What Are The Symptoms Of Folliculitis
In most cases, the main symptom of folliculitis is red bumps that look like pimples on your skin. These could also look like theyre white-filled bumps or they could be filled with pus . Folliculitis can feel itchy and uncomfortable. Many people feel the need to scratch when they have folliculitis. Its best to try and not scratch at the spots because you dont want to open them up .
Atopic Hands And Feet
Localized acral involvement is a relatively common presentation of atopic dermatitis, and is part of the minor criteria by Hanifin and Rajka. Agrup in 1969 showed that one-third of the patients of atopic dermatitis had hand involvement as the initial presentation. Dry scaly, itchy lesions especially on the dorsa and wrists are seen in these patients . Finger pad eczema, discussed before, can either be a sole presentation or part of the more extensive hand eczema. Similar lesions on toes are referred to as atopic feet or atopic winter feet. In children, these lesions tend to improve during summers or after puberty. Soaps and other irritants tend to worsen these lesions. In persistent or patterned lesions, contact dermatitis should be ruled out. Avoidance of known irritants, regular use of greasier emollients and topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors are helpful. As exposure to extraneous irritants cannot be avoided completely, periodic flares are not uncommon.
Figure 12::
How Can Atopic Eczema Be Treated
Topical means applied to the skin surface. Most eczema treatments are topical, although for more severe eczema some people need to take oral medication as well.
Complete emollient therapy is the mainstay of treatment for all patients with eczema as the most important part of their treatment this means regular application of a moisturiser and washing with a moisturiser instead of soap .
Read Also: 4 Month Old Eczema Treatment
Skin: Condition: Infomation Moisturisers
These should be applied several times every day to help the outer layer of your skin function better as a barrier to your environment. The drier your skin, the more frequently you should apply a moisturiser. Many different ones are available, varying in their degree of greasiness, and it is important that you choose one you like to use. The best one to use is the greasiest one you are prepared to apply. Moisturisers containing an antiseptic may be useful if repeated infections are a problem.
Aqueous cream was originally developed as a soap substitute. It is often used as a moisturiser but can irritate the skin and make your AE worse. For this reason it is recommended that aqueous cream is not used as a moisturiser.
CAUTION: This leaflet mentions emollients . When paraffin-containing emollient products get in contact with dressings, clothing, bed linen or hair, there is a danger that a naked flame or cigarette smoking could cause these to catch fire. To reduce the fire risk, patients using paraffin-containing skincare or haircare products are advised to avoid naked flames completely, including smoking cigarettes and being near people who are smoking or using naked flames. It is also advisable to wash clothing and bed linen regularly, preferably daily.
Cause Of Seborrheic Dermatitis
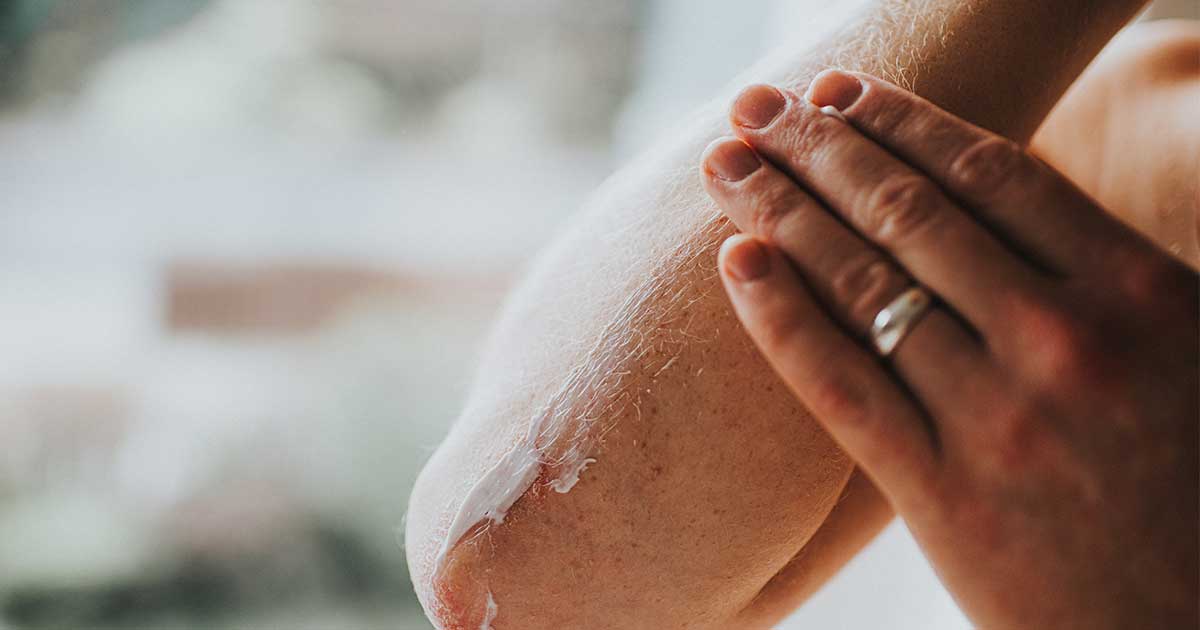

There is no direct cause of seborrheic dermatitis, as this condition often develops in people who are otherwise healthy. Although, there are a few risk factors that may increase a persons chances of developing this chronic condition:
- Weakened immune system
- Chronic stress
- Genetics
- Pre-existing conditions, including psoriasis, HIV, acne, rosacea, Parkinson disease, depression, alcoholism, eating disorders, recovery from stroke or heart attack
You May Like: Is Hydrocortisone Used For Eczema
Treating Stress And Eczema
To reduce eczema flare-ups, treat your skin well and keep stress in check. According to the World Allergy Organization, you can tackle eczema in several ways. Learning about eczema and how to manage it is essential for eczema sufferers, so work with your dermatologist or primary care physician to treat your eczema and educate yourself. Keep skin moisturized by frequently applying rich moisturizing creams, and use topical steroid creams as needed to reduce inflammation. If your doctor suggests it, oral antihistamines, ultraviolet therapy, wet dressings, antifungal creams and antibiotics may also be effective in very serious cases. To soothe stress, the AFP recommends relaxation and stress management techniques, as well as exercise. For serious stress and anxiety, psychotherapy and even anti-anxiety medications may help.
- To reduce eczema flare-ups, treat your skin well and keep stress in check.
- To soothe stress, the AFP recommends relaxation and stress management techniques, as well as exercise.
How To Use It
People can buy aloe vera gel in health stores or online, or they can purchase an aloe vera plant and use the gel directly from its leaves.
Individuals should aim to use aloe gel products with few ingredients others can contain preservatives, alcohol, fragrances, and colors, which can irritate sensitive skin. Additionally, alcohol and other drying ingredients could make eczema worse.
However, start with a small amount of gel to check for skin sensitivity, as sometimes, aloe vera can cause burning or stinging. However, it is generally safe and effective for adults and children.
Don’t Miss: Can Eczema Occur At Any Age
Skin: Condition: Infomation Topical Steroid Creams Or Ointments
These will usually improve the redness and itching of AE when it is active. They come in different strengths and your doctor will advise you on which type needs to be used, where and for how long. Use a fingertip unit to cover an area the size of the front and back of your hand.
Used appropriately topical steroids are very effective and safe to use. Used inappropriately , topical steroids may cause side effects, including thinning of the skin. However insufficient treatment with topical steroids is generally considered by doctors to be more of a problem than overuse.
Weaker topical steroids are usually prescribed for use on the face, breasts, genitals, eyelids and armpits. This is because the skin is much thinner in these sites. Stronger steroids can be used at other sites, especially thicker areas such as hands and feet.
It is recommended that you do not purchase natural herbal creams, as they can cause irritation and allergic reactions. Some so-called natural creams have been shown to contain potent steroids. Other herbal creams have been shown to contain high levels of harmful bacteria including MRSA which may cause skin infections and septicaemia.
Recognizing And Treating Follicular Eczema
Follicular Contact Dermatitis is a common skin condition affecting approximately 10% of the population.1,2 Follicular contact dermatitis is characterized by itchy red bumps which are usually located on your face, neck, chest and back. These bumps may appear anywhere from small to large and they vary in size from those less than 1 mm to larger ones measuring up to 2 cm in diameter.3 Follicular eczema is a type of contact dermatitis caused by bacteria living on the surface of your skin.4 It is not clear why some individuals develop it while others do not.5
The most commonly reported symptoms include: itching, burning, stinging, swelling and irritation.6 The bumps are often painful and may cause severe discomfort.7,8
Itching
Hives are one of the first signs of follicular contact dermatitis.9 They occur when certain types of white blood cells called neutrophils release chemicals into your bloodstream.10 Neutrophils play a role in fighting off invading organisms such as bacteria, fungi and viruses.11 Neutrophil activity causes inflammation throughout the body including the skin.12,13
When you develop hives, your bodys immune system overreacts to an invading allergen such as poison ivy oil or nickel.14-16 Your immune system believes that these elements are harmful invaders and it tries to fight off the threat through release of inflammatory mediators.17
Follicular eczema and hives can be effectively treated with high quality skincare products and lifestyle changes.
Read Also: Best Treatment For Eczema On Feet
Follicular Eczema: Treatment Symptoms And Causes
Follicular eczema describes eczema that has affected the hair follicles. Your hair follicles are the tiny tubes in your skin through which hair grows. As with other types of eczema, you may experience itching, redness, and oozing bumps on your skin, specifically surrounding the follicles. Follicular eczema occurs most commonly surrounding body hair on the chest, arms, back, stomach, or legs.
Can Atopic Eczema Be Cured
No, it cannot be cured, but there are many ways of controlling it. As they get older, most children with atopic eczema will see their AE improve with 60% clear by their teens. However, many of these people continue to have dry skin and so need to continue to avoid irritants such as soaps, detergents and bubble baths.
AE may be troublesome for people in certain jobs that involve contact with irritant materials, such as catering, hairdressing, cleaning or healthcare work. In later life, AE can present as hand dermatitis and as result exposure to irritants and allergens must be avoided both in the home and at work.
Also Check: When To See A Doctor About Eczema
Balancing The Skins Acidity Levels
Vinegar is highly acidic. The skin is naturally acidic, but people with eczema may have less acidic skin than others, which can weaken the skins defenses.
Applying diluted apple cider vinegar could help balance the skins acidity levels, but vinegar can cause burns if it is not diluted.
In contrast, many soaps, detergents, and cleansers are alkaline. They can disrupt the acidity of the skin, which can leave the skin vulnerable to damage. This may explain why washing with certain soaps can cause eczema flares.
My Familys Eczema Treatment Plan
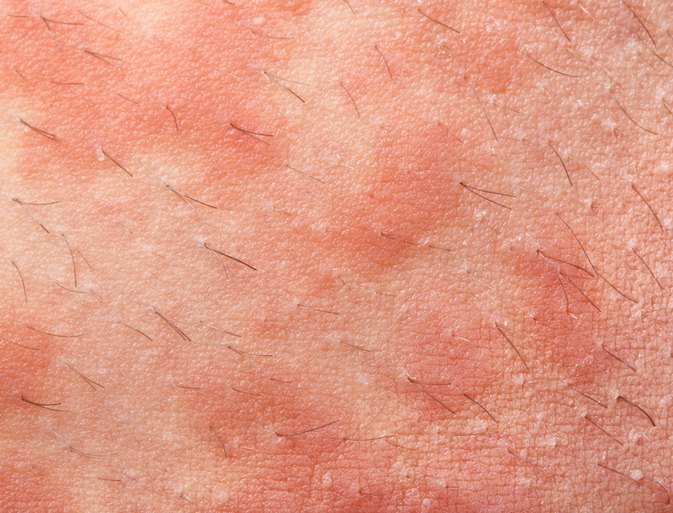
My family has had the enormous project of dealing with my sons eczema and asthma. It began as soon as he turned 3 months old . However, his condition lasted way past the 18 months of age that my pediatrician and I hoped for, that would mark it as transient infant eczema. It was also much more severe. I could write at length about how harrowing his eczema and asthma was, especially for a mother, watching her child writhing in pain, seeing blood patches on his pillow and sheets, nebulizing him morning, noon, and night because he would wheeze if he ran around the house once. I want to focus on what information I have acquired over the two years we have dealt with this.
I am not a physician nor a pediatrician. So, the treatments I am recommending are from what I have gathered from my pediatrician, Dr. Google, and in talking to others about eczema and asthma. And I did not seek approval from our pediatrician before starting each one of these therapies. This is written by a mom who knows her son, agonized over his pain, and determined it was unacceptable that her child exist in a state of such mental and physical anguish.
Two major pieces of information that serve as the core for these suggested therapies:
Here are the highlights of what I have put together as the treatment plan for our son.
Vrinda Nargund
Also Check: Foods To Eat To Get Rid Of Eczema
Chemicals Capable Of Eliciting Follicular Contact Dermatitis
Several chemicals, including topical antibiotics, have been described in either individual reports or larger studies to elicit follicular contact dermatitis. The agents associated with the development of follicular contact dermatitis can be allergens or irritants . Several metals have been associated with follicular patch test reactions: chromium, cobalt, copper, fluoride, and nickel. Allergic and non-allergic development of follicular contact dermatitis has also been observed following exposure to tocopheryl linoleate, a vitamin E derivative.
Follicular Eczema: Symptoms Treatment And Prevention
Follicular eczema is the form of a common skin condition atopic dermatitis with reactions that occur in the hair follicle. Atopic dermatitis occurs when your skins outer layer is unable to protect you from external threats, such as allergens, bacteria, or other irritants.
According to the National Eczema Association, the exact cause of follicular eczema is unknown, but you may be more at risk if there is a history of asthma, hay fever or eczema in your family.
Because it occurs in hair follicles, follicular eczema reactions tend to look like goosebumps that wont go away. Hair in the affected region may stand on end, and inflammation can show up as redness, swelling, itchiness, or warmth.
Other general symptoms of atopic dermatitis include:
- a rash on the face, hands, feet, arms, or legs
- itching
- cracked, dry or scaly skin
- crusty or weepy sores
Although eczema has no cure, you can treat its symptoms. Commonly, dermatologists recommend corticosteroid creams. Your doctor might also suggest specific skin cleansers and moisturizers.
There are several self-care methods of treating active flare-ups of follicular eczema and atopic dermatitis, including:
- placing a warm, clean washcloth on the affected area
- soaking the affected area in warm water
- applying moisturizer immediately after removing the cloth or exiting the bath
- keeping your skin moisturized with fragrance-free moisturizers
- wearing loose-fitting clothes
Don’t Miss: How To Make Eczema Cream
Signs And Symptoms Of Atopic Dermatitis
Incessant pruritus is the only symptom of AD. The disease typically has an intermittent course with flares and remissions occurring, often for unexplained reasons.
Primary physical findings include the following:
-
Xerosis
-
Lichenification
-
Eczematous lesions
The eczematous changes and its morphology are seen in different locations, depending on the age of the patient .
The following is a constellation of symptoms and features commonly seen in AD:
-
Pruritus
-
Peripheral eosinophilia
-
Staphylococcus aureus superinfection
-
Personal history of asthma or hay fever or a history of atopic diseases in a first-degree relative
See Clinical Presentation for more detail.
How To Use Bentonite Clay On Eczema
The application of this clay can be performed using a few different methods.
It can be added to the bath, which will allow a good amount of time for the product to work its magic.
Another topical method is to make it into a paste and apply it directly to the affected area until the clay has dried. The only downside to this paste method is that the longer it can stay on the skin wet, the longer it can do its job and so quicker drying means less benefit.
The final method is as an internal cleanse, used for helping digestion issues and detoxing. Taking bentonite clay in this manner is done by mixing the clay powder with water and drinking. Yummy!
Read Also: Why Is My Eczema So Bad In Summer
Fish Oil For Eczema Treatment
The skin and tissues of specific fishes are used to obtain fish oil and is considered very good for eczema. Gel capsules are the most common form of fish oil. The capsules can either be consumed internally or can even be squeezed to extract the oil. However, make sure that a sterilized or clean pin is made use to puncture them and obtain the oil to prevent contamination with bacteria.
Ways To Diagnose And Treat Eczema And Acne
Eczema is diagnosed by a dermatologist based on personal and family history and the physical appearance of the skin. A skin biopsy, removing a small tissue of skin for further examination, may help confirm a diagnosis and rule out other skin conditions, like fungal infections.
Eczema cannot be cured, but treatments like moisturizing the skin and managing stress can help reduce symptoms. Topical steroids, Eucrisa , Elidel , or coal tar can help reduce pain, redness, and itching.
Acne is also diagnosed by a dermatologist based on the physical appearance of the skin. Risk factors such as changing hormone levels during puberty, menstruation, medications, and family history increase the likelihood of developing acne.
Acne treatment includes regularly cleansing the skin and keeping it properly moisturized. Oral or topical antibiotics, steroids, and retinoids may also be prescribed to reduce acne and improve the appearance of your skin.
Also Check: Foods That Cause Eczema On Face
How Different Skin Types Are Affected
The features of eczema differ depending on the persons skin type.
On paler skin, the typical pattern is inflamed, red or dark pink patches, with dry itchy skin, which in severe flares may ooze with small vesicles .
On darker skin, inflammation is more difficult to detect, as it is seen as various stages of hyper-pigmentation and is more subtle, so often redness is not seen. As a result, the severity of eczema can be underestimated.
Post-inflammatory hypo- and hyper-pigmentation are a much greater concern in people with darker skin, as it can take months for this to resolve and the discoloration can sometimes be a greater concern than the eczema itself.
Another feature of eczema, more commonly found in darker skin, is follicular prominence. This is where the eczema appears in small, itchy bumps or papules on the skin mainly on the trunk and forearms. Dry skin and scale can also be more prominent, as its white or grey colour shows up most noticeably.
A UK longitudinal study into ethnic variations in atopic eczema reported that children with darker skin were more likely to develop atopic eczema than their white counterparts and were six times more likely to develop severe eczema.
What Makes The Skin Get Drier
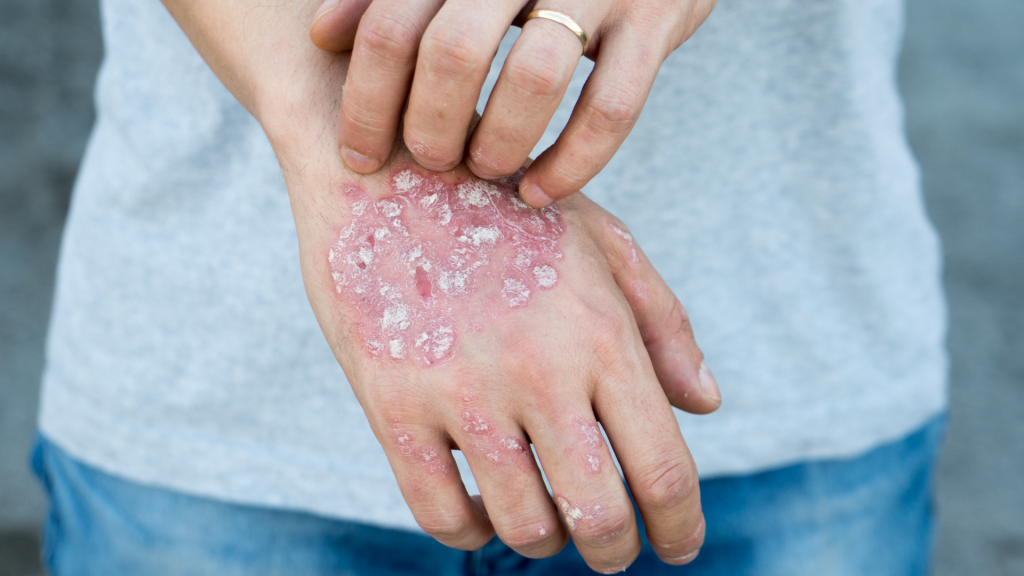
Dry skin is a sign of the loss of barrier function. Factors that make the skin even drier may make eczema harder to control:
- Winter weather
- Prescribed and over-the-counter treatment creams
- Dusty environments
It is common sense to avoid the substances that irritate.
- Dilute washing powder: use a small amount in each load and make sure the clothes are well rinsed out in freshwater. Select non-fragranced laundry detergent.
- If you use soap to wash your hands, rinse off thoroughly.
- Wear gloves and covering clothing to protect against detergents, cleaning chemicals, solvents etc. at work and at home.
- Limit preparations applied to the skin to those specifically prescribed for eczema.
Also Check: Forces Of Nature Eczema Control