Emollients And Fire Safety
Lotions, creams or ointments used to moisturise your childs skin are also known as emollients.
Emollients are very effective at treating chronic dry skin conditions, such as eczema.
But it is important to be aware of the fire risk linked with them.
Emollients won’t cause a fire on their own. But if there is a build-up of emollient residue on clothing and bedding, this can quicken the speed of a fire.
Do not smoke near your baby or allow them near naked flames:
- while they are wearing emollient
- if they are wearing clothes or bandages that may have emollient on them
There is a fire risk with all paraffin-containing emollients. There may also even be a fire risk with paraffin-free emollients. There might also be a fire risk with other products that you put on skin over large body areas for more than a few days.
Washing clothing or fabric at a high temperature may reduce emollient build-up. But it might not totally remove it.
What To Do About Itching
Try to keep your baby from scratching their itchy skin. Scratching can make the rash worse, lead to an infection, and cause the irritated skin to get thicker and more leathery.
Trim their nails often, and then take the edge off of them with a file if you can. Some parents also slip “scratch mittens” onto their little one’s hands. Others try long socks, tucked in under a long-sleeved shirt, so they’re harder for a baby to remove. View a slideshow to get more eczema skin care tips.
What Causes Eczema In Infants And Children
Eczema is brought about by the complex interplay of a genetic predisposition and the childs environment. Many things from the climate to possible allergens can cause eczema to flare. We know that eczema tends to run in the families with a predisposition to other atopic diseases, such as food allergies, asthma and hay fever. Individuals with atopic dermatitis may lack certain proteins in the skin, which leads to greater sensitivity. Parents with eczema are more likely to have children with eczema. However, the exact way it passes from parents to children is still not known. Most children who have eczema will show signs of the condition in the first year of life. It tends to wax and wane in severity.
Also Check: Eczema On Child’s Face
What Does Eczema Look Like
In babies with paler skin, when eczema is flaring the skin is red and itchy. In babies with darker skin, the irritated, itchy areas may be red but are more likely to show as darker patches. They may also appear paler around the front or back of knees or elbows.
When an area of darker skin is treated for eczema, it may become lighter and may take several months to return to the babys normal skin tone.
Does Your Child Need To See A Doctor About Eczema
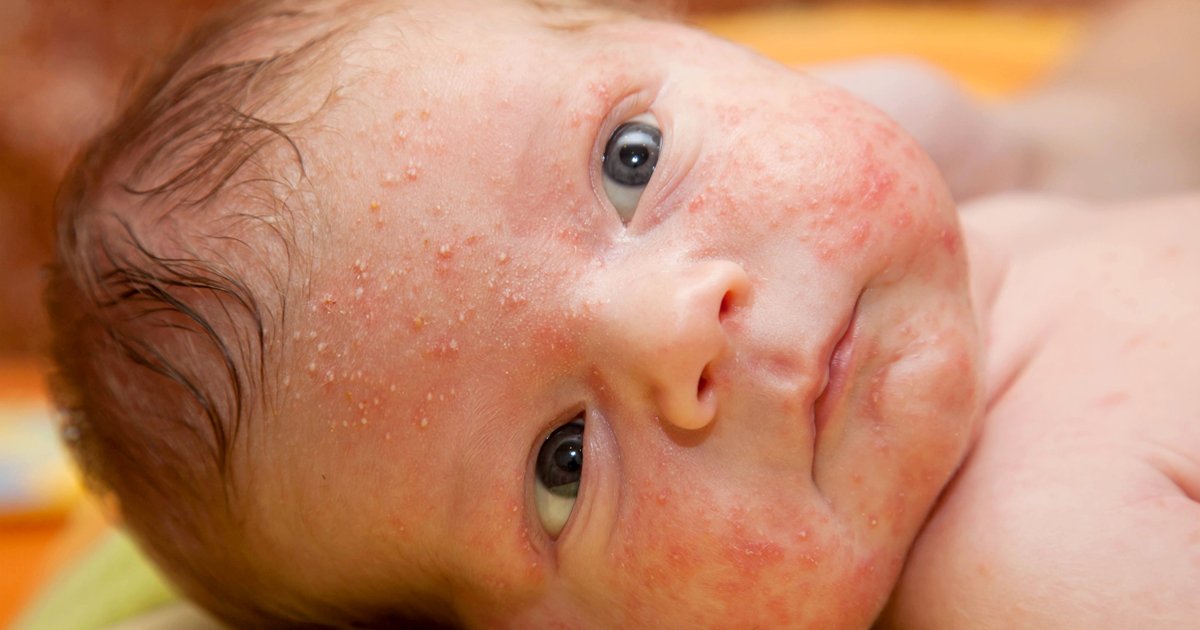
Yes. Take your child to see your GP if your child:
- might have eczema for the first time
- is very itchy and uncomfortable
- has eczema thats weeping or bleeding
- has eczema that hasnt improved much after a few days, even though youve been treating it as usual
- is having trouble sleeping because the rash is so itchy
- has painful or eczema that has developed pus
- has eczema and is generally unwell for example, has a fever and/or is sweating, feeding poorly or tired.
You should also take your child to the GP if youre not sure whether the rash is eczema.
If your childs eczema doesnt improve with a combination of medical treatment and management at home, your GP might refer your child to a dermatologist. If the GP thinks your childs eczema might be from allergies, they might also refer you to an allergy and immunology specialist.
You May Like: Is Epsom Salt Good For Eczema
Why Did My Child Develop Eczema
The exact cause of eczema is unknown. Researchers do know that children who develop eczema do so because of a combination of genes and environmental triggers. When something outside the body switches on the immune system, skin cells dont behave as they should causing flare ups.
We also know that children who come from families with a history of atopic dermatitis, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis.
Can Food Allergy Cause Eczema
Although food allergy is more common in children who have eczema, they are separate conditions.
Food allergy does not normally cause eczema, but having eczema may increase the chance that a food allergy develops. For a description of how eczema may increase the risk of food allergy, please refer to the section on the next page called: How can good eczema control help prevent food allergy?
Also Check: What Milk Is Good For Eczema
Managing Eczema In Winter And Year Round: A Parents Guide
Cold, dry outdoor air and indoor heating can rob skin of its natural moisture in the winter. Red, crusty, dry patches can be common on a baby’s skin, particularly in winter, and cause concern for parents. Such symptoms can be treated, however, and many babies and children do outgrow the dry, itchy skin of atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema.
We spoke with pediatric dermatologist Katherine Puttgen to learn more.
Evidence At A Glance On Childhood Eczema
The NIHR has invested significant research activity into identifying treatment options for childhood eczema that are helpful, and those that are probably ineffective. Whilst there is no cure, treatments aim to sooth sore skin, reduce itching, or prevent infection. The main types of treatment are moisturisers and topical corticosteroids. These can be onerous to apply so parents and children are keen to search for other things that might work for eczema NIHR research is helping.
You May Like: Best Natural Cure For Eczema
Key Points About Atopic Dermatitis In Children
-
Atopic dermatitis is a long-term skin condition. It’s common in babies and children.
-
A child with allergies or family members with atopic dermatitis has a higher chance of having atopic dermatitis.
-
Itching, dryness, and redness are common symptoms.
-
The goals of treatment are to ease itching and inflammation of the skin, increase moisture, and prevent infection.
-
Staying away from triggers is important to manage the condition.
-
It usually gets better or goes away as a child gets older.
What Triggers My Childs Eczema Or Causes It To Get Worse
Some of the most common eczema triggers include:
Even your babys stuffed animals may be a trigger for eczema
- Dry skin
- Infection
- Allergens such as pet dander, pollen or dust
Your childs eczema may be worse in the winter when the air is dry. Saliva from drooling can also cause irritation on your babys cheeks, chin and neck.
The best way to manage your childs eczema is by getting to know their symptoms and triggers so that you can help keep it under control.
Read Also: Best Bar Soap For Eczema
Ways To Prevent Baby Eczema
Eczema itself cannot be prevented, but knowing and avoiding triggers can help prevent flare-ups of the condition.
Some ways to reduce triggers include:
- Keep your child out of cold, dry air.
- If they are 6 months or older, make sure your child gets an annual flu shot.
- Read labels on products to help your family avoid common irritants.
- Double-rinse your laundry to remove detergent residue.
It Goes Away And Comes Back
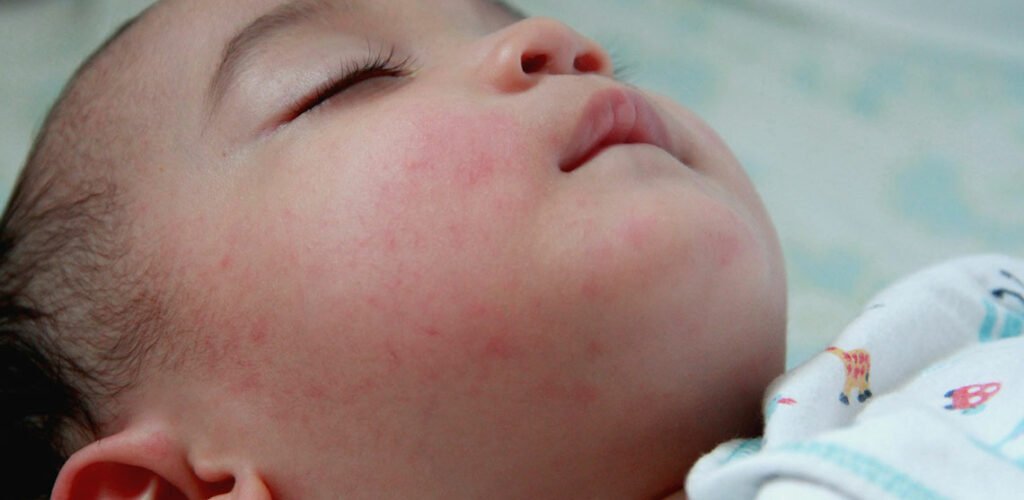
Most skin rashes go away within a few days or weeks, but eczema goes away for a short period of time and then reappears. Everyday elements in the environment like smoke, pollen, pet dander and fragrances can cause eczema to flare up.
The best way to prevent eczema flare ups is to use a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer at least twice a day over your childs entire body.
Also Check: How To Use Aloe Vera Gel For Eczema
What Causes Eczema In Children
Researchers dont know exactly what causes baby eczema, but they believe its most likely due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Eczema is not contagious.
Infants are more likely to develop eczema if family members have a history of eczema, hay fever, or asthma.
While these conditions don’t cause one another, infants are more likely to develop hay fever or asthma if they already have baby eczema.
Scientists believe eczema results from an immune-system dysfunction that affects the skin barrier and its ability to hold in moisture.
Eczema is a general term to describe a number of inflammatory skin conditions. Aside from atopic dermatitis, other types of eczema that commonly affect children include contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema , and seborrheic dermatitis, or scalp eczema .
Breastfeeding May Reduce Eczema Risk
For years, findings from studies indicated that breastfeeding had no effect on whether a child developed AD. Recently, thats changed.
Findings from one study suggest that breastfeeding may help newborns at high risk of developing AD.
A child has a high risk of developing AD when a parent, brother, or sister has one or more of the following diseases:
-
Atopic dermatitis
-
Asthma
-
Hay fever
In this study, breastfeeding a high-risk newborn reduced the childs chance of developing AD by 33%. Researchers also discovered that breastfeeding a child with a high risk of developing AD may protect the child from getting severe AD.
According to this study, the childs risk was lower when mothers:
-
Breastfed for 4 to 6 months
-
Began weaning at 4 to 5 months
The findings also suggest that for the babys first 4 months of life, a mother should breastfeed only. No solid foods should be given during this time. The risk of developing AD was higher when babies were fed solid foods before 4 months of age.
Breastfeeding and AD risk: Bottom line
Results from studies differ. If your child has a high risk of developing AD, breastfeeding for the first 4 months may reduce your childs risk. Breastfeeding also has many other health benefits.
Don’t Miss: Best Way To Treat Eczema On Baby
What Are The Differences Between The Skin Symptoms Of Food Allergy And Eczema
An allergic reaction to a food typically happens quickly. Symptoms of an allergic reaction then go away, usually after several hours, as long as the food is not eaten again. Eczema is a chronic condition that does not go away quickly. Eczema tends to show up in predictable places, such as on the cheeks of young babies or elbow creases of older children. The places on the skin where symptoms of an allergic reaction to food appear are more unpredictable. Hives, redness and itching from an allergic reaction can show up just about anywhere on the body and even in different places each time the food is eaten.
Baby Eczema Risk Factors And The Environment
While baby eczema is the result of immune-system dysfunction, likely from a genetic predisposition, studies have found a number of risk factors.
For example, a study published in February 2018 in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health suggested that children have a higher risk of developing eczema if their mothers experienced high-stress situations during pregnancy.
In a study published in May 2018 in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, researchers in the United Kingdom analyzed the sociodemographic characteristics of about 675,000 children in a primary-care database. They found that the children were more likely to be diagnosed with eczema if they fit one of the following descriptions:
- Male
- Black Caribbean
- Of high socioeconomic status
Another study, published in May 2018 in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, looked at how the outdoor environment specifically air pollutants and meteorological conditions affected eczema risk in children of both sexes. The researchers concluded that high levels of carbon monoxide, ammonia, formaldehyde, lead, particulate matter, and ozone levels may all influence the development of infantile eczema.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Oozing Eczema
Did My Baby Develop Eczema Because I Couldnt Breastfeed
As eczema is caused by genetic factors, bottle-feeding a baby definitely cannot cause eczema. In fact, current research is divided, with some studies showing positive effects of breastfeeding and others showing no significant effects at all.
Neither is there enough evidence to advise pregnant or breastfeeding women to avoid specific foods to protect unborn children from atopic eczema or any other atopic condition.
How To Tell If Your Child Has Eczema
Is it just a rash, or is it a more serious skin condition? Dermatologist Dr. Anna Kirkorian shares four ways you can spot signs of eczema on your child.
Kids get skin rashes from time to time, so when your little one has red patches on their face, how do you know if its eczema or another skin condition such as heat rash, acne or hives? Dermatologist Dr. Anna Kirkorian shares four ways you can spot signs of eczema on your child.
Read Also: Eczema On One Side Of Body
What Causes Atopic Dermatitis In A Child
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not known. But some things are linked to it. They include:
-
Genes. This skin problem can be passed on from parents to a child.
-
Immune system. An immune system that isnt fully developed may affect how much protection the skin can give.
-
External factors. These include being in winter weather, using hot water for bathing, using soap, and being in dry, hot temperatures.
How Can You Help A Toddler With Their Eczema
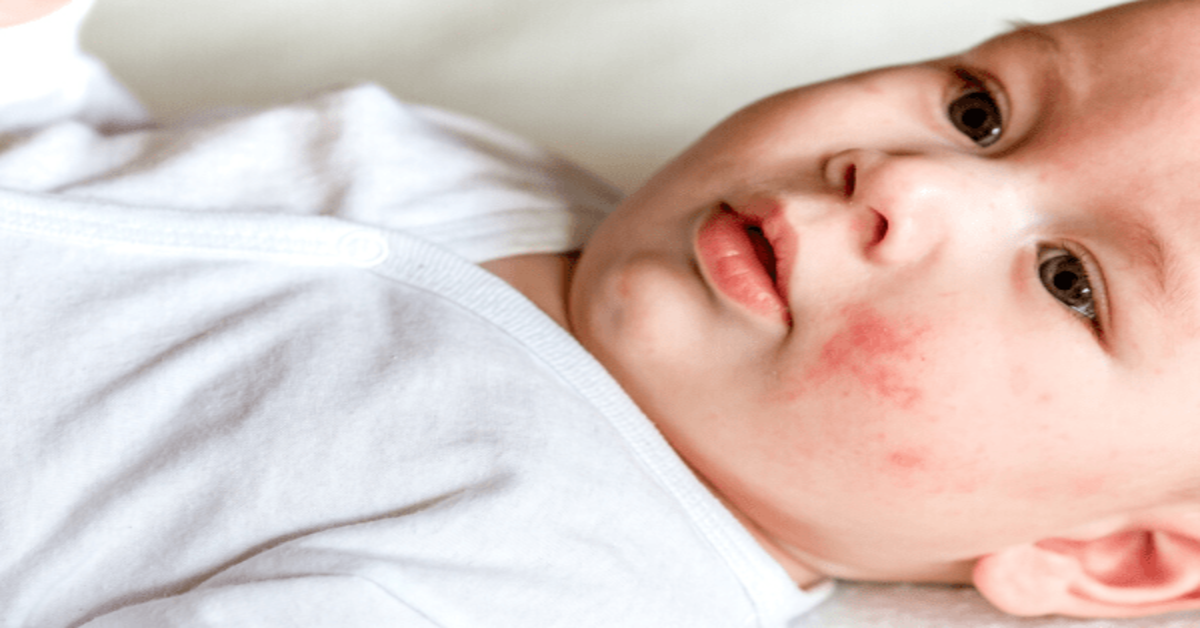
Helping your toddler deal with the itch can go a long way in helping them manage their eczema. When you notice your toddler scratching, distract them with another activity, particularly one that keeps their hands busy, like coloring.
You can also try wet wrapping the affected skin to help alleviate the itch and keep little hands from getting at the rash.
Wet wrapping involves wrapping the skin with a cloth or bandage dressing thats first moistened with warm water. When the wrap is in place, apply a dry cloth or dressing over the wet one.
Clothing can act as another barrier between your child and their eczema. If your child has eczema around their elbows, dress them in long sleeves when possible. If its on their legs, try long pants.
Read Also: Is Sauna Good For Eczema
When To See A Doctor
If your eczema is causing you a lot of trouble itching, flaking, bleeding or if its making you feel stressed, depressed, or If your child has itchy swelling, externally or internally, then see a doctor.
Ask your doctor about prescription medications. If too much medicine is not enough, your doctor may prescribe strong medicine for your child.
Your doctor may give you a strong immunosuppressant, e.g. Prescribe strong topical corticosteroids or other creams, or oral medications.
However, the latter is rarely used. Your doctor may also recommend alternatives such as anti-inflammatory drugs.
Follow your doctors advice, as he or she will most likely know what your childs help will be.
Why Is It Important To Control My Child’s Eczema
When eczema is not well controlled, it can affect a child’s quality of life and health. It increases the chance of skin infections, and it can also be painful. Itching and scratching can be distressing for your child and for you as a parent to watch. Physical comfort, sleep, social interactions and self-image can all be affected. Good control allows your child to feel well and stay focused on childhood activities such as learning and playing.
Some new research shows there may be an additional benefit to keeping eczema under good control. Good control might help prevent food allergy. This is especially good news for parents who have babies and toddlers who are at increased risk for food allergy.
Also Check: How To Calm Eczema On Hands
What Causes Eczema In Toddlers
Before you panic that your child will have lifelong bouts of itchy rashes, its important to remember that some kids are just prone to eczema because of their unique skin makeup. And even thats not always fixed or permanent.
Theres no way to predict what will happen in the future, but lots of kids outgrow their eczema when they reach their preschool years.
Your child is more likely to have eczema if they also have:
- a family history of eczema
- asthma
Food allergies dont cause eczema, but they are related.
According to a , other conditions that may be related to eczema may include attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder.
For the most part, though, environmental triggers are the biggest cause of eczema flares. Common triggers include:
- excessive heat or sweating
Although eczema is bothersome and often hard to treat, you can take some steps to get your toddlers eczema under control.
Treating Eczema With Antibiotics
Secondary infections with bacteria like Staphylococcus Aureus can makethe babys eczema much worse.
Infected eczema is usually treated with topical antibiotic ointmentslike Bactroban or Fucidin. Dermol 500 Lotion is an antimicrobial emollient andmoisturizer used to care for dry and pruritic skin conditions likeeczema and dermatitis, and for use as a soap substitute.
However, if the infection is more severe, your child feels unwell or has a fever, a course of oral antibiotics is usually necessary to clear the infection. All creams and ointments used during the infection are likely contaminated with bacteria. In this case, buying moisturizers with a pump is the best way to avoid contamination.
Also Check: How Do You Cure Eczema
Don’t Miss: Why Does Eczema Come And Go
Tips For Dealing With Babys Eczema
Parents often invest time in a day to day routines of their child and when a child has eczema, dealing with eczema also becomes a daily routine. School or surroundings will expose your child to many aggravators of their eczema. Along with that, Its obvious that your kid will definitely start to notice that not everybody has a skin disease and not all are troubled with eczema/atopic dermatitis.
Here are a few ideas you can do to boost up your childs health and confidence:
1. Praise and Communicate:
As a parent you always want your little one to stay cheerful and sound. A little talk from your side can help your understand eczema. Whether its about their interests, gaming, school, friends or something else, prepping your child about certain social situations will help them ease into the environment. Its important that your child may understand his/her condition and should also know that eczema is not a communicable disease. Applaud them while they are doing great as kids are more dynamic to positive attitude from his/her friends and family that can do wonders in enhancing the fearlessness. Attempt to make them flawlessly agreeable in their own particular skin.
2. Encourage your child to express emotions:
3. Focus on childs capabilities:
4. Give time to your Kids:
5. Address Carefully: