Does Eczema Mean You Have A Weak Immune System
In this article, I examine the role that immune system plays in the development of eczema, whether eczema is an indication of a weak immune system or one that is just over sensitive? I also look at small and easy steps that can support the immune system and that may improve eczema symptoms.
Sarah Hyland
Strengthen The Skin’s Protective Barrier
Much of the skin’s protective barrier is dependant on the natural moisturising factor and sebum it can produce, and how much water it can absorb from the atmosphere.
Keeping the moisture in: Skin can dry out in dry, windy weather and when exposed to indoor heating. Long soaks in hot baths can also strip the skin’s naturals oils leaving it permeable and undefended.
Here are a few tips that may help strengthen the skin’s protective barrier:
- Wash in warm, not hot, water and avoid long sessions in the bath or shower.
- Consider a humidifier if the air in your home is very dry and cover up in dry, windy weather.
- Avoid soaps and detergents that will strip naturals oils from the skin and are likely to irritate sensitive skin. Wear rubber gloves when doing housework and consider hypoallergenic toiletries that will have a gentle action.
- Keep the body cool to avoid a loss of fluid through sweating. Salt in sweat can also irritate eczema-prone skin.
- Moisturise the skin as often as necessary, and definitely after any water exposure. Applying a moisturiser immediately after washing will trap a layer of water molecules in the skin. Using a rich, active cream will help counter redness and skin flare-ups. Neem is a natural skincare ingredient that is useful for calming and conditioning dry, sore and eczema-prone skin.
The Inherited Barrier Defect
There is emerging evidence that inflammation in atopic dermatitis is associated with immune-mediated and inherited abnormalities in the skin barrier. This barrier failure causes increased permeability of the skin and reduces its antimicrobial function.
The main inherited abnormality causing disordered barrier function is filaggrin expression. Filaggrins are filament-associated proteins which bind to keratin fibres in the epidermal cells. The gene for filaggrin resides on chromosome 1 . This gene was first identified as the gene involved in ichthyosis vulgaris. Abnormal filaggrin is associated with early-onset, severe and persistent atopic dermatitis.
It is postulated that the loss of filaggrin results in:
- Corneocyte deformation , which disrupts the organisation of the extracellular lipid the lamellar bilayers.
- A reduction in natural moisturising factors, which includemetabolites of pro-filaggrin.
- An increase in skin pH which encourages serine protease activity these are enzymes which digest lipid-processing enzymes and the proteins that hold epidermal cells together. Serine proteases also generate active cytokines like IL-1a and Il-1beta and promote skin inflammation.
Proteins under investigation in atopic eczema include structural compounds, such as hornerin, cornulin, claudin 1/23 and ceramides, enzymes, such as kallikrein and serine peptidases.
Also Check: How To Get Eczema Out Of Your Hair
What Are The Symptoms Of Dyshidrotic Eczema
Often, the first symptom is sudden itching on the palms, the sides of your fingers, or the soles of the feet. Next, small fluid-filled blisters may start to appear. These cause more intense itching and pain. These blisters may get bigger. In some people, these symptoms can cause a lot of problems with daily activities. The blisters often last for a few weeks before they dry up and flake away.
Dyshidrotic eczema is more likely to affect the hands than the feet. In most cases, the symptoms happen on both hands or both feet.
Some people have symptoms in frequent episodes. The episodes may happen every month or so for months or years. Over time, this may cause chronic hand dermatitis and lead to more symptoms, such as:
- Reddened, hard skin
- Color changes in your nails
If Eczema Is Not An Autoimmune Disease What Is It
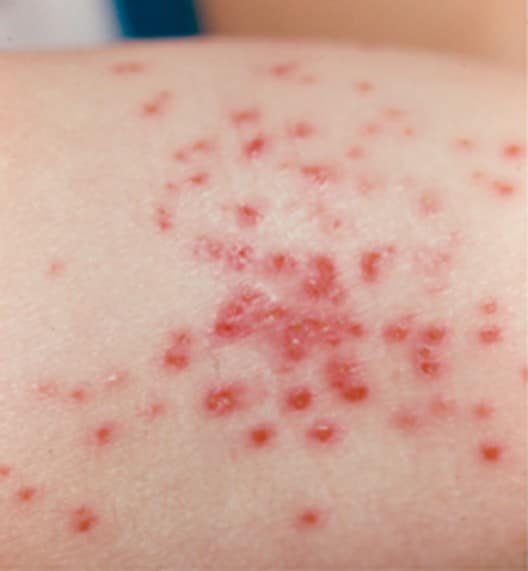
Atopic dermatitis, or eczema, said Dr. Yu, is the most common inflammatory skin disease, affecting 15-20% of children and 10% of adults. Its considered inflammatory, he said, due to the important role inflammation and the immune system play in its symptoms. But inflammation and immune responses are not, he said, eczemas only causes. Another skin condition in this category is seborrheic dermatitis, which causes stubborn dandruff and scaly, red patches on the scalp.
If all this talk of medical definitions and semantics has you scratching your head, youre not alone. There is still some debate about whether certain elements of eczema do share attributes of an autoimmune disease or not and, certainly, new scientific discoveries could evolve and provide for clarity about this topic in the future.
In the meantime, perhaps the classification of eczema is not as important as how we learn to care for it how we help ourselves and our skin, in our personal environments, and how to be healthy while also accepting that theres no one way to label our individual dermatologic experiences.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Eczema On Private Parts
Activated Immune System Alters Lipids Impairs Skin Barrier
- Date:
- National Jewish Health
- Summary:
- Researchers have discovered a cause of the dry, inflamed and itchy skin that plagues eczema patients. Medical researchers have now shown that an immune system skewed toward allergy alters the lipids in the skin. The altered lipids allow the skin to crack, water to leave and irritants to enter, setting the stage for eczematous lesions to develop.
Researchers at National Jewish Health have discovered a cause of the dry, inflamed and itchy skin that plagues eczema patients. A team led by Donald Leung, MD, PhD, has shown that an immune system skewed toward allergy alters the lipids in the skin. The altered lipids allow the skin to crack, water to leave and irritants to enter, setting the stage for eczematous lesions to develop. The research, supported by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Atopic Dermatitis Research Network, appeared in the February 22, 2018, issue of the journal JCI Insight.
“We have long known that an activated immune system and a defective skin barrier are both important factors in eczema, but not how they are related and which one drives the disease,” said Dr. Leung. “We have now shown that the allergic immune response shortens lipids in the skin, making them less effective at maintaining moisture and more susceptible to irritants.”
Story Source:
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider About Eczema
- How can you tell that I have eczema?
- If I dont have eczema, what other skin condition might I have?
- Is there a specific brand of moisturizer that you recommend?
- Is there a prescription cream that you can prescribe?
- How often should I see a dermatologist regarding my eczema?
- What soaps, lotions, makeup, etc. should I avoid?
- What medications do you recommend?
- What at-home treatments do you recommend?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Eczema is very normal, very common, and very, very uncomfortable. It can affect your quality of life. At its worse it can keep you from sleeping, distract you and make you feel self-conscious in public. See your dermatologist or other healthcare provider as soon as you start to see signs of it. Explore at-home remedies and prescribed treatments.
Youre not alone! 15% to 20% of people experience eczema or another type of dermatitis at some point in their lives.
Read Also: Forces Of Nature Eczema Control
For The First Time Study Proves Eczema Is An Autoimmune Disease
An experimental drug that works by blocking the immune response that causes unsightly, itchy skin patches looks promising for treating atopic dermatitis , also known as eczema.
Atopic dermatitis , or eczema, affects 10 percent of adults in the United States and about 25 percent of children worldwide.
AD is an inflammatory disorder in which the skin becomes covered in itchy, scaly lesions. These lesions cause cracks in the skins outer barrier, exposing patients to infection. AD is always accompanied by activation of the immune system.
Learn the Difference Between Psoriasis and Eczema »
A new study shows that dupilumab, a type of drug called a monoclonal antibody , can reverse the immune response that causes AD skin lesions. Many of the scientists who conducted the study are employed by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, the makers of dupilumab. The study was published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Eczema Coping Tips Diet
In most cases, eczema isnt caused or made worse by diet. If you notice that your eczema seems to get worse after eating a particular food, you may be an exception to this. See your doctor or dietitian for proper allergy testing and dietary advice.Never self-diagnose or you risk depriving yourself of enjoyable and nutritious foods for no good reason. Unnecessarily avoiding certain foods can lead to nutritional deficiencies.
You May Like: Gold Bond Ultimate Eczema Relief Lotion
Eczema Coping Tips Avoid Changes In Temperature
Abrupt temperature and humidity changes can sometimes irritate the skin for example, going in and out of air-conditioned buildings on hot days or heated buildings on cold days.Hard physical activity or exercise that makes you sweat heavily can also trigger the itch of eczema.Suggestions include:
- In winter, dont overheat your house. Dress warmly when going outdoors and remove the extra layers as soon as you return.
- In summer, dont over cool your house. Air conditioners can dry out the air and irritate your skin.
- Avoid hard physical activity in hot weather. For example, do your gardening first thing in the morning, or in the evening when the sun is lower in the sky.
Whats The Difference Between Dermatitis And Psoriasis
Psoriasis and dermatitis can appear similar. Both cause patches of red skin. However, in psoriasis, the scales are thick and the edges of those scales are well-defined.
Discuss with your healthcare provider your questions about which type of skin condition you have. You can have more than one skin condition at a time. Treatments for one may not work for the other.
Recommended Reading: Is There Any Treatment For Eczema
Is Eczema An Autoimmune Disease Spoiler Alert: Nope
According to the National Institutes of Health , autoimmune disease occurs when the immune system makes a mistake and attacks the bodys own cells, tissues or organs and unfortunately the problem seems to be getting more common. Immunity is our bodys defense system: when our immune system is working properly, it fights off infections and cancers, whereas autoimmunity is when this process goes wrong.
In a recent study done by the American College of Rheumatology, researchers demonstrated that the most common biomarkers of autoimmunity have been increasing in the U.S. population since the late 1980s, especially among young people.
Can Eczema Be A Sign Of Other Conditions
Eczema isnt a sign that you have other illnesses. However, it can look similar to or happen alongside other conditions.
Symptoms like itchy and red skin are also common with other skin conditions that are easy to mistake for eczema. These conditions are:
- Psoriasis: an autoimmune disease that causes your skin cells to multiply too fast
- Hives: large red welts on the skin caused by an allergic reaction
- Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: a cancer of the white blood cells that starts in the skin
- Scabies: a skin infestation by a type of mite
- Ringworm: a skin infection caused by a fungus
Eczema is sometimes part of a cluster of allergic conditions that healthcare professionals call the atopic march. These include:
- allergic rhinitis
If you have one of these three conditions, youre more likely to have another one.
In addition, your eczema may be more severe if you have one of these primary immunodeficiency diseases:
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
2020 research . Stress can trigger eczema flare-ups and make symptoms worse.
When youre feeling overwhelmed or threatened, your body releases certain chemicals, including stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol. These substances suppress your immune system, boost inflammation, and weaken your skins barrier even more.
Stress and eczema may become connected in a cycle. The more your eczema flares, the more stressed you may become. And the more stressed you are, the more your eczema flares.
Read Also: How Long Can An Eczema Flare Up Last
What Questions Might My Healthcare Provider Ask To Diagnose Eczema
The conversation with your healthcare provider will need to cover a lot of information. Be sure to be specific about your symptoms.
- Where is your eczema located?
- What have you used to try to treat your eczema?
- What medical conditions do you have? Allergies? Asthma?
- Is there a history of eczema in your family?
- How long have you had symptoms of eczema?
- Do you take hot showers?
- Is there anything that makes your symptoms worse?
- Have you noticed that something triggers or worsens your eczema? Soaps? Detergents? Cigarette smoke?
- Is there so much itchiness that you have trouble sleeping? Working? Living your normal life?
Is Atopic Dermatitis An Autoimmune Disease
The American Academy of Dermatology Association states that is a common form of eczema that does not have a single cause. Researchers think AD develops due to a combination of genetics, a sensitive immune system, and environmental factors that trigger the symptoms. Some evidence suggests that autoimmunity may also drive it.
Dermatologists believe that people with AD have a genetic trait that means their skin loses moisture too quickly, causing gaps in the skin barrier. This can lead to dry, less well-protected skin.
This alone is not always enough to cause AD. Other factors that may put people predisposed to the condition at risk of developing it include:
- living somewhere that is cold and damp for at least some of the year
- exposure to pollution and tobacco smoke
Autoimmunity may also contribute to AD. The authors of a 2021 study suggest that AD may start as an allergic response before progressing to an autoimmune response. They argue that this may be what causes chronic inflammation and relapses.
A large 2021 population-based study also found higher AD rates in people with one or more autoimmune condition, particularly those that affect the skin and digestive tract. This suggests one may increase the risk of, or cause, the other.
However, more research on how AD develops is necessary to confirm that it is an autoimmune disease, and if so, what treatments might help.
Recommended Reading: Humidifier For Eczema And Allergies
Home Treatments For Eczema
As we anxiously wait for a cure, its important to continue treating your childs eczema symptoms. Note that a well-rounded treatment plan should include medicine, skin care, and lifestyle changes. If you want to keep your child as comfortable as possible, you must work with them in avoiding trigger factors.
Smoking And Central Nervous System
Smoking can damage the central nervous system as nicotine increases blood pressure and heart rate and weakens the organs over time.
A study showed that smoking tobacco could seriously impact neurological health.
Smoking cigarettes harms a persons health and increases the risk of many conditions. Quitting smoking may reduce the risk of health problems and improve a persons overall health.
Also Read:
Also Check: How To Treat Bad Eczema On Hands
How Is Dyshidrotic Eczema Diagnosed
You may be diagnosed by a general healthcare provider or a dermatologist. A dermatologist is a healthcare provider who specializes in diseases of the skin.
Your healthcare provider will ask about your medical history and your symptoms. Tell him or her about contact youve had to possible irritants. You will also have a physical exam. Your healthcare provider will need to make sure your symptoms arent caused by other conditions. These may include allergic contact dermatitis, ringworm, herpes, or a rare autoimmune disease. You may also have tests such as:
- Skin scraping or biopsy, to check for infection
- Patch skin testing, to look for allergic causes
- Blood tests, to check for an autoimmune cause
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Eczema
There are steps you can take that may prevent eczema outbreaks:
- Establish a skin care routine, and follow your healthcare professionals recommendations for keeping your skin healthy.
- Wear gloves for jobs where you have to put your hands in water. Wear cotton gloves under plastic gloves to absorb sweat, and wear gloves outside, especially during the winter months.
- Use mild soap for your bath or shower, and pat your skin dry instead of rubbing. Apply a moisturizing cream or ointment immediately after drying your skin to help seal in the moisture. Reapply cream or ointment two to three times a day.
- Take baths or showers with tepid rather than hot.
- Drink at least eight glasses of water each day. Water helps to keep your skin moist.
- Try to avoid getting too hot and sweaty.
- Wear loose clothes made of cotton and other natural materials. Wash new clothing before wearing. Avoid wool.
- Avoid sudden changes in temperature and humidity.
- Learn to recognize stress in your life and how to manage it. Regular aerobic exercise, hobbies and stress-management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, might help.
- Limit your exposure to known irritants and allergens.
- Avoid scratching or rubbing itchy areas of skin.
Recommended Reading: Is Eczema An Immune Disorder
Debunking The Myth Of Eczema And Your Immune System
Having a fragile and/or faulty outer layer of skin makes it easier for microbes, bacteria and allergens to enter the body and cause an immune system response, which results in inflammation.
Think of it like this: if your body is more susceptible due to a compromised skin barrier, the more likely it is that these unwanted foreign substances come and crash the party under your skin.
When your body is under attack, the immune system sends its best soldiers to the source of the crime the affected area of skin and releases substances to fight off the intruders.
Ultimately, this is what causes the inflammation – the heat, swelling and itchiness – thats so common in eczema-prone skin. Similar to how your temperature rises when youre fighting off a flu these are all responses from the immune system to alert the body and demonstrate that something is being done to tackle the nasty infection or whatever it may be.
The trouble with the immune systems of those with atopic conditions is that for some reason they react super-speedily and super-intensely to any perceived threat!
So, rather than your immune system being too weak to handle the foreign substances that are entering your body, the issue lies with the barrier of the skin not being resilient enough to repel invaders, coupled with having a hair-trigger immune system response.