What To Do About Itching
Try to keep your baby from scratching their itchy skin. Scratching can make the rash worse, lead to an infection, and cause the irritated skin to get thicker and more leathery.
Trim their nails often, and then take the edge off of them with a file if you can. Some parents also slip “scratch mittens” onto their little one’s hands. Others try long socks, tucked in under a long-sleeved shirt, so they’re harder for a baby to remove. View a slideshow to get more eczema skin care tips.
Does Breastfeeding Prevent Baby Eczema
There is some evidence that breastfed babies may be less likely to develop eczema. Although unproven, the antimicrobial properties in breast milk have also been studied as a type of treatment when directly applied to an eczema rash. To try this, rub a few drops of your liquid gold onto the rash regularly for a few days and watch for any reduction in symptoms.
What Are The Differences Between The Skin Symptoms Of Food Allergy And Eczema
An allergic reaction to a food typically happens quickly. Symptoms of an allergic reaction then go away, usually after several hours, as long as the food is not eaten again. Eczema is a chronic condition that does not go away quickly. Eczema tends to show up in predictable places, such as on the cheeks of young babies or elbow creases of older children. The places on the skin where symptoms of an allergic reaction to food appear are more unpredictable. Hives, redness and itching from an allergic reaction can show up just about anywhere on the body and even in different places each time the food is eaten.
Don’t Miss: Best Eye Makeup Remover For Eczema
Managing Babys Eczema: Moisturizing
Regular moisturizing is just as crucial for managing baby eczema as the daily bath. In fact, its the seal part of the soak and seal method.
After your baby’s bath, moisturize their skin right away to “seal” the remaining moisture from the bath into their skin, and help prevent it from escaping.
- Follow the 3-minute rule! Moisturize babys skin within 3 minutes after the bath. The moisture from the bath will escape through babys skin barrier if you wait too long to moisturize.
Choose a moisturizer that mimics and supplements the skin’s natural barrier, which is made up of cholesterol, fats, and fatty acids.
This barrier usually lets the skin hold in enough moisture. But babies with eczema have a compromised skin barrier, so they need support from moisturizer to build up their barrier.
- Look for moisturizers that contain ceramides. Ceramides are the fats that the skin naturally makes to form the skin barrier.
- You could also use coconut oil, because it moisturizes, eases inflammation, and helps fight against skin bacteria with lauric acid.
- Ointments that are free from alcohol are also recommended. Avoid creams that contain alcohol, as alcohol can sting and burn the skin.
Please read this article to learn more about the best baby eczema moisturizer ingredients, as well as moisturizer ingredients to avoid.
Liberally moisturize all areas of babys body, especially the areas where the eczema is worst. Theres no such thing as too much moisturizer!
How Is Eczema Diagnosed
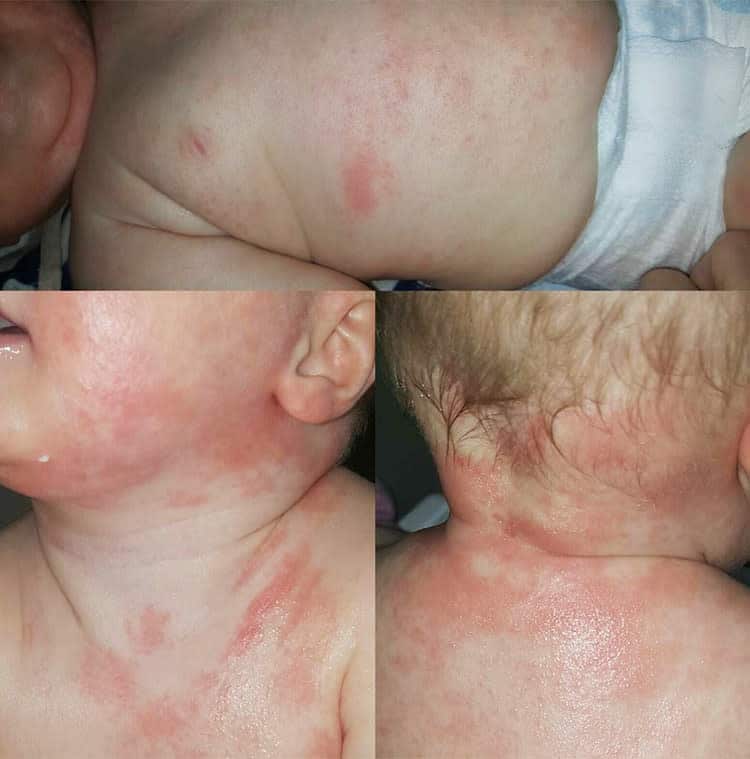
There is no specific test used to diagnose eczema. The doctor will look at the rash and ask about symptoms, the child’s past health, and the family’s health. If family members have any atopic conditions, that’s an important clue.
The doctor will rule out other conditions that can cause skin inflammation, and might recommend that your child see a dermatologist or an allergist.
The doctor may ask you to ban some foods from your child’s diet, switch detergents or soaps, or make other changes for a time to see if your child is reacting to something.
Read Also: How Did I Get Dyshidrotic Eczema
Baby Eczema: Diagnosis And Treatment
Your childs doctor will diagnose eczema based on symptoms, the appearance of the rash, family and individual medical history, and evaluation for potential allergies.
There is no specific test to diagnose eczema, but a doctor might order blood tests and skin tests to look for allergies or rule out other skin conditions.
How Is It Treated
Because there is not yet a cure for eczema, our treatment goals are to reduce itching and skin inflammation, and to prevent infection. The best treatment for eczema is a proactive one, using gentle skin care and moisturizers to re-establish the skin barrier.
Infants and older childrens skin should be kept well moisturized, and washed with fragrance-free non-soap cleansers. We also recommend a fragrance-free ointment-based moisturizer, with petrolatum as either the only or the first ingredient. In young children and infants, it is reasonable to use an over-the-counter topical hydrocortisone ointment, which is a mild topical steroid, for up to a week.
But if the rash either persists or you find that you need to use the hydrocortisone more than one week out of the month, you should discuss further use with your childs pediatrician. You can apply the ointment, as prescribed, then a coat of petrolatum-based moisturizer, to help keep in the moisture.
If your childs skin does not respond well to any of these measures or becomes infected, contact your pediatrician, who can diagnose the condition and then prescribe another topical cream or antihistamine.
You May Like: How To Stop Scratching Eczema In Sleep
Odds Of Developing Asthma And Rhinitis
Unadjusted analyses showed that children with eczema at baseline had more than a 2-fold increase in the odds of developing asthma and a 3-fold increase in the odds of developing rhinitis compared with children without eczema at baseline. The odds for developing asthma and rhinitis remained increased after adjustment for eczema, sex, age, family history of allergic disease, asthma, length of breastfeeding, PVC-flooring material in the home, type of building, environmental tobacco smoke, and number of adults living with the child .
Table 2 Factors associated with the 5-year cumulative incidence of asthma and incidence of rhinitis in eczema patients aged 12years in Sweden
Ways To Prevent Baby Eczema
Eczema itself cannot be prevented, but knowing and avoiding triggers can help prevent flare-ups of the condition.
Some ways to reduce triggers include:
- Keep your child out of cold, dry air.
- If they are 6 months or older, make sure your child gets an annual flu shot.
- Read labels on products to help your family avoid common irritants.
- Double-rinse your laundry to remove detergent residue.
Recommended Reading: Mejor Crema Para Eczema En Bebes
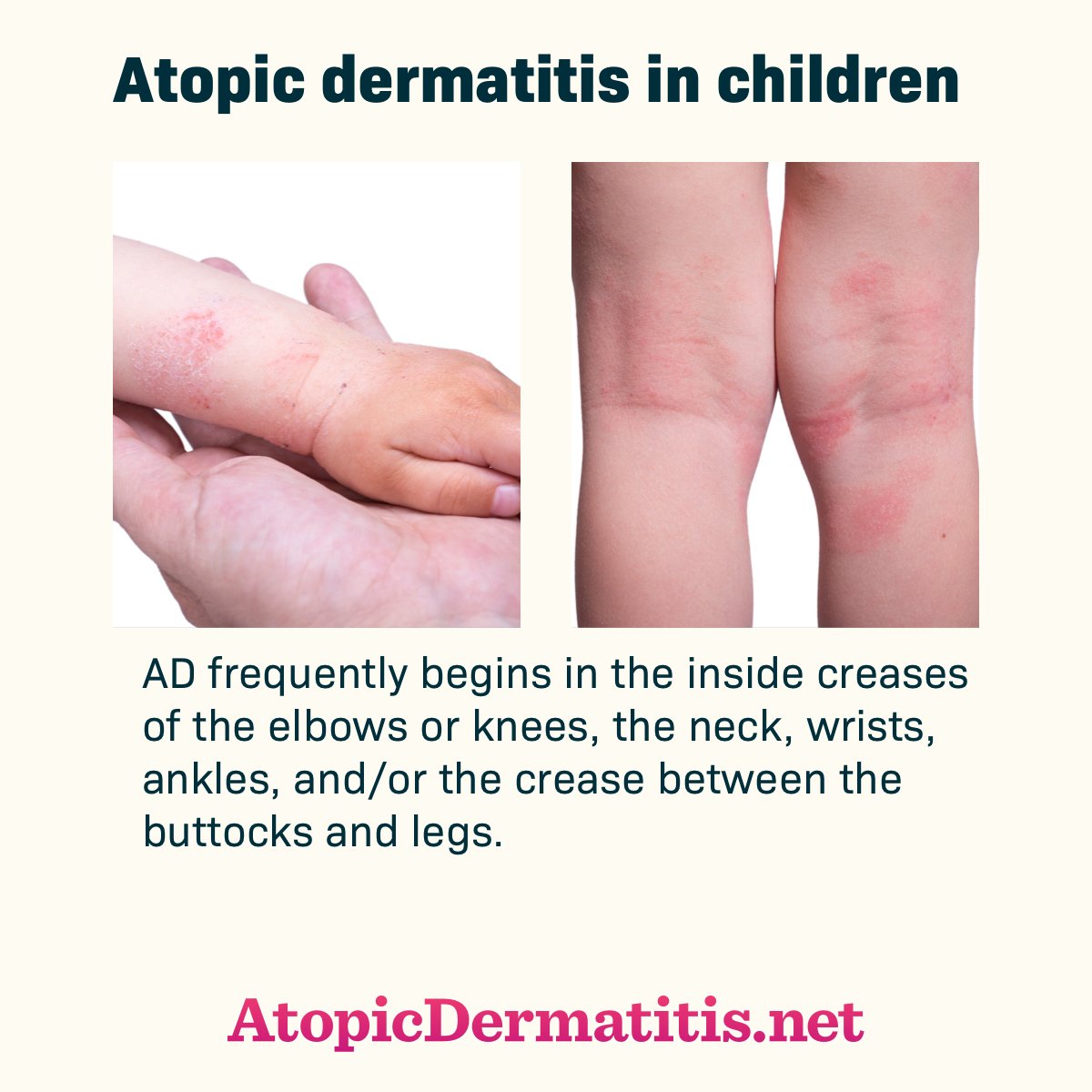
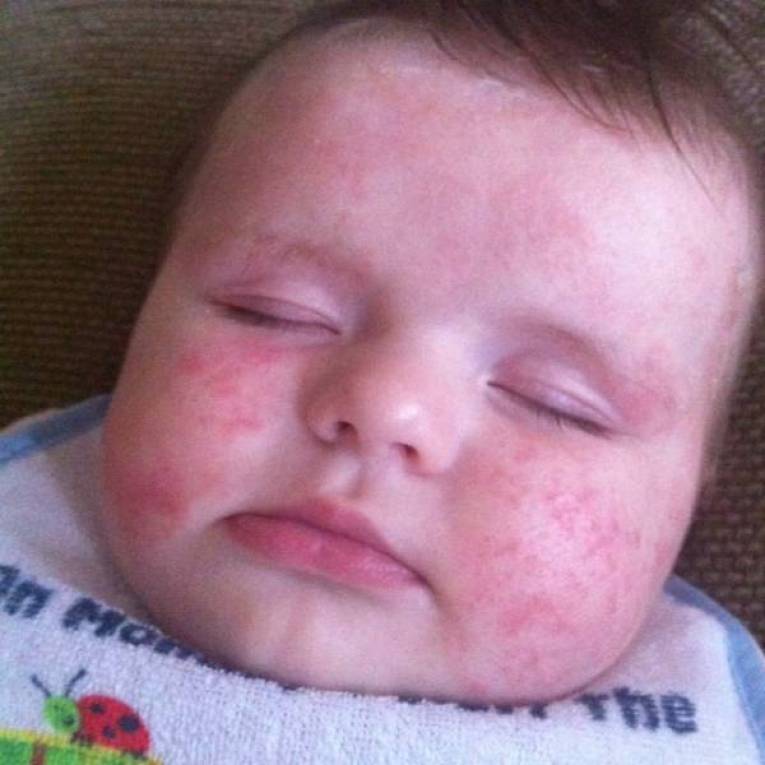
What Are The Symptoms Of Atopic Dermatitis In A Child
Symptoms may come and go, or occur most or all of the time. Any area of the body may be affected. In babies, symptoms usually affect the face, neck, scalp, elbows, and knees. In children, symptoms usually affect the skin inside the elbows, on the back of the knees, the sides of the neck, around the mouth, and on the wrists, ankles, and hands.
Symptoms can occur a bit differently in each child. They can include:
-
Dry, scaly skin
-
Pale skin on the face
-
Small, raised bumps that may become crusty and leak fluid if scratched
-
Rough bumps on the face, upper arms, and thighs
-
Darkened skin of eyelids or around the eyes
-
Skin changes around the mouth, eyes, or ears
-
Raised, red areas
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis can be like other health conditions. Make sure your child sees his or her healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
What Are The Factors That Causes Eczema In Babies
The actual cause for the development of eczema in babies is unknown, however, it is most commonly linked to genetics and environmental factors. The outside elements might trigger the immune system to generate a response that results in red and itchy skin.
Family history of Atopic Dermatitis, hay fever or asthma is another factor linked to the occurrence of Atopic Dermatitis in babies. As these babies grow, they may develop symptoms of hay fever or asthma.
However, the skin condition is not a communicable disease, so the baby cant get infected by another person. Same way the baby cant transmit the infection to someone else.
Most children get itchy rashes at some time during their childhood. Eczema generally is a nuisance that will make you scratch until bleeding and cracking of skin. The word atopic describes conditions that occur when immune system is overly sensitive to environmental allergens or irritants. These include pollens, molds, dust, animal dander, and targeted foods. Dermatitis signifies that the epidermis is infected, or red and sore.
Kids who get eczema normally have household members with hay fever, bronchial asthma, or other allergies. Some professionals suppose that these children may be genetically inclined to get eczema, which means that characteristics were handed on from mothers and fathers by way of genes that make a child more likely to get it.
Also Check: Ingredients To Avoid With Eczema
When To Speak With A Doctor
It is advisable to speak with a doctor if symptoms become more severe or if it is difficult to manage the condition at home. If eczema is beginning to impact a childs everyday life, such as disrupting sleep or there are frequent infections from scratching their skin, a parent caregiver can consider contacting a doctor.
Who Should Be Tested
With up to 70 percent of infants and young children with eczema having an underlying allergy that contributes to disease severity,â¯healthcare providers can use specific IgE testing to enhance the diagnostic process and pinpoint those allergensâ¯thatâ¯may be triggeringâ¯eczema symptoms.16,17 The specific information gleaned from test results can also be used to develop a personalized treatment plan.â¯â¯
Also Check: Alternative To Hydrocortisone For Baby Eczema
Introducing Allergens To Babies With Eczema
Introducing common allergenic foods to eczema babies early and often may be especially beneficial.
New dietary guidelines from the U.S. Department of Agriculture recommend the early, frequent introduction of peanut, particularly for babies who have eczema.
According to the USDAs new Dietary Guidelines, if an infant has severe eczema…age-appropriate, peanut containing foods should be introduced into the diet as early as age 4 to 6 months. This introduction is especially important for babies with eczema, because of their increased food allergy risk.
Also, as other international medical guidelines state, early introduction of other common food allergens may be beneficial for eczema babies as well.
For instance, guidelines from the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology recommend that babies with eczema be introduced to allergenic foods, such as egg and peanut, as early as 4 months of age.
——————————–
All health-related content on this website is for informational purposes only and does not create a doctor-patient relationship. Always seek the advice of your own pediatrician in connection with any questions regarding your babys health.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. Products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
See the FDA Peanut Allergy Qualified Health Claim at the bottom of our homepage.
A Potent Remedy For Childhood Eczema
As for the effect of the combined anti-inflammatory compounds on both conditions, this was also quite successful.
Cutaneous combined activation of reduced skin inflammation to a higher extent compared to single activation, write the authors.
The combined therapy effectively alleviated , but was insufficient at preventing allergic asthmatic response in the lungs, says Dr. Deckers.
This was done by counteracting the response of the so-called T helper 17 cells a type of immune cell.
However, the treatment did significantly reduce the severity of the asthma by counteracting one aspect of the specific immune response in the lungs. In this way, the therapy represents a potent remedy against allergic skin inflammation and the aggravation of atopic march.
Dr. Julie Deckers
In future, the scientists are looking to bring their findings to human clinical trials and simultaneously work on developing new therapies that could effectively stop the development of the atopic march.
Neither atopic dermatitis nor asthma have a known cure, so the need for prevention strategies for these conditions remains dire.
Read Also: How To Calm Down An Eczema Flare Up
Icipation And Summary Of Symptoms
At the follow-up at 4.5 years of age, 115 out of 123 children participated and several of them displayed more than one symptom. Of the 115, 60 still suffered from eczema, 26 had ARC, 37 had asthma and 35 had no symptoms of atopic disease at all. Ninety-four out of 123 completed the entire study until 10 years of age, of whom 60 continued to have eczema, 44 had ARC, 27 had asthma and 13 had no symptoms of allergy at all.
Causes Of Atopic Eczema
The exact cause of atopic eczema is unknown, but its clear it is not down to one single thing.
Atopic eczema often occurs in people who get allergies. Atopic means sensitivity to allergens.
It can run in families, and often develops alongside other conditions, such as asthma and hay fever.
The symptoms of atopic eczema often have certain triggers, such as soaps, detergents, stress and the weather.
Sometimes food allergies can play a part, especially in young children with severe eczema.
You may be asked to keep a food diary to try to determine whether a specific food makes your symptoms worse.
Allergy tests are not usually needed, although theyre sometimes helpful in identifying whether a food allergy may be triggering symptoms.
Also Check: Remedios Caseros Para El Eczema En Bebes
Symptoms Of Discoid Eczema
Discoid eczema causes distinctive circular or oval patches of eczema. It can affect any part of the body, although it does not usually affect the face or scalp.
The first sign of discoid eczema is usually a group of small spots or bumps on the skin. These then quickly join up to form larger patches that can range from a few millimetres to several centimetres in size.
On lighter skin these patches will be pink or red. On darker skin these patches can be a dark brown or they can be paler than the skin around them.
Initially, these patches are often swollen, blistered and ooze fluid. They also tend to be very itchy, particularly at night.
Over time, the patches may become dry, crusty, cracked and flaky. The centre of the patch also sometimes clears, leaving a ring of discoloured skin that can be mistaken for ringworm.
You may just have 1 patch of discoid eczema, but most people get several patches. The skin between the patches is often dry.
Patches of discoid eczema can sometimes become infected. Signs of an infection can include:
- the patches oozing a lot of fluid
- a yellow crust developing over the patches
- the skin around the patches becoming hot, swollen and tender or painful
Hypoallergenic Formula Vs Soy
Some parents resort to using soy protein-based formula for their children who are at risk of milk protein allergies. Soy formula is made from soy protein, and therefore it is plant-based. While soy-based formula might be slightly cheaper than hypoallergenic formula, it is not very useful for children who are diagnosed with a cow’s milk protein allergy. This is because babies who are allergic to milk are also likely to be allergic to soy protein. Studies show that 10% to 14% of babies who are allergic to cows milk protein are also allergic to soy protein.
There are also other concerns around using soy formula, including the health effects of phytoestrogens found in soy. Soy formula is not recommended for preterm babies. There is a high prevalence of osteopenia in preterm babies who feed on soy formula. Soy formula should only be used if medically necessary at the recommendation of a qualified health professional.
You May Like: Eczema And Pimples On Face
Natural Remedies For Baby Eczema
If you need some extra help soothing babys skin, these natural eczema treatments may make things better.
- Wet a washcloth. Drape cool, wet washcloths or gauze over your babys irritated skin for five to ten minutes at a time or however long you can get your squirmy worm to cooperate.
- Try an oatmeal bath. Sprinkle a bit of uncooked oatmeal, colloidal oatmeal or even baking soda into the tub when you wash your baby. All can naturally relieve eczema and irritation.
- Combat dry air. Running a cool-mist humidifier in your baby’s bedroom can help keep her skin super-hydrated. Clean it frequently to prevent bacteria and mold buildup.
- Dress your little one in layers. Sweating can reboot the eczema cycle, and thats the last thing you want. Layers let you customize babys outfit for toasty temps.
- Ask your pediatrician about probiotics. Studies are underway to see whether probiotics may ease eczema when added to dry baby formula or served as a dietary supplement. Get your doctor to weigh in before giving it a go.
What Causes Atopic Dermatitis In A Child
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not known. But some things are linked to it. They include:
-
Genes. This skin problem can be passed on from parents to a child.
-
Immune system. An immune system that isnt fully developed may affect how much protection the skin can give.
-
External factors. These include being in winter weather, using hot water for bathing, using soap, and being in dry, hot temperatures.
You May Like: Can Eczema Be Caused By Hypothyroidism
Is A Cure Or Better Treatment For Eczema On The Horizon
Without a cure on the near horizon, we here at Johns Hopkins are creating an Eczema Day Treatment Unit to help our patients with moderate to severe eczema keep their symptoms under control and prevent flare-ups. We anticipate that this novel, multidisciplinary program will include experts from Child Life, behavioral psychology, allergy, dermatology and infectious diseases to provide the comprehensive care these children need care that cannot be provided in an average clinic visit.
A primary goal of the day treatment unit will be education children and their families will learn techniques such as wet-wrap therapy, to help deeply moisturize the skin. This therapy involves coating the skin with a topical ointment, followed by a greasy ointment like petroleum jelly, then dressing in wet pajamas, followed by dry pajamas, allowing the skin to soak in the moisture.