Eczema Coping Tips Diet
In most cases, eczema isnt caused or made worse by diet. If you notice that your eczema seems to get worse after eating a particular food, you may be an exception to this. See your doctor or dietitian for proper allergy testing and dietary advice.Never self-diagnose or you risk depriving yourself of enjoyable and nutritious foods for no good reason. Unnecessarily avoiding certain foods can lead to nutritional deficiencies.
Does Histamine Cause Itch In Eczema
Histamine is not a mediator of itch in atopic dermatitis, but its role remains controversial. In atopic dermatitis, it has been found that nerve fibers that transmit itch both peripherally and centrally are histamine insensitive. These peripheral nerve fibers have been found to be mechanically sensitive but unresponsive to histamine. It is thought that these specific nerve fibers may be more clinically relevant to atopic dermatitis itch rather than those nerve fibers that are histamine sensitive. This is the reason why even high doses of antihistamine do not relieve itch, unless they are centrally sedating antihistamines. Therefore sedating antihistamines are probably the only ones that help itch in eczema that does not have a urticarial component .
Skin conditions that cause an eczematous reaction including urticaria are histamine mediated, as are insect-bite reactions and allergic drug reactions. Histamine directly stimulates histamine type 1 receptors on itch-specific nerve fibers. This is why for these conditions antihistamines taken in tablet form are the mainstay of treatment. several types of antihistamine drugs may be prescribed. Treatment generally starts with non-sedating H1 antihistamines , but there are several other treatment options available.
Other Types Of Eczema
Eczema is the name for a group of skin conditions that cause dry, irritated skin.
Other types of eczema include:
- discoid eczema a type of eczema that occurs in circular or oval patches on the skin
- contact dermatitis a type of eczema that occurs when the body comes into contact with a particular substance
- varicose eczema a type of eczema that most often affects the lower legs and is caused by problems with the flow of blood through the leg veins
- seborrhoeic eczema a type of eczema where red, scaly patches develop on the sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears and scalp
- dyshidrotic eczema a type of eczema that causes tiny blisters to erupt across the palms of the hands
Page last reviewed: 05 December 2019 Next review due: 05 December 2022
Recommended Reading: Does Coconut Oil Work For Eczema
What Is Eczema What Does It Look And Feel Like
Eczema is a condition that causes your skin to become dry, red, itchy and bumpy. Its one of many types of dermatitis. Eczema damages the skin barrier function . This loss of barrier function makes your skin more sensitive and more prone to infection and dryness.
Eczema doesnt harm your body. It doesnt mean that your skin is dirty or infected, and its not contagious. There are treatments that can help manage your symptoms.
In the word dermatitis, derm means skin and itis means inflammation. The word as a whole means inflammation of the skin. Eczema originates from the Greek word ekzein which means to boil over or break out.
When To Talk With Your Doctor
Any eczema flare-up that doesnt respond to your current treatment plan or home remedies should be evaluated by a doctor. They may also refer you to a dermatologist, a type of doctor that specializes in skin and hair diseases. An allergist or immunologist may also help.
Talk with your doctor if your eczema rashes are unusually painful or if youve developed any skin infections as a result of scratching. You should also see them if your eczema itch keeps you up at night and inhibits your ability to get good sleep.
Recommended Reading: Can Lyme Disease Cause Eczema
The Epidermis As The Itch Receptor Unit
The epidermis consists of keratinocyte cells, which are constantly reproducing then moving upward and being shed as dead skin cells. In addition to keratinocytes, the epidermis contains nerve receptors and chemical mediators, which also appear to be involved with the sensation of itch. One theory concerns nerve endings in the epidermis, as it is thought that an itch sensation is generated through nerve receptors adjacent to the keratinocyte cells. specific nerve receptors for itch have not yet been identified in the epidermis. However, scientific experiments have shown that if the epidermis is removed, itch is abolished. This proves that itch must generate from the epidermis. In addition, itch is uniquely restricted to the skin, mucous membranes and the cornea of the eye, where there are epidermal layers. No other body tissue experiences itch.
When To Seek Medical Advice
See a GP if you have symptoms of atopic eczema. They’ll usually be able to diagnose atopic eczema by looking at your skin and asking questions, such as:
- whether the rash is itchy and where it appears
- when the symptoms first began
- whether it comes and goes over time
- whether there’s a history of atopic eczema in your family
- whether you have any other conditions, such as allergies or asthma
- whether something in your diet or lifestyle may be contributing to your symptoms
Typically, to be diagnosed with atopic eczema you should have had an itchy skin condition in the last 12 months and 3 or more of the following:
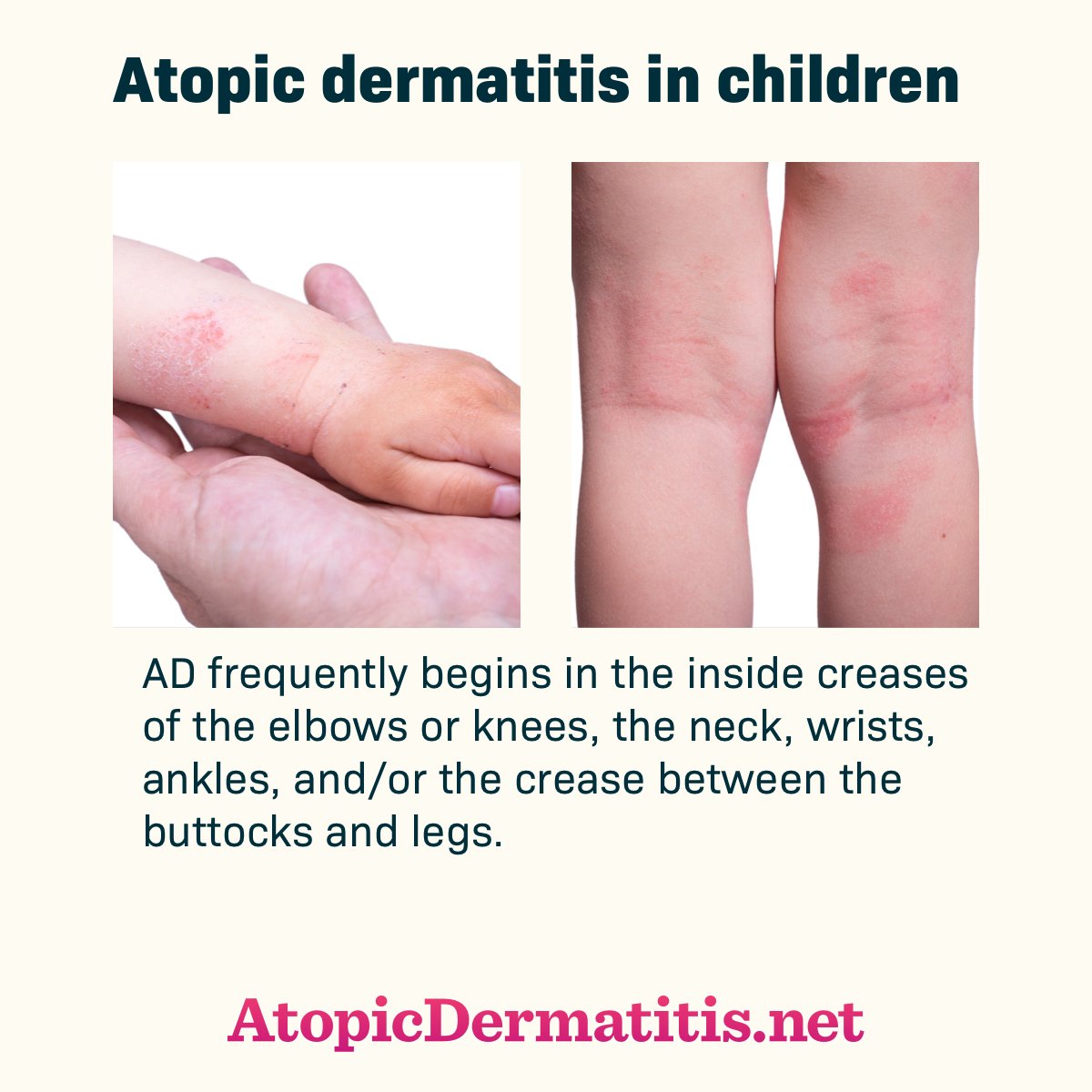
- visibly irritated red skin in the creases of your skin such as the insides of your elbows or behind your knees at the time of examination by a health professional
- a history of skin irritation occurring in the same areas mentioned above
- generally dry skin in the last 12 months
- a history of asthma or hay fever children under 4 must have an immediate relative, such as a parent, brother or sister, who has 1 of these conditions
- the condition started before the age of 2
Also Check: Best Body Wash To Use For Eczema
Prevent Skin Damage Caused By Scratching
Constant scratching can break the skin. To prevent bleeding and an infection, dermatologists recommend the following:
Keep your child’s nails short: Checking nails after your child’s bath lets you know when the nails need trimming.
Cover itchy skin: When skin is covered, children seem less likely to scratch. When dressing your child, be sure to:
Dress your child in lose-fitting clothes made from a soft, natural fiber-like cotton, a cotton blend, silk, or bamboo.
Consider using eczema mittens and eczema sleeves.
Eczema mittens can be effective when eczema flares on your baby’s face. Your baby may still scratch, but the scratching will cause less damage because the fingernails cannot dig into the skin.
Itch relief can be fickle
You may find that a technique works one day and not the next. If one technique fails, try another.
Related AAD resources
ReferencesEichenfield, LF, Tom WL, et al. Part 2: Guidelines of care for the management and treatment of atopic dermatitis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Jul 71:116-32.
Sidbury R, Tom WL, et al. Part 4: Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis. Part 4: Prevention of disease flares and use of adjunctive therapies and approaches. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014: 71 1218-33.
All content solely developed by the American Academy of Dermatology
The Itchy Dozen Worst Foods For Eczema
People are often surprised to find the Itchy Dozen includes some of the so-called ‘good’ foods for eczema. I know the Itchy Dozen contradicts some popular beliefs published in online blogs. However, according to Australian research conducted over the past thirty years, these foods could be the reason your skin is dry, flaky and incredibly itchy .
I’ve seen this information help hundreds of so called ‘hopeless’ cases of eczema. People who have had eczema for 20, 30 or 40 years and more, who thought they were stuck with eczema for life, are seeing their eczema clear up for the first time. It can really change lives but it requires a change in beliefs about healthy eating. This quote sums it up:
“One man’s medicine is another man’s sleepless night itching.”
So a food that is good for an eczema-free person, such as avocado, could trigger a bout of maddening itching in another person.
Not counting allergy foods , here are the surprising foods and beverages most likely to give you itchy eczema …
1. Dairy products
Dairy products, including cows milk, yoghurt, butter and cheese, are the second most common allergy food seen in eczema sufferers .
- Yoghurt is particularly bad for eczema as it often contains added sugar, fruit flavourings, amines and a natural colour called Annatto which can trigger eczema.
Calcium deficiency can cause eczema
If you are itchy, one heaped scoop of Skin Friend PM mixed into water or food will quickly calm down the itch.
2. Grapes
Read Also: Can Baby Formula Cause Eczema
How You Can Treat Eczema Itch
Soaking in an oatmeal bath may help alleviate eczema itch and discomfort. Use store-bought colloidal oatmeal and run it under lukewarm water. You may soak in the bath for 10 to 15 minutes at a time. Cool compresses can also help when applied throughout the day.
Applying a fragrance-free moisturizer can alleviate itchiness, but it may also help protect the skin barrier and ward off flare-ups. You can apply moisturizer throughout the day as needed. Its important to use a skin moisturizer within a few minutes of bathing or swimming to lock in moisture immediately.
While these methods can help treat short-term eczema itching, youll also want to learn to manage long-term eczema itching. An effective eczema treatment plan is one that focuses on long-term management, not just treating flare-ups.
In the case of moderate to severe eczema, your doctor may recommend medications or other treatments. These may include a combination of:
- over-the-counter or prescription emollient creams
- topical corticosteroids
- dupilumab injections
Besides moisturizers and medications, you may be able to manage eczema and alleviate itchiness by making some simple lifestyle changes. Consider trying one or more of the following home remedies:
Complications Of Itchy Skin
It’s quite common to find that after you have scratched an itch that it becomes more persistent and you get into a cycle of itching and scratching. This can be painful and can sometimes lead to an infection if the skin is broken.
The scratching can also lead to brown or pale marks on the skin, lumps, bruising or scarring.
Recommended Reading: Why Am I Getting Eczema On My Face
How To Prevent Eczema From The Inside Out
Here are two ways to treat your eczema naturally:
12-week low chemical diet
The Eczema Detox is a healthy low chemical diet that is low in sugar and totally free of glutamates/MSG, preservatives/additives and dairy. It also has plenty of gluten-free and vegan options.
The Eczema Detox, which was published in 2018 and is the new version of The Eczema Diet, also shows you how to successfully diagnose food intolerances and chemical intolerances , so you know what to avoid and what to eat to become eczema free.
Skin friendly supplements
There are a range of nutrients to help prevent chemical sensitivity and repair eczema-prone skin, including magnesium, molybdenum, zinc, biotin, vitamin B6 and a range of vitamins to deactivate salicylates and other itch-promoting chemicals. Molybdenum deactivates sulphite preservatives and amines anti-histamine vitamin C and vitamin B6 to help reduce allergic reactions .
But it’s also what you avoid that can make a difference… Supplements usually contain hidden additives that can cause adverse reactions if you are a sensitive type of person that is prone to eczema.
Skin Friend AM is the supplement I created to prevent my daughter’s eczema more than fifteen years ago. It took years of testing before I felt confident that it could help others, and I worked with hundreds of eczema patients who tried the product and provided feedback for years before this product was manufactured in bulk and sold online.
Use A Moisturizer On Your Skin Every Day
Moisturizers help keep your skin soft and flexible. They prevent skin cracks. A plain moisturizer is best. Avoid moisturizers with fragrances and a lot of extra ingredients. A good, cheap moisturizer is plain petroleum jelly . Use moisturizers that are more greasy than creamy because creams usually have more preservatives in them.
Regular use of a moisturizer can help prevent the dry skin that is common in winter.
Also Check: Does Taking Collagen Help Eczema
Eczema Affects Everyone Differently
Eczema affects everyone differently. One persons triggers may not be the same as anothers. You might experience eczema symptoms at certain times of the year or on different areas of your body.
Symptoms of eczema are as varied as the potential environmental factors that can lead to irritation: everyone is affected by this skin disease differently. Regardless of vaccine status, Covid-19 is also a potential trigger for eczema, possibly due to the stress of recovering from the virus, or the bodys heightened immune system response to the virus.
Use Emergency Itch Creams
I like to call them that way because it makes sense. I personally use Greenridges Chickweed Gel. Its completely natural and busts the itch almost right away.
But try not to use this method every time or else youll be too dependent on it.
Remember, dont use itch creams that are filled with chemicals only use natural products, preferably with herbs with cooling properties like Mentholatum.
Read Also: How To Stop Dyshidrotic Eczema From Spreading
How Is Eczema Treated What Medications Are Used
Treating eczema can be difficult if the cause is something you cant control, like genetics. Fortunately, you may have some influence over your environment and stress levels. Do your best to figure out what triggers or worsens your eczema, and then avoid it. The goal is to reduce itching and discomfort and prevent infection and additional flare-ups.
Consider these treatment tips:
If your child has skin problems, such as eczema, you can:
- Avoid long, hot baths, which can dry the skin. Use lukewarm water instead and give your child sponge baths.
- Apply lotion immediately after bathing while the skin is still moist. This will help trap moisture in the skin.
- Keep the room temperature as regular as possible. Changes in room temperature and humidity can dry the skin.
- Keep your child dressed in cotton. Wool, silk and manmade fabrics such as polyester can irritate the skin.
- Use mild laundry soap and make sure that clothes are well rinsed.
- Watch for skin infections. Contact your healthcare provider if you notice an infection.
- Help them avoid rubbing or scratching the rash.
- Use moisturizers several times daily. In infants with eczema, moisturizing on a regular basis is extremely helpful.
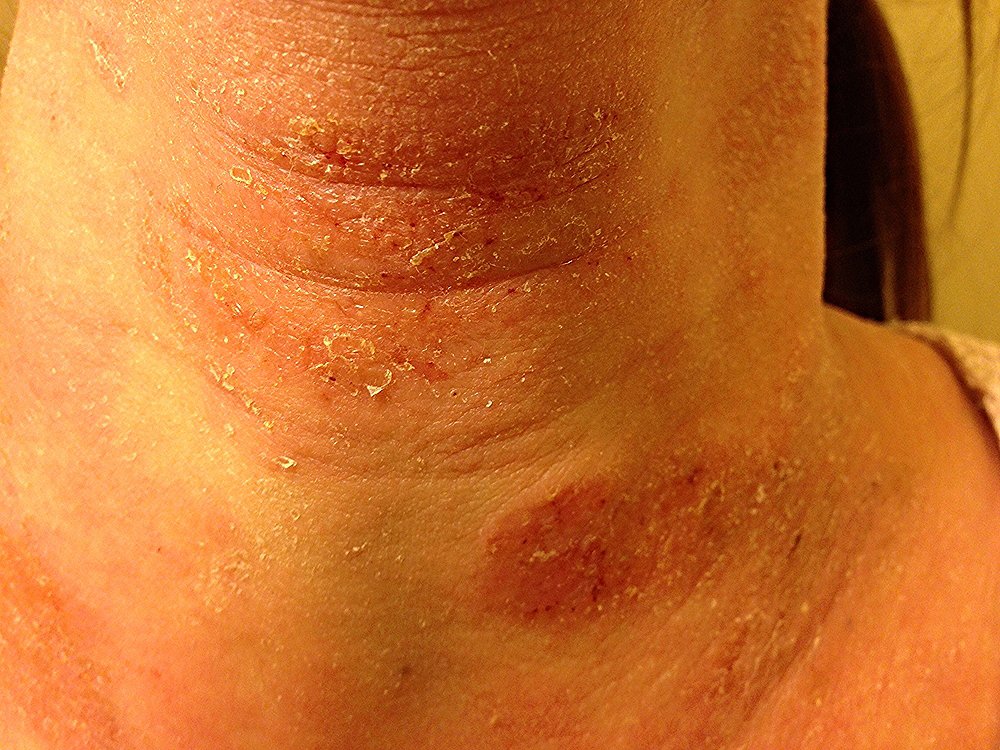
Similarities Between Ad In Adults And Children
While AD tends to change how it looks and where it appears as we age, there are still many similarities between having AD as an adult and as a child.
The list of similarities often includes that AD can:
-
Appear anywhere on the skin
-
Be intensely itchy
-
Cause sleep loss due to the itch
-
Make you feel depressed, anxious, or both
-
Lead to skin infections
ImageUsed with permission of the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. J Am Acad Dermatol 2001 44:89-93.
ReferencesEichenfield LF, Tom WL, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of atopic dermatitis. Section 1. Diagnosis and assessment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 70:338-51.
Ellis CN, Mancini AJ, et al. Understanding and managing atopic dermatitis in adult patients. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2012 31:S18-22
Kanwar AJ. Adult-onset atopic dermatitis. Indian J Dermatol. 2016 Nov-Dec 61: 6623.
Kim JP, Chao LX, et al. Persistence of atopic dermatitis : A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 75:681-7.
Silverberg JI, Vakharia PP, et al. Phenotypical differences of childhood- and adult-onset atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2017 Nov 10. pii: S2213-219830757-2.
All content solely developed by the American Academy of Dermatology
The American Academy of Dermatology gratefully acknowledges the support from Leo Pharma, Inc., and Sanofi and Regeneron.
Also Check: What Makes Eczema Go Away Fast
What Happens When A Person Scratches Eczema
People experiencing a flare-up of eczema often experience an itch-scratch cycle. This is when a person is itchy, and they scratch their eczema, which causes more inflammatory mediators to release, which in turn causes more itchy dry skin. The dry skin leads to more itching, and so the cycle continues.
Scratching, not eczema itself, is one of the main causes of skin damage. Scratching can lead to painful, red skin, which may break and bleed.
If a persons skin breaks, they are at higher risk for infection. Broken skin also makes it easier for irritants and allergens, such as dust and pet dander, to enter the skin barrier and cause eczema to flare.
Scratching can also cause the skin to become thick and leathery through a process called lichenification, which may cause changes to skin color. It may take weeks or months for the skin to return to its typical appearance.
Some people with eczema may have itchy lumps that may become thick and dark if they scratch them. This is called nodular prurigo. If this occurs in someone with a darker skin tone, there is an increased risk of the skin areas having permanent discoloration.
Scratching can also lead to scarring in the skin.
The best way to stop skin damage with eczema is to stop scratching. A person may be better able to help prevent scratching by treating or taking steps to help prevent the itch.
A person may help prevent flare-ups in a variety of ways, including:
Quality Of Life And Itching
Itching is a constant problem for people with eczema. MyEczemaTeam members often describe their frustrations with this pervasive symptom.
- It’s 3:30 a.m. and I’m trying to stop itching. Most of my itching is at nighttime.
- Itching like crazy!
- Can I please go a day without itching?
Watch Dr. Brian Kim explain how itching can affect sleep and quality of life.
I think that most patients come in actually having suffered for years, said Dr. Kim. He explained that doctors often get a very narrow snapshot of someones eczema because they may come in on a good day.
Dr. Kim added that some people with eczema may be so accustomed to symptoms like itching that they may not let their doctors know how bad they are feeling. I think thats where we get it wrong, he said. I think the thing that’s important to understand, for me as a provider, is that if youve never had a disease-free life, your expectations are incredibly low.
You May Like: La Roche Posay Lipikar Eczema