivers. A 2020 study highlights that many experience sleep disturbance, exhaustion, worry, and social isolation relating to their childs atopic dermatitis. Following treatment regimens, coordinating appointments, and communicating with insurance can create time and financial pressures.
This highlights the need for caregivers to seek support and advice for both emotional and physical well-being.
Emollients And Fire Safety
Lotions, creams or ointments used to moisturise your childs skin are also known as emollients.
Emollients are very effective at treating chronic dry skin conditions, such as eczema.
But it is important to be aware of the fire risk linked with them.
Emollients won’t cause a fire on their own. But if there is a build-up of emollient residue on clothing and bedding, this can quicken the speed of a fire.
Do not smoke near your baby or allow them near naked flames:
- while they are wearing emollient
- if they are wearing clothes or bandages that may have emollient on them
There is a fire risk with all paraffin-containing emollients. There may also even be a fire risk with paraffin-free emollients. There might also be a fire risk with other products that you put on skin over large body areas for more than a few days.
Washing clothing or fabric at a high temperature may reduce emollient build-up. But it might not totally remove it.
How Is Eczema Treated
There is no cure for eczema. But treatments can help with symptoms. The doctor will recommend different treatments based on how severe the symptoms are, the child’s age, and where the rash is. Some are “topical” and applied to the skin. Others are taken by mouth.
Topical moisturizers. Skin should be moisturized often . The best time to apply moisturizer is after a bath or shower, with the skin patted dry gently. Ointments and creams are best because they contain a lot of oil. Lotions have too much water to be helpful.
Topical corticosteroids, also called cortisone or steroid creams or ointments. These ease skin inflammation. It’s important not to use a topical steroid prescribed for someone else. These creams and ointments vary in strength, and using the wrong strength in sensitive areas can damage the skin, especially in infants.
Other topical anti-inflammatory medicines. These include medicines that change the way the skin’s immune system reacts.
Medicine taken by mouth. These can include antihistamines to help itchy kids sleep better at night, antibiotics if a rash gets infected by bacteria, and corticosteroid pills or other medicines that suppress the immune system.
Other types of treatment can include:
- wet wraps: damp cloths placed on irritated areas of skin
- bleach baths: bathing in very diluted bleach solution
Don’t Miss: Get Rid Of Eczema Patches
Is Milk Or Food Allergy A Problem And Should I Make Any Changes To My Babys Diet
Dietary allergy can occur in any child usually between three months and two years of age. Babies with eczema have a slightly higher risk of allergy, but lots of babies with eczema have no milk or other food allergy.
A baby with an immediate allergic reaction may have a sudden flare of eczema, become very itchy or start to wheeze, while a baby with a delayed reaction is more likely to have colic, reflux, vomiting and reluctance to feed.
If you think your baby has a food allergy, keep a diary, note any reactions, and ask for a referral to a paediatric dermatologist or allergist.
The vast majority of food allergy is limited to nine food groups: milk, egg, peanut, soya, wheat, tree nuts, sesame, shellfish and kiwi. Diagnosing food allergy in children up to the age of three is based on a history of symptoms. Treatment involves avoiding the food and then gradually reintroducing it. The only exceptions are peanut and shellfish as these are lifelong allergies.
Whatever happens, dont change your babys diet unless youve been advised to by a healthcare professional, as this may affect your babys growth and development.
How Is Baby Eczema Treated
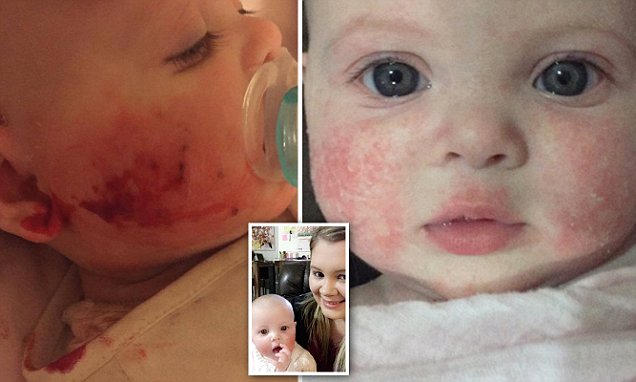
Treatment varies for baby eczema based on what caused your childs symptoms to flare up and the severity of their symptoms. Treatment for baby eczema could include:
- Eliminating or avoiding triggers: Avoid scented or fragranced soaps, lotions or detergents. These things can cause eczema to flare. Your provider might test your babys skin to identify if theyre allergic to certain things in their environment that they contact regularly. If youre able to identify what causes your babys eczema triggers, avoiding those causes helps your babys skin heal and prevents future eczema flare-ups.
- Using topical corticosteroids: These are prescription-strength ointments that you rub on your babys skin like a lotion. Corticosteroids help reduce itching and swelling. For mild eczema, apply topical OTC 1% hydrocortisone ointment twice a day for no longer than two weeks. For moderate to severe eczema, your healthcare provider may recommend prescription-strength steroid ointments. Any steroid ointment should not be applied for longer than two weeks since it may lead to discoloration by thinning out the skin.
- Applying moisturizer to your babys skin: Keeping your babys skin hydrated can reduce symptoms, soothe their skin, remove discomfort and prevent flare-ups. Choose moisturizers designed for babies and products that dont contain fragrances. The best time to apply moisturizers to your babys skin is after a bath and a couple of times throughout the day when their skin appears dry.
Read Also: 1 Month Old Baby Eczema On Face
When To Speak With A Doctor
It is advisable to speak with a doctor if symptoms become more severe or if it is difficult to manage the condition at home. If eczema is beginning to impact a childs everyday life, such as disrupting sleep or there are frequent infections from scratching their skin, a parent caregiver can consider contacting a doctor.
How Do I Get Rid Of Eczema
Your treatment for eczema is unique to you and what caused your symptoms to flare up. Treatment for eczema could include:
- Using gentle or sensitive skin moisturizers throughout the day when you have dry skin. Apply moisturizer when your skin is damp after a bath or shower.
- Apply topical medications to your skin as advised by your provider, like topical steroids.
- Take oral medications like anti-inflammatory medicines, antihistamines or corticosteroids to reduce itchiness and swelling.
- Immunosuppressant drugs help regulate how your immune system functions.
- Light therapy to improve the appearance of your skin and remove blemishes.
- Avoid triggers that cause symptoms of eczema to flare up.
Also Check: Does Heat Flare Up Eczema
Does Your Child Need To See A Doctor About Eczema
Yes. Take your child to see your GP if your child:
- might have eczema for the first time
- is very itchy and uncomfortable
- has eczema thats weeping or bleeding
- has eczema that hasnt improved much after a few days, even though youve been treating it as usual
- is having trouble sleeping because the rash is so itchy
- has painful or eczema that has developed pus
- has eczema and is generally unwell for example, has a fever and/or is sweating, feeding poorly or tired.
You should also take your child to the GP if youre not sure whether the rash is eczema.
If your childs eczema doesnt improve with a combination of medical treatment and management at home, your GP might refer your child to a dermatologist. If the GP thinks your childs eczema might be from allergies, they might also refer you to an allergy and immunology specialist.
Should I Worry About Using The Topical Steroids Prescribed By My Healthcare Professional
No, you dont need to worry, as long as you follow your healthcare professionals specific instructions. Topical steroids are first-line treatments for babies with eczema. These creams have been used to treat eczema for more than 50 years, so there is a good understanding of how they work.
If you dont treat the eczema promptly and adequately, skin damage is far more likely to occur through scratching into the deeper layers of skin.
Also Check: Good Face Cleanser For Eczema
What Does Baby Eczema Look Like
Eczema often appears on the face and scalp in infants under 6 months old. The rash will usually be red and it may bubble up, ooze fluid, then crust over. Older babies may develop eczema on their elbows and knees.
Eczema usually does not occur in the diaper area because the skin stays too moist. Rashes in this area are more likely diaper rash.
The itchiness of eczema can make an infant very uncomfortable. A baby cannot tell a caregiver what is wrong, but their behavior may hint that eczema is causing them discomfort.
Signs to look for include:
- Trouble sleeping
What Causes Atopic Dermatitis In A Child
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not known. But some things are linked to it. They include:
-
Genes. This skin problem can be passed on from parents to a child.
-
Immune system. An immune system that isnt fully developed may affect how much protection the skin can give.
-
External factors. These include being in winter weather, using hot water for bathing, using soap, and being in dry, hot temperatures.
Also Check: How Long Does Eczema Rash Last
How To Use It
People can buy aloe vera gel in health stores or online, or they can purchase an aloe vera plant and use the gel directly from its leaves.
Individuals should aim to use aloe gel products with few ingredients others can contain preservatives, alcohol, fragrances, and colors, which can irritate sensitive skin. Additionally, alcohol and other drying ingredients could make eczema worse.
However, start with a small amount of gel to check for skin sensitivity, as sometimes, aloe vera can cause burning or stinging. However, it is generally safe and effective for adults and children.
Causes Triggers And Risk Factors
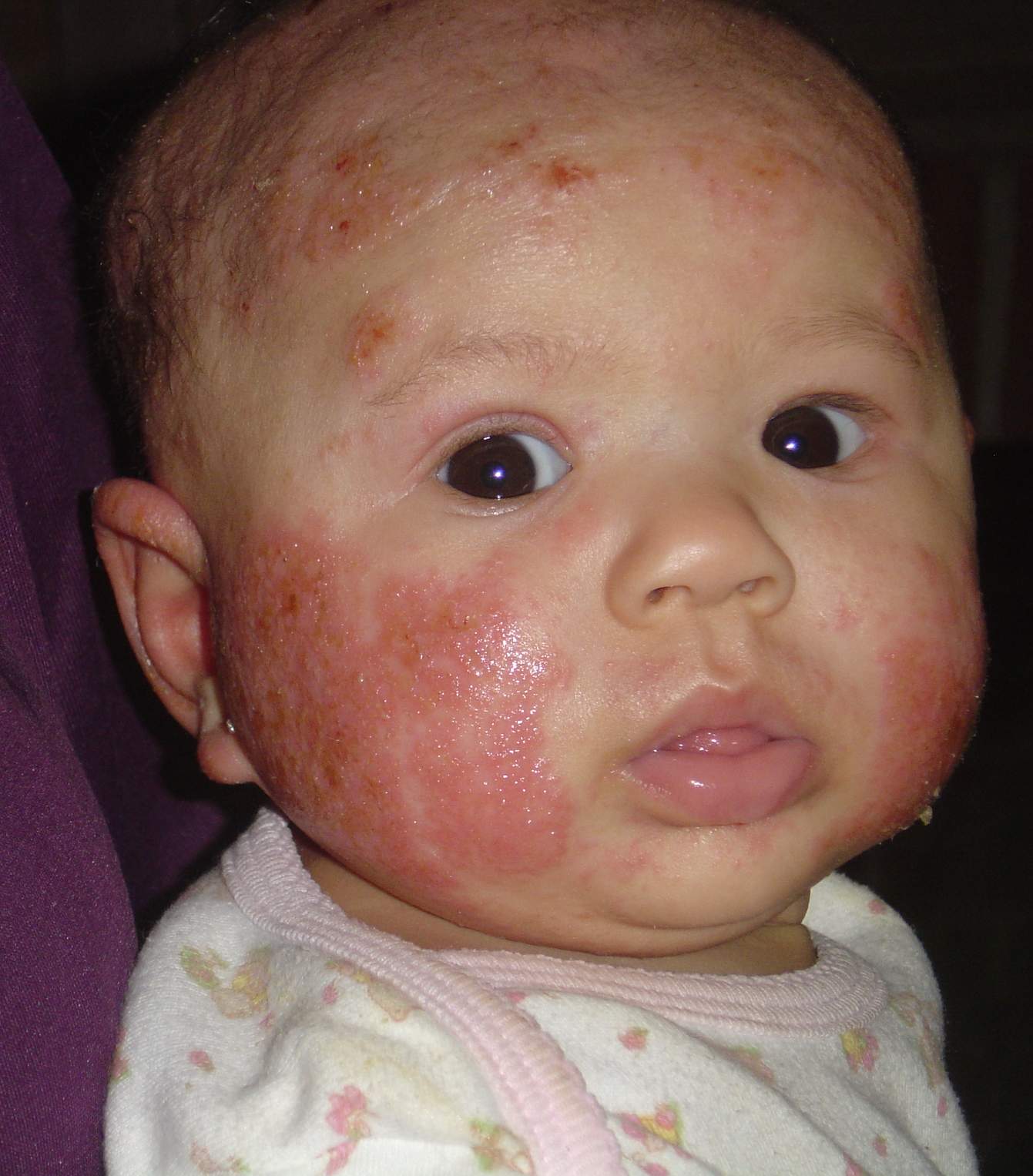
Researchers are still unsure of the exact cause of pediatric eczema. However, the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology suggests that it may result from the leakiness of the skin barrier. This can lead to the skin drying out, making it more prone to irritation and inflammation. Factors that can contribute to the development of eczema in children include :
- Genetics: Children with a family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma are more susceptible to developing eczema. Mutations in certain genes, such as CARD11 and FLG, also have associations with eczema.
- The immune system: A person may experience a flare of eczema when their immune system overreacts and causes an exaggerated response to a trigger.
- The environment: The envirome refers to potential triggers an individual may have exposure to, including pollutants, such as tobacco smoke, climate factors, such as temperature, and social factors, such as stress.
Evidence also highlights a link between allergies and eczema in younger children. Many experts refer to the progression of allergic conditions as the . It typically begins with atopic dermatitis and food allergies in infancy, then develops into allergic asthma and allergic rhinitis in childhood.
People with eczema are
When diagnosing eczema, doctors will likely ask about:
Currently, there is no cure for eczema, but the condition is manageable. Treatments typically involve keeping the skin moist and reducing inflammation. A treatment plan may include:
Recommended Reading: Calamine Lotion For Babies Eczema
Are There Complications From Eczema
Complications are possible with eczema and could include:
- Weeping eczema: Weeping eczema causes fluid-filled blisters to form on your skin.
- Infected eczema: Infected eczema occurs when bacteria, fungus or a virus breaks through your skin to cause an infection.
Symptoms that are a sign of complications include:
- Fever and chills.
- A clear to yellow fluid leaking out of blisters on your skin.
- Pain and swelling.
-
Learn about the best diet, home remedies, topical creams and more.
Is Baby Eczema Contagious
While eczema isn’t contagious, it can make your baby more prone to skin infections. The reason? People with eczema have less of the protein filaggrin in their skin. Normally filaggrin acts like a sentry maintaining a strong barrier to keep viruses and bacteria out, so with less of it, nasty germs can more easily sneak through, boosting the risk of infection. Plus, dry skin associated with baby eczema can crack, allowing bacteria, viruses, and other germs to get inside your little ones body.
Read Also: Eczema In Armpit And Groin
Questions To Ask Your Childs Doctor
After your child is diagnosed with atopic dermatitis, you may feel overwhelmed with information. It can be easy to lose track of the questions that occur to you.
Lots of parents find it helpful to jot down questions as they arise- that way, when you talk to your childs doctors you can be sure that all of your questions are answered. If your child is old enough, you may want to suggest that she writes down what she wants to ask her health care provider too.
- How could the medication or treatments interact with my childs current medication regiments?
- How could creams or ointments interact with other creams or sprays, such as suntan lotion or bug repellent?
- Are there any dietary restrictions my child needs to follow while taking atopic dermatitis medications?
- What treatments and medications are covered by my insurer?
- What are some things I can do to help my childs itching and scratching?
- How can I find out if any of the products, substances and foods around the house triggers my childs atopic dermatitis?
- How will atopic dermatitis impact my childs social life?
- What resources are available to help my child cope with the stress of having atopic dermatitis?
- How could atopic dermatitis impact my childs experience in the classroom?
- How will Childrens Hospital Boston coordinate with my childs school nurse to continue care at school?
Why Did My Toddler Develop Eczema
Similar to when babies develop eczema, children who develop eczema do so because of a combination of genes and environmental triggers, but researchers dont know a lot more about why eczema manifests on a childs skin. When something outside the body switches on the immune system, skin cells dont behave as they should causing eczema flare ups.
We also know that children who come from families with a history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to developatopic dermatitis.
Common eczema symptoms in children include itchiness, rashes and the breaking down of skin barriers that protect children from skin infections.
Prevention and treatment are often similar for toddlers and babies. No matter what age your child is, consult with a pediatrician or pediatricdermatologist before deciding on a treatment plan.
You May Like: Good Face Wash For Eczema
How Is Atopic Dermatitis Treated In A Child
Treatment will depend on your childs symptoms, age, and general health. It will also depend on how severe the condition is. There is no cure for atopic dermatitis. The goals of treatment are to ease itching and inflammation, add moisture, and prevent infection.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis includes:
-
Staying away from irritants, as advised by your child’s healthcare provider
-
Bathing with a gentle cleaner or body wash advised by the healthcare provider
-
Keeping your child’s fingernails short, to help prevent scratching that can cause skin irritation and infection
-
Using moisturizing lotion advised by the healthcare provider
Your child’s healthcare provider may also prescribe medicines. They may be used alone or together. The following are most commonly used to treat atopic dermatitis:
What To Do About Itching
Try to keep your baby from scratching their itchy skin. Scratching can make the rash worse, lead to an infection, and cause the irritated skin to get thicker and more leathery.
Trim their nails often, and then take the edge off of them with a file if you can. Some parents also slip “scratch mittens” onto their little one’s hands. Others try long socks, tucked in under a long-sleeved shirt, so they’re harder for a baby to remove. View a slideshow to get more eczema skin care tips.
Recommended Reading: How To Help An Eczema Flare Up
Seattle Children’s Urgent Care Locations
If your childâs illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.