Foods To Avoid In Babies And Toddlers With Eczema
Eczema can be a frustrating and uncomfortable issue to deal with.
It can be especially difficult to manage in infants and toddlers, as many factors can contribute to the severity of your childs symptoms.
In some cases, making changes to your childs diet can help reduce symptoms, and eliminating certain foods from their diet may even help prevent flare-ups.
Here are 7 foods to consider avoiding for babies and toddlers with eczema. Keep in mind that its always best to speak with a healthcare professional before eliminating foods from your childs diet.
How To Help Prevent Your Babys Eczema From Recurring
Always follow your healthcare providerâs advice on treating your baby’s eczema. Your provider may suggest taking the following steps to help prevent eczema from recurring or getting worse:
-
Bathe your baby no more than three times per week.
-
Keep bathtime to no more than 15 minutes.
-
Use only mild, unscented soaps.
-
After bathtime, moisturize your babyâs skin with a fragrance-free cream or an ointment such as petroleum jelly or one prescribed by your healthcare provider.
-
Moisturize your babyâs skin at least twice a day . Diaper changes can be a good time to do this.
-
Launder your babyâs clothes in mild, unscented detergent.
-
Dress him in soft clothing. Avoid wool or any rough woven fabrics.
-
To help protect your little oneâs skin, keep his nails clipped short so that he canât scratch himself. You could also slip cotton mittens on his hands before bedtime to help prevent him from scratching.
If your baby has eczema, it can look scary, but with care from your provider supplemented by effective at-home treatment, your little oneâs skin should improve in time. In the meantime, keep showering your little one with lots of love and kisses.
To earn rewards for all your Pampers purchases, including diapers and wipes, download the Pampers Rewards app today.
- See all sources
Identifying Baby Eczema On His Face And Body
So what does baby eczema look like? With eczema, your babyâs skin will look dry and scaly or bumpy with red patches. The condition usually starts on the face, especially on the cheeks, forehead, or scalp.
In many cases, the rash goes away on the face before spreading to other areas, such as the bends of the elbows and the area behind the knees.
The patches caused by eczema can be mild and small, but they can also be extremely itchy, which can make your baby irritable. If this is the case with your little one, speak to your healthcare provider.
Keep in mind that eczema on your babyâs head might look a little like cradle cap, which is another skin condition that can affect some babies. Your healthcare provider will be able to diagnose the condition.
Read Also: Is Yogurt Good For Eczema
How Is Atopic Dermatitis Diagnosed In A Child
The healthcare provider will ask about your childs symptoms and health history. He or she may also ask if you or other family members have atopic dermatitis, asthma, or nasal allergies such as hay fever or allergic rhinitis. He or she will also ask about allergy symptoms in your child. The healthcare provider will examine your child, looking for signs of atopic dermatitis. There is no specific test for atopic dermatitis. Testing is usually not needed, but it may be done. Tests may include:
-
Blood tests. Your childs blood may be checked for levels of immunoglobulin E . IgE is released by the body’s immune system. Its high in most children with allergies and with atopic dermatitis. Other blood tests may also be done.
-
Skin tests. Skin tests may be done to check for allergies or other skin conditions.
What Does Baby Eczema Look Like

Eczema doesn’t look the same on every baby. In babies with light skin, it usually shows up as patches of red skin. In darker-skinned babies, the rash might look purplish, brownish, or grayish. Eczema can be harder to see on babies with dark skin.
These patches are almost always dry, itchy, and rough.
Babies can get the condition just about anywhere on their body. Most often, it affects their cheeks and the joints of their arms and legs.
Its easy to confuse baby eczema with cradle cap. But there are some key differences.
Cradle cap is much less itchy and irritated. It generally clears up by age 8 months and usually appears on the scalp, sides of the nose, eyelids and eyebrows, and behind the ears. See a photo of what cradle cap looks like.
Also Check: Shea Moisture Eczema & Psoriasis Therapy African Black Soap
Adjust Your Shampoo Schedule
Shampooing your babys hair not only removes dirt and oil from their delicate strands, but it helps remove excess dirt and oil from their scalp, too. The amount of times you shampoo your babys scalp can vary based on their condition, though.
For cradle cap, shampooing daily can help remove oil and loosen the flakes on your babys scalp. All other causes of dry scalp may benefit from shampooing every other day to avoid excess dryness.
What Does It Look Like
The signs of eczema in infants include itchy, dry and scaly skin, redness and swelling of the skin and small bumps that open and weep when scratched. In infants and young children, eczema is usually found on the face, outside of the elbows, and on the knees.
In older children and adults, eczema tends to be on the hands and feet, the arms, and on the back of the knees.Keep in mind that all patches of dry skin are not eczema. The cold, dry outdoor air and indoor heating can dry all babies skin in winter, causing dry patches. In children prone to dry skin, so can the sun, air conditioning, and pool and salt water.
We dermatologists usually say if its not itchy, its not eczema you cant make a diagnosis of eczema unless there is an itchiness that goes with the rash. Babies with cradle cap, also known as seborrheic dermatitis, can also have a wide-spread rash, which is not eczema in itself. But it is common for cradle cap and eczema to co-exist in the first several months of life.
Also Check: Is Salicylic Acid Good For Eczema
Key Points About Atopic Dermatitis In Children
-
Atopic dermatitis is a long-term skin condition. It’s common in babies and children.
-
A child with allergies or family members with atopic dermatitis has a higher chance of having atopic dermatitis.
-
Itching, dryness, and redness are common symptoms.
-
The goals of treatment are to ease itching and inflammation of the skin, increase moisture, and prevent infection.
-
Staying away from triggers is important to manage the condition.
-
It usually gets better or goes away as a child gets older.
Why Is Nummular Eczema Difficult To Diagnose And How Is It Different Than Atopic Dermatitis
Nummular Eczema Symptoms, also known as Discoid Eczema and Nummular Dermatitis, is one of seven different types of the broader category called eczema. The other six types are Atopic Dermatitis, Contact Dermatitis, Hand Eczema, Dyshidrotic Eczema, NeuroDermatitis, and Stasis Dermatitis.
Nummular Eczema is a chronic condition that affects people of all ages including infants and young children. Nummular Eczema baby issues can be especially difficult and complex to treat and should be treated by a pediatric dermatologist that specializes in Nummular Eczema baby treatments. An outbreak, or flare-up, of Nummular Eczema has a very different physical appearance than other types of eczema with its round, coin-like lesions surrounded by red, inflamed skin on the hands, arms, legs and/or chest.
Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms start early in childhood and is characterized as extremely dry, scaly, rough skin with a rash of lightened and darkened skin spots. AD is categorized into three levels: mild, moderate and severe. Atopic Dermatitis rashes frequently appear in the creases of the elbows and/or the knees, rashes on the neck, face and around the eyes. Moderate to severe cases of Atopic Dermatitis can cover the entire body. Some children as young as newborn infants have AD rashes on their scalp and cheeks. Adults with AD often have discolored, leathery skin as a result of years of Atopic Dermatitis flare-ups that are easily irritated by what can be a long list of triggers.
Also Check: Is Eucerin Cream Good For Eczema
Why Did My Child Develop Eczema
The exact cause of eczema is unknown. Researchers do know that children who develop eczema do so because of a combination of genes and environmental triggers. When something outside the body switches on the immune system, skin cells dont behave as they should causing flare ups.
We also know that children who come from families with a history of atopic dermatitis, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis.
What Causes Eczema In Toddlers
Before you panic that your child will have lifelong bouts of itchy rashes, its important to remember that some kids are just prone to eczema because of their unique skin makeup. And even thats not always fixed or permanent.
Theres no way to predict what will happen in the future, but lots of kids outgrow their eczema when they reach their preschool years.
Your child is more likely to have eczema if they also have:
- a family history of eczema
- asthma
Food allergies dont cause eczema, but they are related.
According to a , other conditions that may be related to eczema may include attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder.
For the most part, though, environmental triggers are the biggest cause of eczema flares. Common triggers include:
- excessive heat or sweating
Although eczema is bothersome and often hard to treat, you can take some steps to get your toddlers eczema under control.
Don’t Miss: Best Baby Wash And Lotion For Eczema
How Is Eczema Treated
There is no cure for eczema. But treatments can help with symptoms. The doctor will recommend different treatments based on how severe the symptoms are, the child’s age, and where the rash is. Some are “topical” and applied to the skin. Others are taken by mouth.
Topical moisturizers. Skin should be moisturized often . The best time to apply moisturizer is after a bath or shower, with the skin patted dry gently. Ointments and creams are best because they contain a lot of oil. Lotions have too much water to be helpful.
Topical corticosteroids, also called cortisone or steroid creams or ointments. These ease skin inflammation. It’s important not to use a topical steroid prescribed for someone else. These creams and ointments vary in strength, and using the wrong strength in sensitive areas can damage the skin, especially in infants.
Other topical anti-inflammatory medicines. These include medicines that change the way the skin’s immune system reacts.
Medicine taken by mouth. These can include antihistamines to help itchy kids sleep better at night, antibiotics if a rash gets infected by bacteria, and corticosteroid pills or other medicines that suppress the immune system.
Other types of treatment can include:
- wet wraps: damp cloths placed on irritated areas of skin
- bleach baths: bathing in very diluted bleach solution
Managing Eczema In Winter And Year Round: A Parents Guide
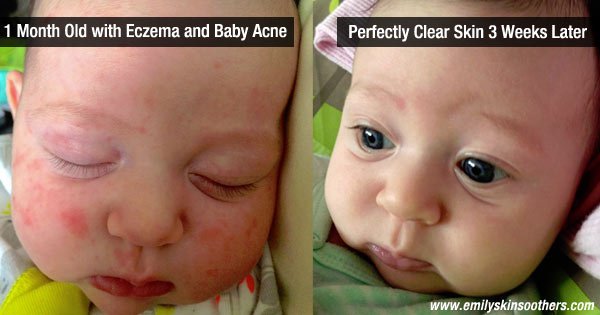
Cold, dry outdoor air and indoor heating can rob skin of its natural moisture in the winter. Red, crusty, dry patches can be common on a baby’s skin, particularly in winter, and cause concern for parents. Such symptoms can be treated, however, and many babies and children do outgrow the dry, itchy skin of atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema.
We spoke with pediatric dermatologist Katherine Puttgen to learn more.
Recommended Reading: How To Get Rid Of Eczema Scars On Babies
What Is Baby Eczema
Though it can occur at any age, eczema is a skin condition that’s common in children â about 10 percent of children get it. Itâs not contagious.
Baby eczema usually appears after your infant turns about 1 month old. Most children grow out of it between the ages of 2 and 3.
Itâs not always known why the condition affects some people and not others however, your infant might be more susceptible to eczema if certain conditions run in your family. These may include hay fever, asthma, food allergies, or environmental allergies.
Interestingly, about half of the children who had eczema develop hay fever or asthma in adulthood.
When To Talk To Your Doctor About Baby Eczema
Always talk with your pediatrician if you have any questions or concerns about your babys skin. Thanks to telemedicine, a video visit or quick photo is often all that’s needed to check for eczema.
Occasionally, infections develop on top of an eczema rash. If you see any yellow-colored crusting and scabbing, oozy skin, blisters or pus bumps, be sure to call your doctor right away. Always call if your baby has a fever. Your baby may need an antibiotic and to be evaluated in person.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Get Eczema In Your Ear
Does Your Child Need To See A Doctor About Eczema
Yes. Take your child to see your GP if your child:
- might have eczema for the first time
- is very itchy and uncomfortable
- has eczema thats weeping or bleeding
- has eczema that hasnt improved much after a few days, even though youve been treating it as usual
- is having trouble sleeping because the rash is so itchy
- has painful or eczema that has developed pus
- has eczema and is generally unwell for example, has a fever and/or is sweating, feeding poorly or tired.
You should also take your child to the GP if youre not sure whether the rash is eczema.
If your childs eczema doesnt improve with a combination of medical treatment and management at home, your GP might refer your child to a dermatologist. If the GP thinks your childs eczema might be from allergies, they might also refer you to an allergy and immunology specialist.
Clothes That Work For Him
Buying organic clothes can be very expensive. To cut down on costs, I conducted an elimination test of various nonorganic brands. I introduced a particular nonorganic brand of clothing into Ethan’s clothing rotation for four days if no reactions appeared, it was a safe bet that all clothing from this nonorganic brand was safe for his skin.
Brands that Work for Ethan: Carter’s and Baby Gap
Also Check: How Do You Get Rid Of Dark Spots From Eczema
How Common And Who Gets Atopic Dermatitis
Many think of Atopic Dermatitis as common eczema because it affects the most number of people globally. According to the National Eczema Association, about 31 million people have eczema in the US and of that, 17.8 million people have Atopic Dermatitis. It usually starts in childhood, with approximately 60% of the people affected experience symptoms getting milder or completely goes away by adulthood. According to the American Academy of Dermatology , 90% of people with AD get it before age 5. Its rare that somebody will be diagnosed with AD if they didnt have it as a child. There seems to be a genetic component to AD as people with AD typically have a family member affected by AD, allergies, or asthma. People dealing with Atopic Dermatitis frequently also have asthma and hay fever and many people with Atopic Dermatitis have all three conditions.
There are five additional types of eczema besidesNummular Dermatitis and Atopic Dermatitis.
Does Your Baby Have Eczema
Our babies inherit a lot from us: our height, our hair color — and our tendency toward sensitive skin, including eczema.
If someone in your immediate family has allergic tendencies, eczema may be the first sign that your baby shares that tendency, too, says pediatrician Chris Tolcher, MD, clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of Southern California School of Medicine.
Eczema can start as early as your baby’s second month. Symptoms can be mild and barely noticeable, or itchy and intense. Know the signs of baby eczema, how to treat it, and what eczema treatments to avoid.
You May Like: Dyshidrotic Eczema And Rheumatoid Arthritis
Emollients And Fire Safety
Lotions, creams or ointments used to moisturise your childs skin are also known as emollients.
Emollients are very effective at treating chronic dry skin conditions, such as eczema.
But it is important to be aware of the fire risk linked with them.
Emollients won’t cause a fire on their own. But if there is a build-up of emollient residue on clothing and bedding, this can quicken the speed of a fire.
Do not smoke near your baby or allow them near naked flames:
- while they are wearing emollient
- if they are wearing clothes or bandages that may have emollient on them
There is a fire risk with all paraffin-containing emollients. There may also even be a fire risk with paraffin-free emollients. There might also be a fire risk with other products that you put on skin over large body areas for more than a few days.
Washing clothing or fabric at a high temperature may reduce emollient build-up. But it might not totally remove it.
Does Breastfeeding Prevent Baby Eczema

There is some evidence that breastfed babies may be less likely to develop eczema. Although unproven, the antimicrobial properties in breast milk have also been studied as a type of treatment when directly applied to an eczema rash. To try this, rub a few drops of your liquid gold onto the rash regularly for a few days and watch for any reduction in symptoms.
Read Also: Medical Description Of Eczema Rash