What Causes Eczema In Babies
Eczema is caused by the inheritance of specific predisposing genes. Eczema tends to run in families with a predisposition to other atopic diseases like asthma, food allergies, and hay fever.
Children with eczema are likely to have filaggrin deficiency. Filaggrin is a protein that plays an essential role in the skin’s barrier function and hydration. It acts by binding the structural proteins in the outermost skin cells to form tight bundles and strengthening them to create a strong barrier.
Moreover, the processing of filaggrin protein leads to the production of molecules that form part of the skin’s natural moisturizing factor, keeping the skin hydrated. These molecules also help maintain the skin’s pH level, which is an essential aspect of the barrier.
The Connection Between Weather & Skin
The skin acts as a barrier to protect the body from outside elements. Healthy skin offers protection from winter cold and summer heat. When an individual has eczema, the protective barrier fails to work as it should. Moisture leaks from the skin, which causes it to dry out and become more irritated. The weather also affects eczema when wind causes pollen in the air to be blown onto the skin. For people who are allergic, the winter season exposes them to various eczema triggers. The infant skin fails to work at the optimum level due to adverse weather.
How Often Should I Bathe My Baby
If your baby has eczema, a daily bath with an emollient will help soothe the eczema and reduce dry skin and itching, while cleansing the skin, removing dirt and repairing the skin barrier. Use leave-on emollients instead of soaps, baby washes or bubble bath, or alternatively use emollient wash products or bath additives. Avoid any perfumed products and keep the water tepid, as heat can aggravate eczema.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Eczema Without Medication
Hipp Comfort Formula For The Management Of Eczema
HiPP Comfort is meant specifically for children who struggle with colic and constipation. About 40% of infants experience unspecific indigestion such as wind, colic, and constipation in the first months of life. Symptoms of unspecific digestion include excessive crying and discomfort. HiPP Comfort is made to help prevent and soothe these symptoms. HiPP Comfort contains partially hydrolyzed protein, fats that have a unique structure mimicking the fatty acids in breast milk, and reduced lactose content. This makes it easier to digest and more easily absorbed by the body.
Both HiPP HA and HiPP Comfort contain DHA and Arachidonic Acid . These are fatty acids that are essential for brain development, promote eye health, proper functioning of the heart, and reduce inflammation.
HiPP formulas are developed to mimic the structure and composition of human breast milk as much as possible. These formulas contain all the nutrients required by law, omega 3 and 6 fatty acids, human milk prebiotics, and probiotics, and are appropriately low in protein content, just like breast milk. Prebiotics and probiotics are responsible for developing positive gut microbiota that promotes the maturation of the immune system and helps protect infants from infections.
What Does Baby Eczema Look Like

Eczema often appears on the face and scalp in infants under 6 months old. The rash will usually be red and it may bubble up, ooze fluid, then crust over. Older babies may develop eczema on their elbows and knees.
Eczema usually does not occur in the diaper area because the skin stays too moist. Rashes in this area are more likely diaper rash.
The itchiness of eczema can make an infant very uncomfortable. A baby cannot tell a caregiver what is wrong, but their behavior may hint that eczema is causing them discomfort.
Signs to look for include:
- Trouble sleeping
You May Like: Is Mango Butter Good For Eczema
When To Call A Doctor
Make the call if your babyâs eczema doesnât begin to get better within a week of starting over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams. It may be time for a prescription medicine.
Also check with your doctor if yellow or light brown crust or pus-filled blisters appear on top of the eczema. This could be the sign of a bacterial infection that needs antibiotics.
You should call your doctor if your baby is around anyone who has cold sores or genital herpes. Eczema can make your little one more likely to pick up those germs.
Show Sources
How Can I Prevent Baby Eczema
Since several factors can cause eczema in your baby, theres no way to completely prevent the condition. You can help your baby reduce their risk of developing a flare-up of symptoms by:
- Avoiding triggers, irritants and allergens.
- Using moisturizer on your babys skin daily.
- Giving your baby baths with warm, not hot, water that is between five to 10 minutes long.
- Choosing moisturizers or ointments without fragrance, designed for babies.
Don’t Miss: What’s The Difference Between Rosacea And Eczema
Does Breast Milk Help Eczema
Breast milk is amazing!
For generations, moms have used their milk to treat various skin problems. However, the scientific community has recently been studying the powers of breast milk a bit more closely, and theyve discovered some promising results using breast milk on eczema.
In fact, preliminary studies suggest that breast milk may help improve eczema symptoms. If you want to try this natural remedy, apply some of your milk to a cotton ball. Then, apply it to the eczema patches on your babys skin.
When To Speak With A Doctor
A person should see their doctor if they suspect they have a skin infection. This is particularly true when the infection develops in an area where their eczema tends to flare up.
If a person has noticed their eczema has worsened or is no longer responding to their usual treatment, they may benefit from speaking with a doctor or dermatologist.
A dermatologist can help a person identify the type of eczema they have and prescribe treatments that may be more effective. They can also refer someone for diagnostic tests, such as allergy testing, if necessary.
If a rash appears suddenly, spreads quickly, or shows signs of infection, see a doctor as soon as possible.
Recommended Reading: Is Pool Water Good For Eczema
Outlook For People With Eczema
Eczema is a chronic disease, so you will likely always have flares. You can help control it by learning to avoid triggers, treating it as your healthcare provider recommends, and keeping your skin well-moisturized.
Eczema can make you more prone to skin damage, infections, or scars. It can also be harder to control if it started when you were very young, other people in your family have it, or it’s severe.
How Reducing Indoor Allergens Can Ease Your Eczema Symptoms
Eczema usually isnt a persistent condition, but rather one marked by long symptom-free periods followed by flare-ups.
Various environmental factors may cause the immune system to respond as if the body has encountered a harmful substance, resulting in inflammation and worsening eczema symptoms.
- Pet dander, pollen, mold, and dust mites
- Allergenic foods
- Clothing made of wool or synthetic fibers
- Cigarette smoke
Theres no cure for baby eczema, but the condition usually becomes less severe over time.
Treatment focuses on managing skin dryness to prevent flare-ups and on reducing skin inflammation.
Don’t Miss: Types Of Eczema On Fingers
The Difference Between Child And Adult Eczema
There is very little difference between child eczema and adult eczema. The main difference is the frequency with which flare-ups occur. As your child grows older, their skin becomes thicker and less sensitive. And with the right ongoing treatment, the occurrence of eczema flare-ups can be reduced.
So now that you know a bit about eczema, what causes flare-ups, and the difference between baby, child, and adult eczema, lets turn our attention to treatment and prevention.
Can Atopic Eczema Be Cured
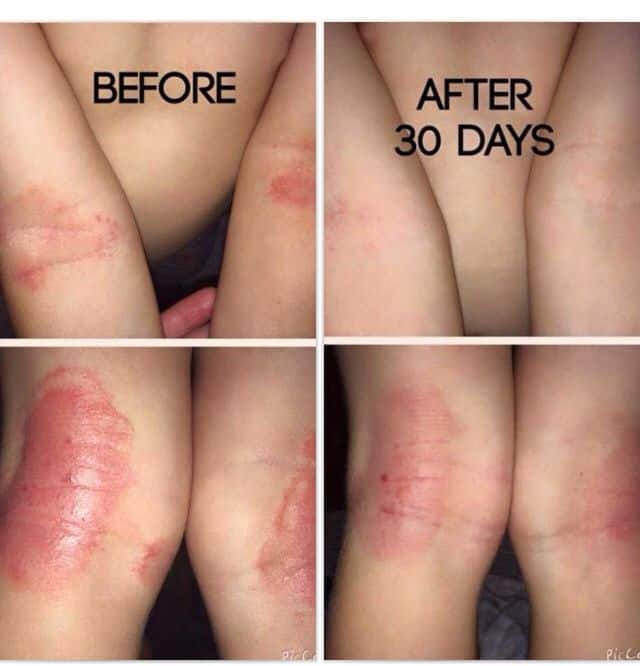
The bad news is that atopic eczema cannot be cured but there are many ways of controlling it. Most children with atopic eczema improve as they get older . However, many of those who have had eczema continue to have dry skin and need to avoid irritants such as soaps or bubble baths. Eczema may persist in adults but it should be controllable with the right treatment.
You can help reduce your childs discomfort by:
- keeping their fingernails short to reduce the damage to their skin from scratching
- washing them with aqueous cream instead of soap ask your pharmacist about aqueous creams and always follow the instructions on the product
- using non-biological detergent and a double rinse cycle when washing their clothes or bedding
- avoiding herbal, natural or alternative creams these can make eczema worse, as they may contain bacteria or high doses of steroids
- rinsing and drying them well after swimming
- dressing them in cool, breathable fabrics like cotton
- keeping them away from anyone with a cold sore as the cold sore virus can cause eczema to become infected
- using extra moisturiser on areas your child scratches a lot
- avoiding anything you know that causes your childs eczema to get worse
Around 6 out of 10 children with eczema will grow out of it by the time theyre teenagers.
You May Like: Is Calendula Good For Eczema
How To Find A Food Trigger
Some are obvious. If your child eats lobster for the first time and breaks out in hives 15 minutes later, itâs probably not hard to figure out.
But with eczema, its often tougher. Symptoms may not show up for days after you eat something. If you do find a trigger food and get rid of it, that may help. Still, it may not make the eczema go away. Remember, 2 out of 3 kids with eczema dont have a food allergy at all.
Thats why working with a doctor is so important. They can guide you toward the real cause through tests like:
Elimination diets. If your doctor thinks a food may be harmful, they may ask you not to give it to your kid for 10 to 14 days. Watch to see if it makes a difference.
Food challenges. After youve taken a food out of your childs diet, your pediatrician might want you to add a small amount back in to see if it causes symptoms. They may want to do this in the office, just in case your child has a reaction.
Skin testing. A doctor can take an extract of the food and use it to scratch the skin lightly. If the area swells up, that could be an allergic reaction. However, its not always accurate.
Blood tests. RAST a radioallergosorbent test can check for special cells in the blood that signal specific food allergies. Again, its not always accurate. Other lab tests can check for cells that trigger swelling.
Tracking down a food trigger can take patience and detective work.
Show Sources
When To See A Doctor
While you can do a lot to control your babys eczema, sometimes you have to seek medical attention. Look out for the following signs and see a doctor if any of these occur.
- Unresponsiveness to over-the-counter medications. There are a lot of over-the-counter creams available that can sooth eczema. These ointments are very good at treating eczema for your baby. If they arent working, however, you should see a doctor to get prescription medicine instead.
- Changes in responsiveness to prescription medicine. Just because one medicine is working today doesnt mean it will always work. If you have prescription medication for your babys eczema and you see it doesnt work as well as it previously did to control symptoms, its time to reevaluate the medicine. Your doctor will be able to examine your baby and see if another medicine will be better.
- Appearance of yellow crust on the eczema patches. Yellow crust indicates that there may be a bacterial infection. This needs to be checked out immediately by a doctor because if it goes untreated, it will get worse. Your doctor will be able to determine if antibiotics should be prescribed to stop the infection.
- Development of pus-filled blisters on the eczema patches. Blisters are also a sign that there may be an infection. They are also very painful and a sign that the eczema isnt being managed adequately. A doctor can evaluate your management plan and make adjustments, so you can better control your childs eczema symptoms.
Also Check: Eczema Shampoo For African American Hair
Emollients And Fire Safety
Lotions, creams or ointments used to moisturise your childs skin are also known as emollients.
Emollients are very effective at treating chronic dry skin conditions, such as eczema.
But it is important to be aware of the fire risk linked with them.
Emollients wont cause a fire on their own. But if there is a build-up of emollient residue on clothing and bedding, this can quicken the speed of a fire.
Do not smoke near your baby or allow them near naked flames:
- while they are wearing emollient
- if they are wearing clothes or bandages that may have emollient on them
There is a fire risk with all paraffin-containing emollients. There may also even be a fire risk with paraffin-free emollients. There might also be a fire risk with other products that you put on skin over large body areas for more than a few days.
Washing clothing or fabric at a high temperature may reduce emollient build-up. But it might not totally remove it.
Recommended Reading: Vitamin E Oil For Eczema
Does Baby Eczema Go Away On Its Own
Baby eczema needs treatment to go away completely. The best treatment is using moisturizer daily or several times each day to keep your babys skin hydrated.
Most cases of baby eczema clear up by the time they start school, around age 4 or 5. Sometimes eczema can go away or reduce in severity as your child reaches adolescence or by the time they turn into adults. As your child grows, they may have sensitive skin or flare-ups of eczema symptoms throughout their life.
Recommended Reading: Dyshidrotic Eczema Over The Counter Treatment
Managing Eczema In Winter And Year Round: A Parents Guide
Cold, dry outdoor air and indoor heating can rob skin of its natural moisture in the winter. Red, crusty, dry patches can be common on a baby’s skin, particularly in winter, and cause concern for parents. Such symptoms can be treated, however, and many babies and children do outgrow the dry, itchy skin of atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema.
We spoke with pediatric dermatologist Katherine Puttgen to learn more.
Causes Of Atopic Eczema
The exact cause of atopic eczema is unknown, but it’s clear it is not down to one single thing.
Atopic eczema often occurs in people who get allergies. “Atopic” means sensitivity to allergens.
It can run in families, and often develops alongside other conditions, such as asthma and hay fever.
The symptoms of atopic eczema often have certain triggers, such as soaps, detergents, stress and the weather.
Sometimes food allergies can play a part, especially in young children with severe eczema.
You may be asked to keep a food diary to try to determine whether a specific food makes your symptoms worse.
Allergy tests are not usually needed, although they’re sometimes helpful in identifying whether a food allergy may be triggering symptoms.
Read Also: Tips For Eczema On Hands
How Is Eczema Treated
There is no cure for eczema. But treatments can help with symptoms. The doctor will recommend different treatments based on how severe the symptoms are, the child’s age, and where the rash is. Some are “topical” and applied to the skin. Others are taken by mouth.
Topical moisturizers. Skin should be moisturized often . The best time to apply moisturizer is after a bath or shower, with the skin patted dry gently. Ointments and creams are best because they contain a lot of oil. Lotions have too much water to be helpful.
Topical corticosteroids, also called cortisone or steroid creams or ointments. These ease skin inflammation. It’s important not to use a topical steroid prescribed for someone else. These creams and ointments vary in strength, and using the wrong strength in sensitive areas can damage the skin, especially in infants.
Other topical anti-inflammatory medicines. These include medicines that change the way the skin’s immune system reacts.
Medicine taken by mouth. These can include antihistamines to help itchy kids sleep better at night, antibiotics if a rash gets infected by bacteria, and corticosteroid pills or other medicines that suppress the immune system.
Other types of treatment can include:
- wet wraps: damp cloths placed on irritated areas of skin
- bleach baths: bathing in very diluted bleach solution
How To Prevent Flares

While there is no medication currently available that cures eczema, there are a few ways to prevent and treat flares.
First, knowing your personal eczema triggers can help you make informed choices around diet and activities. Keeping a journal may help you connect certain foods, weather, products, or activities to flares.
Moisturizing your skin as much as possible can also help, as can bathing after exercising or other high-energy activities.
If your eczema is more severe, your doctor may have prescribed topical and/or immunosuppressant medications to reduce itching. Using these medicines as prescribed can help prevent eczema flares.
Read Also: How To Treat Mild Eczema
Foods That Cause Eczema Flare
Eczema is a skin condition that causes inflammation and a number of uncomfortable issues. The way that kids eat can affect how bad their case of eczema is and whether or not they experience a flare-up after eating.
It is important for parents to know what they should and should not feed their kids so that they can help those kids deal with the least eczema issues possible.
1. Eggs Can Cause Eczema Issues
There are certain foods that can cause allergies in kids, and the allergies that a kid faces can lead to eczema issues. Eggs are one of the foods that are considered to be an allergy risk, and those who have kids who are dealing with eczema may want to cut eggs out of the diet of those kids.
2. Cows Milk Probably Should be Avoided
Just as eggs are a common allergen when it comes to kids, cows milk is another food that can cause issues. It is important for a person to monitor whether or not their child and their eczema symptoms seem to be affected by the intake of cows milk. If a kid is bothered by cows milk, there are milk alternatives out there that a parent can use to replace this beverage.
3. Yogurt And Other Foods Made of Dairy Can Cause Eczema
Products that are made from cows milk can cause issues for kids in the same way that plain cows milk can. It is important for parents to cut dairy products out of the diet of any kids who are faced with eczema and its symptoms.
4. Fish Can Be An Issue For Some Who Have Eczema
5. Nuts Can Cause Eczema Issues