What Are Common Triggers
Atopic eczema is aggravated by different factors depending on the individual, but common triggers include cold, dry weather, stress, hot water and harsh soaps, says Anderson. In the winter, cold outdoor temperatures and indoor heating make for an irritating combination. Most people with eczema get better in the summer as the temperature and humidity levels tend to be higher, leaving the skin more moist, says Anderson.
As for contact eczema, Anderson says skin will flare up whenever its touched by an irritating substance, regardless of the season.
When Eczema Is Under Control
Its important to continue treatment once the eczema is under control. Many parents find that they can control eczema by:
-
Keeping their childs skin hydrated
-
Finding out what triggers the eczema and helping their child avoid these triggers
Even with daily care, eczema can flare. Common eczema triggers like stress or a change in the weather can cause a flare. When your childs skin flares, medicine may be necessary. For children who have eczema that flares frequently, applying a low-dose medicine to the skin a few times per week can reduce flares.
Following your dermatologists treatment plan is worthwhile. It helps to control eczema and make your child feel better. It can also reduce your childs need for medicine.
Additional related content
What Kind Of Products Are Best Avoided
There are several products that can act as irritants and worsen eczema, so are important to avoid where possible to maximise treatment benefits. Air pollution itself can irritate dry skin and bring on inflammation. Whilst this can be difficult to avoid in busy cities, there are some everyday products that can be substituted to avoid additional irritation. Many soaps, cleansing and beauty products are alcohol based or contain chemicals and fragrances that dry out the skin. These are best avoided and substituted with mild, non-soap cleansers or an emollient-based soap or shampoo. It is also helpful to wear protective gloves when using household cleaning products to avoid direct contact.
Recommended Reading: Is Cetaphil Lotion Good For Eczema
What Foods Should I Eat Or Avoid To Reduce My Risk Of Eczema
The connection between eczema and food allergies is unclear. If you have food allergies, then one of the reasons why you must avoid that food is that it may cause or worsen dermatitis. Examples of common allergies include peanuts, dairy, eggs, sugar, alcohol and gluten. Pay attention to what you eat. If your eczema flares up after you eat a certain food, then you might have an allergy to it.
If you dont have a food allergy then there are no foods, including chicken, that will cause or worsen your eczema.
Who Gets Atopic Dermatitis
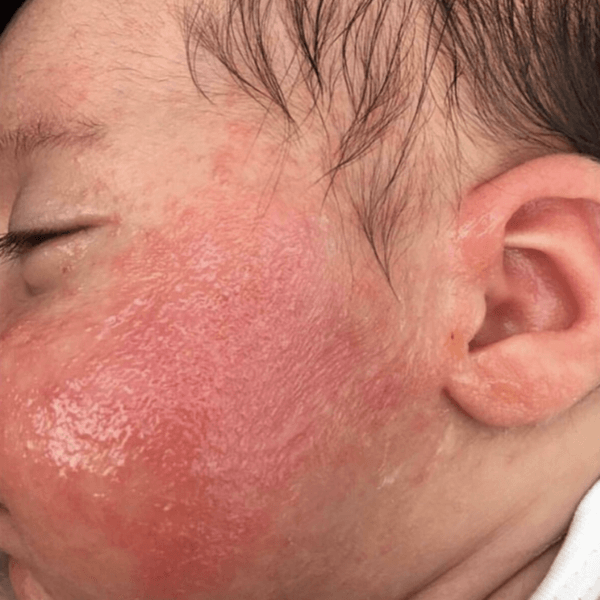
Around the world, between 10% and 20% of children have AD. About 1% to 3% of adults have AD. People of all skin colors get AD.
Most people get AD before their 5th birthday. AD rarely starts when a person is an adult.
AD is much more common today than it was 30 years ago. Dermatologists are not sure why. They do know that some children have a greater risk of getting AD.
The following seem to increase a childs risk of getting AD:
- Family members have AD, asthma, or hay fever: Does the childs mother or father have AD? Does a parent have asthma or hay fever? A family history of these diseases remains the strongest risk factor. If one or both parents have AD or an allergic condition, the child is much more likely to get AD. Some children get all 3 diseases. Asthma and hay fever usually appear before the age of 30. People often have asthma and hay fever for life.
- Where child lives: Living in a developed country, city , or a cold climate seems to increase the risk. For example, Jamaican children living in London are twice as likely to develop AD as those who live in Jamaica.
- Gender: Females are slightly more likely than males to get AD.
- Mothers age when child born: When the mother gives birth to the child later in her childbearing years, a child is more likely to get AD.
- Social class: AD seems more common in higher social classes.
Also Check: Why Do Eczema Flare Up
How Do Dermatologists Diagnose Dyshidrotic Eczema
If your dermatologist suspects that you have dyshidrotic eczema, your dermatologist will:
-
Look closely at the skin on your hands and feet
-
Take a bit of fluid from a blister if it looks infected
-
Ask you questions about your health, what you do for work and hobbies, and when you usually develop blisters
During your appointment, be sure to tell your dermatologist if you have a metal implant in your body or recently:
-
Noticed that your skin reacts when you wear certain jewelry
-
Smoked tobacco
-
Worked with cutting oil or cement
-
Took a medication, including aspirin or birth control pills
If your dermatologist thinks that the dyshidrotic eczema could be due to an allergy, an allergy test called patch testing may be recommended. During patch testing, small amounts of substances that you may be allergic to are placed on your skin often the skin on your back.
Thats often all thats needed to determine whether you have dyshidrotic eczema. If you do, your dermatologist will create a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Having an infection can stop dyshidrotic eczema from clearing
In one study, researchers found that about 33% of patients who had dyshidrotic eczema on their hands got rid of the dyshidrotic eczema only after treating an infection on their feet.
How Is Eczema Treated
Treatment for eczema typically involves lifestyle changes, over-the-counter moisturizers, medications, and phototherapy.
Lifestyle changes and moisturizers. Anyone with eczema should try to avoid exposure to allergens and contact with chemicals or other substances known to trigger symptoms. If a flare-up occurs, people should try to avoid scratching to prevent additional skin damage and thickening of the skin.
Over-the-counter moisturizers and hydrocortisone cream may be soothing and can help relieve itching. Bathing or showering with lukewarm, rather than hot, water will help, too.
Medications. If symptoms continue, a doctor may prescribe one or more of the following treatments:
- Antihistamines: These may be used to treat eczema symptoms caused by exposure to allergens. They may be available over-the-counter or by prescription.
- Corticosteroids: While over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream is available, sometimes higher doses of topical corticosteroids are necessary to reduce and control skin inflammation. Sometimes these medications must be taken orally, as a pill or tablet.
- Antibiotics or Antifungals: Because skin lesions caused by eczema are prone to infections, a doctor may prescribe these to eliminate infections that may accompany eczema.
- Immunosuppressive drugs: These medications reduce the bodys immune response, which lessens inflammation and other symptoms.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of An Eczema Patch
How To Use Emollients
Use your emollient all the time, even if you’re not experiencing symptoms.
Many people find it helpful to keep separate supplies of emollients at work or school, or a tub in the bathroom and one in a living area.
To apply the emollient:
- use a large amount
- do not rub it in smooth it into the skin in the same direction the hair grows
- after a bath or shower, gently pat the skin dry and apply the emollient while the skin is still moist to keep the moisture in
You should use an emollient at least twice a day if you can, or more often if you have very dry skin.
During a flare-up, apply generous amounts of emollient more frequently, but remember to treat inflamed skin with a topical corticosteroid as emollients used on their own are not enough to control it.
Do not put your fingers into an emollient pot use a spoon or pump dispenser instead, as this reduces the risk of infection. And never share your emollient with other people.
Eczema Remedies For Children
About 10% to 20% of infants develop eczema, with the rash typically appearing on the face and scalp. In most cases, this condition improves after age five and may disappear for good.
Medical experts believe itâs a genetic condition or passed from parents to their kids. Symptoms can vary depending on the age of the child.
In more severe cases, infants can develop eczema on uncommon areas like the torso, elbows, and knees. Children and teens will notice the rash in the inner elbows, behind the knees, on the neck, or wrists and ankles. The skin may appear drier, thicker, and develop a scaly texture.
There are some steps you can take to treat your child’s eczema or prevent future flare-ups:
- Avoid skincare products with heavy fragrances and other possible irritants.
- Cut your childâs fingernails and encourage them to wear gloves to prevent skin damage from excessive scratching.
- Maintain a routine of bathing, moisturizing, and applying age-appropriate treatments recommended by a pediatrician. Ask your doctor about the âsoak and sealâ method.
- Talk to a pediatrician or dermatologist about the benefits of oatmeal baths or bleach baths to reduce inflammation and discourage bacterial growth.
- Boost the effectiveness of any topical medication and rehydrate the skin by using wet wrap therapy. This can also prevent your child from scratching their skin.
Show Sources
You May Like: Natural Eczema Treatment For Toddlers
How To Use Your Emollients To Get The Best Results
Regular application indicates a minimum of twice-daily application, which can be increased depending on the dryness of the skin, exposure to daily irritants and current level of eczema-related symptoms. Another way to maximise benefits from your emollients and prevent contamination is to get a product that comes with a pump on top, or use a single-use wooden spatula to get the emollient out of the tub. For maximum comfort following application, it is recommended to apply the emollient in small patches and rub it in either in the direction of the body hair growth or in a downward motion to avoid irritation of the hair follicles.
Something that many studies on the long-term use of emollients have concluded is that it is essential to continue regular application of the emollients even when the skin appears clear and is asymptomatic. This helps to maintain a good skin barrier and effectively prevent eczema. These studies also observe that people often forget to apply such regular emollients when they are not experiencing symptoms and this often contributes to exacerbations later on.
How Is Eczema Diagnosed
Your doctor will begin to make a diagnosis by asking you about your symptoms, when they began, and whether you have allergies or asthma. He or she will conduct a physical exam to look at your skin and assess your symptoms. In most cases, at this point your doctor will be able to make a diagnosis. Sometimes, though, your doctor will order additional diagnostic tests.
The most common diagnostic tests for eczema are patch tests and skin biopsy.
- Patch test: A physician will place one or several adhesive patches on your back. Each of these patches contains a small dose of an allergen. The patches remain in place for two days, at which point the physician examines the skin to determine which, if any, particular allergens cause skin irritation.
- Skin biopsy: In this procedure, a physician removes a small piece of skin tissue. Once collected, a pathologist will examine the tissue sample under a microscope to confirm diagnosis.
Also Check: Cetaphil Bar Soap For Eczema
But First What Is Eczema
According to Breana Wheeler, MSN, NP, at Facile Dermatology + Boutique, eczema is an umbrella term for a group of skin conditions that can cause the skin to become red, itchy, and inflamed. “The word eczema is often used when talking about atopic dermatitis, the most common type of eczema,” she explains. “It’s important to know that patients with atopic dermatitis have an impaired skin barrier, meaning their skin doesn’t hold water in like it’s supposed to, which is what causes the condition’s signature flakes and dryness.”
While eczema can have a genetic component, there’s a variety of things that cause or worsen it, such as our environment and the way in which our immune system responds. Cindy Bae, MD, also points out that while diet and certain foods don’t directly cause eczema, food allergies can often make atopic dermatitis worseanother reason to visit your doc ASAP if you know or think you might be suffering from eczema.
Articles On Atopic Dermatitis
It can be hard to tell for sure if you have atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema. Youâll want to see a dermatologist or other doctor to find out.
At your appointment, your doctor will check your skin and talk with you about your symptoms, your health history in general, and any rashes or allergies that run in your family.
Based on that information, they’ll decide if itâs eczema or something else.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Eczema On Your Feet
Eczema Medication And Therapy
Topical cream and oral/injected medication could be recommended to keep symptoms under control. Prescription creams will help to control itching while repairing the skin. Oral medication can help to fight skin infection and relieve itching. Injected drugs could help to control inflammation in severe cases.
When at-home treatment and medication does not control symptoms, a dermatologist may choose to perform one of the following treatments:
- Xtrac laser therapy Xtrac laser therapy has been approved to treat some types of eczema.
- Ultraviolet Light Therapy UVB or PUVA ultraviolet rays are effective for treating chronic cases, but increase risk for sunburn or skin cancer if used for too long.
- Wet Dressing Application Wrapping the affected area with topical medication and wet bandages has proven effective with certain forms of eczema.
How Do Dermatologists Treat Atopic Dermatitis
Treatment cannot cure AD, but it can control AD.
Treatment is important because it can:
- Prevent the AD from getting worse.
- Calm the skin, relieving pain and itch.
- Reduce emotional stress.
- Prevent infections.
- Stop the skin from thickening. Thickened skin often itches all the time even when the AD is not flaring.
A treatment plan often includes medicine, skin care, and lifestyle changes. Skin care and lifestyle changes can help prevent flare-ups. Many patients receive tips for coping. Doing all of this may seem bothersome, but sticking to the plan can make a big difference.
A dermatologist will create a treatment plan tailored to the patients needs.
Medicine and other therapies will be prescribed as needed to:
- Control itching.
- Loosen and remove scaly lesions.
- Reduce new lesions from forming.
Read Also: Eczema Rash On Dark Skin
Eczema Research And Clinical Trials
We offer a number of clinical trials for patients with all types of eczema. We offer trials for topical treatments, pills, and injection medications in patients of all ages.
Some of these developments directly stem from research conducted in our Eczema Program. One such discovery is a treatment targeting a specific white blood cell called a T-helper 22 lymphocyte , which we found to be highly increased in eczema cases and associated with disease severity.
How A Psychodermatologist Can Help You Manage Your Eczema
While psychologists are very good at dealing with mental health, bringing in a psychodermatologist who also understands the skin aspect of the condition can be really beneficial, Piliang notes.
They can help you get to a point of acceptance about your disease and the routines you have to go through to manage your disease that can help with stress, anxiety, and depression, she says. Knowing you have someone you can turn to and trust when you have a flare or youre experiencing mental health issues related to your disease is incredibly important.
In a typical dermatological visit, your doctor focuses on the skin disease they look, examine and treat. A consultation with a psychodermatologist complements the standard dermatology exam, focusing on the mental and emotional side of the condition, in addition to the physical side, Jafferany says.
A psychodermatology visit includes a detailed interview that focuses on the patients psychosocial history with full examination of the skin, according to Jafferany. That includes what is going on in their work life, family life, and social life. I ask about any marital or relationship problems and work-related stress because all these things can directly or indirectly affect skin disease, he says.
Any kind of stress can lead to an inflammatory response, which can cause eczema to get worse, he adds.
Dont Miss: Causes Of Eczema Flare Ups In Babies
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Oozing Eczema
Why Does Eczema Occur
Although the precise cause of eczema is unknown, dermatologists believe it is linked to an overactive response by the bodys immune system to irritants. This triggers the symptoms of eczema.
Families with a history of allergies or asthma are more likely to experience eczema. An early diagnosis will help your dermatologist treat eczema most effectively, while reducing the risk of flare-ups.
Should You See A Doctor If You Suspect You Have Eczema
If the eczema is mild and doesnt compromise your ability to function and enjoy life, you dont necessarily need to see an MD, says Anderson.
But if the itching is keeping you up at night, if you have blisters or if the affected skin shows any signs of infection, see a doctor as soon as you can.
A family doctor will often be able to treat mild eczema. For more severe casesor if the condition isnt responding to treatmentPurdy advises getting a referral to a board-certified dermatologist.
Don’t Miss: How To Tell If I Have Eczema
How Should Eczema On The Face Be Treated
First things first, if a trigger for your eczema can be identified, it should be eliminated. Not sure where to start? Tanuj Nakra, a cosmetic surgeon and co-founder of Avya Skincare, cites common triggers as foods , fabrics , or skin irritants .
“Unfortunately, some triggers are hard to treat because they are tied to your genetics or where you live. For instance, northern latitudes are a trigger,” Nakra explains. “Secondly, the itching symptoms of eczema should be treated to avoid worsening the inflammation.” He says non-aggressive steroids such as hydrocortisone 1% cream is a good place to start in order to calm irritation, and depending on your results, you can seek further treatment options with your doctor. Of course, choosing gentle, non-inflammatory skincare is key if you’re looking to reduce the chances of a flare-up. Oh, and Bae also recommends investing in an at-home humidifier.