Increased Exposure To Environmental Toxins
There are toxins in the air, water, soil, foods, body products, cosmetics, home furnishings and even clothing. Environmental toxin exposures can directly dampen immune system function, specifically how immune cells develop and how they function. Kids have higher metabolic rates and their bodies absorb more toxins than adults and have difficulty disposing of these toxins.
Children are exposed to these chemicals more than ever. In fact, there are approximately 80,000 chemicals produced and only 8 chemicals are restricted on a government level. This overload of toxins may trigger an immune response, and increase flares of eczema, allergies, and asthma.
Will The Baby React To Breastmilk If I Eat Allergens
Variable levels of a food allergy protein have been found to be detected in breastmilk after ingestion by the mother. There have been reports made of infantile eczema, anaphylaxis, and gastrointestinal distress being triggered from food allergy proteins ingested through breastmilk. It is best to have the infant tested for allergies to determine the severity of the food allergy. The results of these tests can help the allergist to provide guidelines for the breastfeeding mother on elimination, reduction, or safest ways to ingest foods that the infant is allergic to.
Questions To Ask Your Childs Doctor
After your child is diagnosed with atopic dermatitis, you may feel overwhelmed with information. It can be easy to lose track of the questions that occur to you.
Lots of parents find it helpful to jot down questions as they arise- that way, when you talk to your childs doctors you can be sure that all of your questions are answered. If your child is old enough, you may want to suggest that she writes down what she wants to ask her health care provider too.
The commitment and compassion with which we care for all children and families is matched only by the pioneering spirit of discovery and innovation that drives us to think differently, to find answers, and to build a better tomorrow for children everywhere.
Also Check: Palmar Psoriasis Vs Hand Eczema
What Should I Do If My Babys Eczema Gets Worse
If your baby has wet, weepy skin and their eczema is not getting better with steroids, their skin may be infected and they may need antibiotics. If your babys eczema flare does not get better with the standard treatments recommended by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence , your GP should refer them to a dermatology specialist. If they suspect an allergy, they should refer them to an allergist or joint dermatologyallergy clinic.
How Eczema Scratching Can Cause Food Allergies
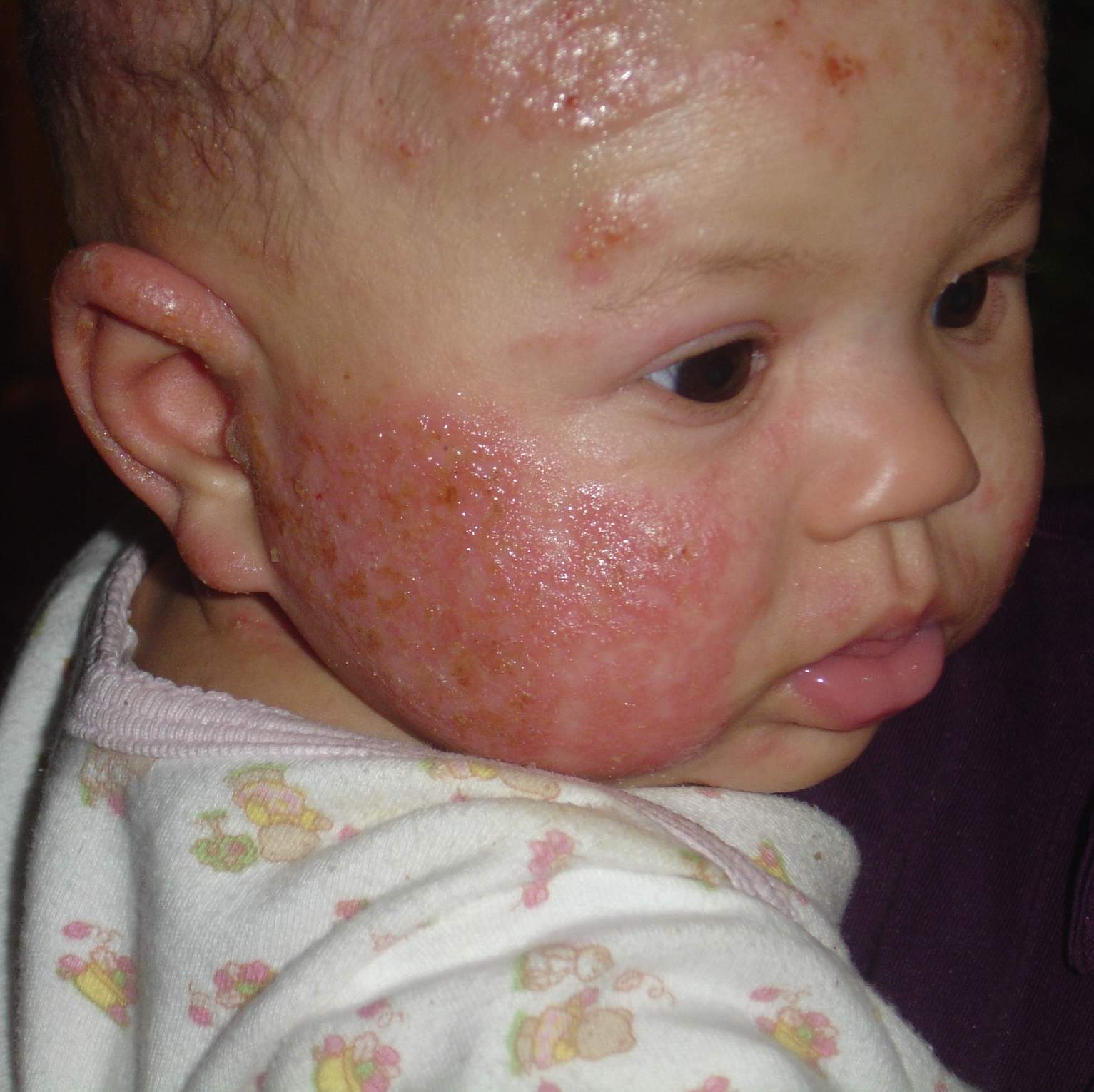
The weirdest way in which eczema itching causes food allergies is the act of scratching.
New research, so far only done in mice, at Boston Childrens Hospital showed that scratching the skin increases the chance of allergic reactions to foods, including anaphylaxis. The study showed that when you injure your skin by scratching, the immune system releases certain immune cells in the small intestine. Putting so many unnecessary immune cells in the small intestine can cause them to overreact to any food proteins that are undigested, leading to a food allergy.
Don’t Miss: Grahams Natural Skin Eczema Cream Review
What Can Trigger Eczema
Known triggers in some people include:
- Dry skin
- Swimming in chlorinated swimming pools
- Playing in sand and particularly sandpits
- Sitting directly on carpets or grass
- House dust mites
- Pollen allergy
- Irritants such as perfumes, soap, chemicals, woollen or synthetic fabrics
- Temperature changes, such as heat, or overly heated rooms
- Stress can make it worse, but eczema is not a psychological condition
These triggers may be relevant for some people however, it is not routinely recommended that everyone should avoid all of these potential triggers.
Most young children like to play in sandpits and swim in chlorinated swimming pools, so it is important that they can do these things, without making the eczema worse.
Simple things like wearing long pants when playing in a sandpit can help your child to enjoy the activity without causing a problem for their eczema.
Talk to your doctor, nurse practitioner or child health nurse for more help about how to manage your babys eczema.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Eczema
The signs of eczema :
- are mainly dry, itchy skin. Because it is so itchy, it is often called “the itch that rashes.”
- include redness, scales, and bumps that can leak fluid and then crust over
- tend to come and go. When they get worse, it is called a flare-up.
- may be more noticeable at night
Symptoms can vary:
- Infants younger than 1 year old usually have the eczema rash on their cheeks, forehead, or scalp. It may spread to the knees, elbows, and trunk .
- Older kids and teens usually get the rash in the bends of the elbows, behind the knees, on the neck, or on the inner wrists and ankles. Their skin is often scalier and drier than when the eczema first began. It also can be thicker, darker, or scarred from all the scratching .
You May Like: Gold Bond Eczema Cream Ingredients
What Do I Do When My Child Has A Flare
Your childs eczema will improve more quickly if it is treated soon after you first notice the rash. Prompt treatment will also reduce the likelihood of complications, so its best to see your doctor or pharmacist at the first sign of a flare-up.
Keep your childs fingernails short to avoid them scratching as much as possible.
Eczema is often treated using a steroid cream or ointment. You should get advice from your doctor or pharmacist about the best one to use for your specific case as different creams are used depending on the part of the body, the severity and the age of the child.
If your childs eczema does not improve after two days of regular treatment or if there are signs of infection, weepy, crusted or broken areas, it is important to see a doctor.
There are many treatments that can be used to treat eczema. For many children, eczema is a condition that comes and goes, and changes in intensity over time, so you may need to see your doctor a few times for the same condition.
Determine Food Allergies Or Intolerances
Food allergy can be a trigger of eczema, especially if the onset or worsening of eczema correlates with exposure to the food. Its important to monitor for vomiting, diarrhea and failure to thrive, as infants with eczema and a food allergy may have these additional findings.
In children and adults, it might be best to start with an elimination diet, the gold standard for identifying food sensitivities, for up to 4-6 weeks. This process of an elimination diet to work toward healing eczema internally is best done in phases and guided by a functional medicine practitioner, like those at Parsley Health. The phases include eliminating common allergens including dairy,gluten, corn, peanuts, soy, sugar, and eggs, closely following any changes in symptoms, and reintroducing foods one at a time to see how symptoms are affected. We recommend working with a provider trained in functional health and experienced with elimination diets for best results.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Hand And Foot Eczema
What Are The Complications Of Eczema
Affected skin can be very itchy. The itchiness can cause sleep difficulties for your child or infant and scratching can also lead to breaking of the skin.
Broken skin may become infected with bacteria that commonly live on childrens hands. Bacterial infections may cause inflamed blisters which can weep and form crusts.
Warts and herpes can also infect eczema rash. Infection with herpes can cause serious problems and is an emergency which needs to be treated urgently. If someone has a cold sore, make sure to keep a distance from a child with eczema.
Preventing Food Allergies For Eczema Babies
In 2017, the National Institutes of Health and American Academy of Pediatrics started recommending early introduction of peanut for babies starting at 4-6 months of age, especially those with eczema. These new recommendations come as a result of recent landmark clinical trials, particularly the LEAP trial.
Medical societies around the world are now issuing new recommendations for infants with eczema. Just recently, the British Society for Allergy and Clinical Immunology issued a recommendation that babies with eczema be introduced to allergenic foods such as egg and peanut as early as 4 months of age.
While research shows that babies with eczema are at highest risk of developing food allergies, fortunately, early and sustained exposure to allergenic foods has been shown to significantly decrease this risk. In fact, new guidelines from the NIH on baby food allergy prevention are specifically focused on infants with eczema as this risk group needs food allergy prevention, and in turn, early allergen introduction the most. Depending on the severity of your childs eczema, parents should follow one of the following guidelines:
Also Check: Shampoo For Sensitive Skin Eczema
Food Allergy And Intolerance
In general, food allergy is caused by immunological mechanisms, food intolerance is not. Food intolerance is relatively common: certain chemicals in foods may cause worsening of the eczemafor example, tartrazine or other colourings in foodby mechanisms that are unclear.
Food allergy is age dependent. It may be severe in the infant and become less so with age. Allergy to some foods is relatively transient, whereas allergy to peanuts or shellfish may continue throughout life.
The association between atopic eczema and food allergy is complex, though it is usually children with severe atopic eczema who have food allergy. Probably less than 10% of all children with atopic eczema have IgE mediated food allergy with angioedema and urticaria, when the diagnosis is obvious from the immediacy of the symptoms and can be confirmed by a wheal > 5 mm in diameter after a skin prick test. Some of these children have multiple food allergies. There is no doubt that IgE mediated food allergy can act as a trigger for exacerbations of eczema, but most parents recognise the allergy and the food is avoided. What is not clear is the role of late phase food reactions, which cause exacerbations of the eczema without urticaria or angioedema. These can be confirmed by atopy patch tests and food provocation tests. This is receiving increasing attention.
What Caused My Babys Eczema
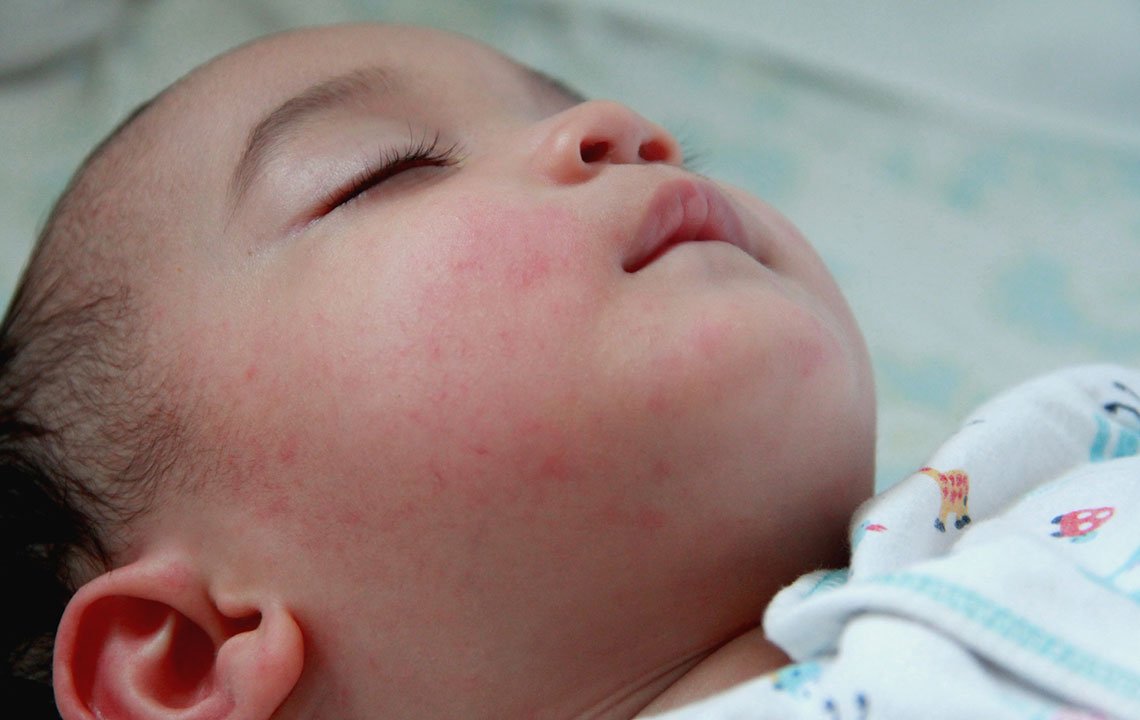
There is no single cause of atopic eczema. Eczema is a complex condition it is genetic but also involves an overactive immune response to environmental factors, which cause eczema flares. Because the atopic gene is hereditary, it runs in families, and is responsible for three conditions: eczema, asthma and hay fever.
Fifty per cent of people with eczema have an additional genetic element a difference in a skin protein called filaggrin which leads to further problems in the skin barrier. All atopic conditions can be linked to allergies in some people, but there are also many universal irritants, such as soap and heat.
Also Check: How To Avoid Itching Eczema
Progression Of Eczema In Infants And Children
Baby eczema is most prominent on the cheeks, forehead, and scalp of an infant within the first few months of life, and often tends to make the skin look more red and weepy than at other ages.
The eczema can appear on other parts of the body as well, including the diaper area.
When the infant begins to crawl, usually between 6 and 12 months, eczema will typically affect the elbows and knees, which rub on the ground. The eczema rash can become infected, resulting in a yellowish crust or tiny bumps of pus.
When the child is around age 2, eczema may begin to appear on the inside of the elbows and behind the knees, as well as on the wrists, ankles, and hands. It may also appear around the mouth and eyelids.
This eczema tends to be drier, scalier, and thicker .
Causes Of Atopic Eczema
The exact cause of atopic eczema is unknown, but it’s clear it is not down to one single thing.
Atopic eczema often occurs in people who get allergies. “Atopic” means sensitivity to allergens.
It can run in families, and often develops alongside other conditions, such as asthma and hay fever.
The symptoms of atopic eczema often have certain triggers, such as soaps, detergents, stress and the weather.
Sometimes food allergies can play a part, especially in young children with severe eczema.
You may be asked to keep a food diary to try to determine whether a specific food makes your symptoms worse.
Allergy tests are not usually needed, although they’re sometimes helpful in identifying whether a food allergy may be triggering symptoms.
You May Like: Why Do I Get Eczema On My Face
Food Allergy And Atopic Eczema
Less than 10% of children with atopic eczema have food allergy or food intolerance as exacerbating factors
Food allergy may be IgE mediated, giving an immediate reaction
Food allergy may be a late phase reaction, as proved by atopy patch tests
Food intolerance to ingested chemicals such as colourings may occur and are not immunologically mediated
Exclusion diets are helpful in a small proportion of children with atopic eczema.
What Causes Atopic Dermatitis In A Child
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is not known. But some things are linked to it. They include:
-
Genes. This skin problem can be passed on from parents to a child.
-
Immune system. An immune system that isnt fully developed may affect how much protection the skin can give.
-
External factors. These include being in winter weather, using hot water for bathing, using soap, and being in dry, hot temperatures.
Read Also: Scalp Eczema And Hair Loss
Foods To Avoid With Eczema In Toddlers
If you have a toddler with eczema issues and youre often wondering what food to give your child, then this article may help you. There are many theories about what causes eczema in children. One article suggests that eczema is due to the immune system not working properly. Eczema is a chronic skin condition due to inflammation. There are many foods that can either help or worsen eczema. Its important to know what foods to give your child and what foods to avoid with eczema in toddlers. I hope the following information will help guide you.
What Are The Differences Between The Skin Symptoms Of Food Allergy And Eczema
An allergic reaction to a food typically happens quickly. Symptoms of an allergic reaction then go away, usually after several hours, as long as the food is not eaten again. Eczema is a chronic condition that does not go away quickly. Eczema tends to show up in predictable places, such as on the cheeks of young babies or elbow creases of older children. The places on the skin where symptoms of an allergic reaction to food appear are more unpredictable. Hives, redness and itching from an allergic reaction can show up just about anywhere on the body and even in different places each time the food is eaten.
Don’t Miss: Is Dial Soap Good For Eczema
When To Seek Medical Advice
See a GP if you have symptoms of atopic eczema. They’ll usually be able to diagnose atopic eczema by looking at your skin and asking questions, such as:
- whether the rash is itchy and where it appears
- when the symptoms first began
- whether it comes and goes over time
- whether there’s a history of atopic eczema in your family
- whether you have any other conditions, such as allergies or asthma
- whether something in your diet or lifestyle may be contributing to your symptoms
Typically, to be diagnosed with atopic eczema you should have had an itchy skin condition in the last 12 months and 3 or more of the following:
- visibly irritated red skin in the creases of your skin such as the insides of your elbows or behind your knees at the time of examination by a health professional
- a history of skin irritation occurring in the same areas mentioned above
- generally dry skin in the last 12 months
- a history of asthma or hay fever children under 4 must have an immediate relative, such as a parent, brother or sister, who has 1 of these conditions
- the condition started before the age of 2
What Happens During An Allergy Test
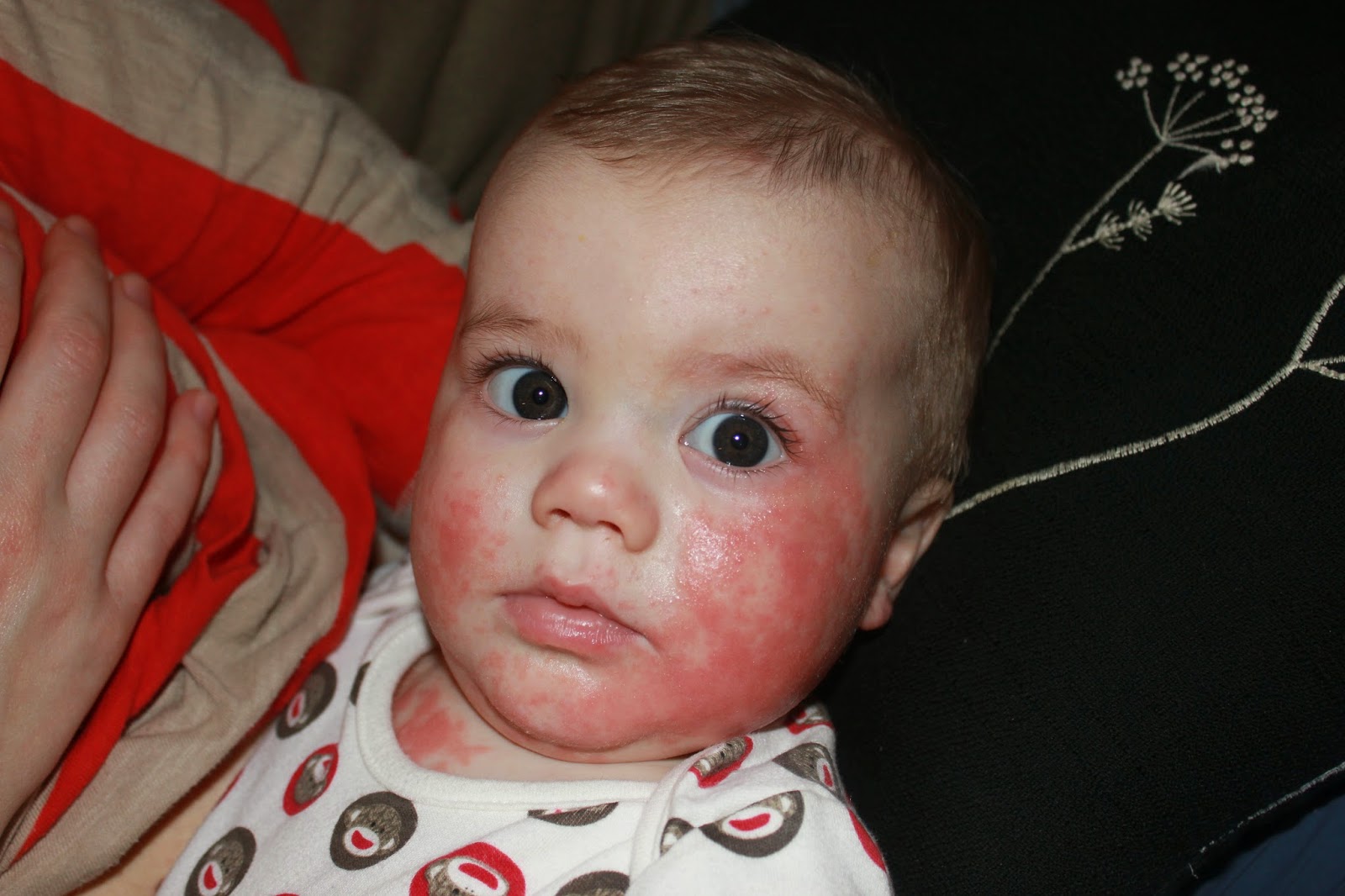
Different types of allergy tests are used. Heres what happens during each:
Skin prick test: During this test, small amounts of substances to which your child may be allergic will be placed on your childs skin. Usually, the substances are placed on the forearm or back. Next, the skin is scratched or pricked. The skin is checked for a reaction at specific times.
Patch test: Substances to which your child may be allergic are applied to discs. The discs are then taped to your childs skin without eczema, usually on the back. Each disc contains a different allergen . Your childs skin be will checked at specific times for reactions.
Food allergy testing: A skin prick test or blood test can tell you what food allergies your child does not have.
If your child has a positive reaction to a food during one of these tests, the results must be confirmed with another type of test. Your childs dermatologist or allergist may refer to this type of type of test as a food challenge.
There are different types of food challenges. If this test is right for your child, the dermatologist or allergist can tell you what to expect.
Related AAD resources
ReferencesSidbury, R. Whats new in atopic dermatitis research? . In Lio PA , What’s boiling over: Atopic dermatitis and other eczematous conditions. Forum presented at the Summer Academy Meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, Chicago, IL.
You May Like: Difference Between Scabies And Eczema
Eczema / Dermatitis Treatments
- Emollients. Emollient lotions and creams are prescribed for treating atopic eczema and dry skin, and are, in their simplest form, mixtures of oil and water.
- Topical steroid creams. It is sometimes necessary to apply topical corticosteroids , as these reduce inflammation in the skin caused by eczema.
- Wet wraps. Sometimes, special pyjama-like garments that are used for children may also help certain areas of your body that have not responded to the usual topical application of emollients and steroids.
- Calcineurin inhibitors. Calcineurin inhibitors are an alternative to steroid creams. Like steroid creams, they reduce the skin inflammation and can lessen itching.
There is more detailed information about each treatment on our downloadable eczema Factsheet
Im constantly physically and mentally exhausted. I have blood and skin in my bed every morning, skin coming off in my clothing, and have to cover myself in emollients etc My children dont want to be near me when Im sticky. Patient with severe eczema.