Atopic Dermatitis Children Foods To Avoid
1 in 3 children with eczema has a food allergy that could make symptoms worse, even though eczema is not, according to experts, a condition caused by a food allergy. However i potentially allergenic foods I’m:
- Latte
- Crustaceans
- Soy
Your pediatrician may recommend that you stop the artificial milk usual to switch to one hypoallergenic formula and check what the reactions are.
What Caused My Babys Eczema
There is no single cause of atopic eczema. Eczema is a complex condition it is genetic but also involves an overactive immune response to environmental factors, which cause eczema flares. Because the atopic gene is hereditary, it runs in families, and is responsible for three conditions: eczema, asthma and hay fever.
Fifty per cent of people with eczema have an additional genetic element a difference in a skin protein called filaggrin which leads to further problems in the skin barrier. All atopic conditions can be linked to allergies in some people, but there are also many universal irritants, such as soap and heat.
What Can Trigger Eczema
Individual trigger factors vary from person to person, some trigger factors may be easy to identify whilst others may not be so easy to work out. If you suspect a specific food or something in the environment may be a trigger factor keeping a symptoms diary can help work out patterns of exposure and signs and symptoms and may be useful to provide to your doctor.
Eczema may be made worse by coming into contact with one or more of the following trigger factors:
- Heat or changes in temperature
- Irritants for example
- Chemicals for example swimming in chlorinated water
- Fabrics like wool or synthetics
- Food allergy or intolerances
- Contact allergens in the environment for example house dust mite, pollen or animal dander can make eczema worse.
- Viral or bacterial infections
- Changes in the weather or sudden changes in temperature
Recommended Reading: Remedies For Eczema On Hands
How Is Atopic Dermatitis In Children Diagnosed
Thereâs no specific test to confirm or diagnose eczema in children. But if you notice eczema-like symptoms, tell your doctor about it. The doctor will do a complete physical exam and take a detailed medical history.
They may ask also important questions regarding family history such as:
- Do any close family members have atopic dermatitis?
- Does anyone have a history of asthma?
- Are any family members prone to nasal allergies like hay fever or allergic rhinitis?
The doctor may also perform certain tests to confirm signs of atopic dermatitis. This includes:
- Blood tests to check for immunoglobulin E levels, a substance your bodyâs immune system releases. Itâs common for children with allergies to have high levels of IgE.
- Skin tests to check for allergies or other skin conditions.
What Can Make Eczema Worse
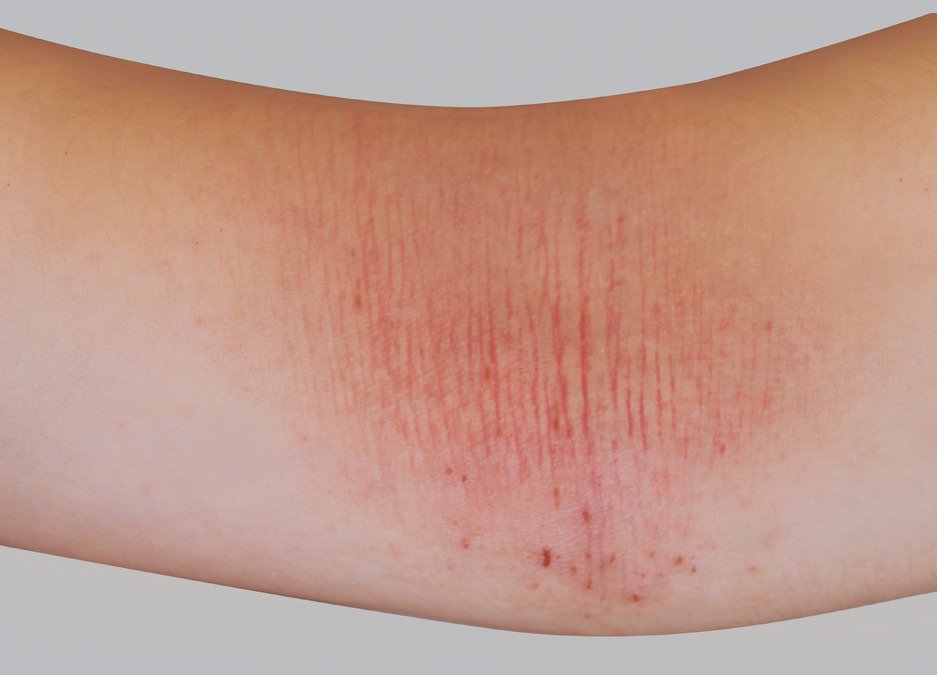
Patients with eczema usually have sensitive and dry skin. Many patients find that during the winter months when the humidity is very low, the dryness and itchiness is worse.
Some patients are very easily irritated by sweat and may have more problems during the summer months.
Sudden changes in temperature are irritating to patients. Use of harsh soaps or detergents and exposure to wool may also cause itching and irritation.
You May Like: California Baby Therapeutic Relief Eczema Shampoo & Bodywash
Triggers Of Eczema Flare
- Soaps. Never use bubble bath. It can cause a major flare-up.
- Pollens. Keep your child from lying on the grass during grass pollen season.
- Animals. Avoid any animals that make the rash worse.
- Foods. If certain foods cause severe itching , avoid them.
- Wool. Avoid wool fibers and clothes made of other scratchy, rough materials.
- Dry Air. Use a humidifier if the air in your home is dry.
- Herpes Virus Infection . Keep your child away from anyone with fever blisters . The herpes virus can cause a serious skin infection in children with eczema.
- Eczema is not caused by laundry soap you use to wash clothing.
Instructions To Soak And Seal
Dont limit moisturizing to just bath time. Slather it on your child throughout the day whenever their skin starts to itch or feel dry. Try using an ointment or a cream rather than a lotion and apply it with your palms, stroking lightly in a downward direction.
Don’t Miss: Eczema Around Eyes How To Treat
How Can You Help A Toddler With Their Eczema
Helping your toddler deal with the itch can go a long way in helping them manage their eczema. When you notice your toddler scratching, distract them with another activity, particularly one that keeps their hands busy, like coloring.
You can also try wet wrapping the affected skin to help alleviate the itch and keep little hands from getting at the rash.
Wet wrapping involves wrapping the skin with a cloth or bandage dressing thats first moistened with warm water. When the wrap is in place, apply a dry cloth or dressing over the wet one.
Clothing can act as another barrier between your child and their eczema. If your child has eczema around their elbows, dress them in long sleeves when possible. If its on their legs, try long pants.
Recommended Reading: Best Diapers For Babies With Eczema
Living With Eczema And Atopic Dermatitis
Eczema can flare up when you are under stress. Learn how to recognize and cope with stress. Stress reduction techniques can help. Changing your activities to reduce daily stress can also be helpful.
The area where you had the eczema may easily get irritated again, so it needs special care. Continue to follow the tips provided here even after your skin has healed.
Don’t Miss: Allergy Test For Toddler With Eczema
Avoid Triggers And Treat Infection
Stay cool
Getting too hot from clothing or heating can make eczema worse – stay cool.
Avoid soap and fragrances
Soap and fragrances are the most common triggers of eczema. Only use skin care products designed for eczema. Many are available on prescription from your doctor or nurse prescriber.
Prevent skin infections
Eczema is made worse by infection such as from:
- school sores
- the cold sore virus which can cause severe painful infection of eczema
Avoid contact with cold sores. See your family doctor urgently if your child gets an infection from cold sores.
Removing foods from your child’s diet does not usually help eczema
Removing foods from your child’s diet does not usually help eczema and can be dangerous, leading to anaphylaxis.
Please talk with your doctor about this.
Eczema Treatment For Children
With a good regimen of bathing, moisturizing and prescription medications , you can help your child be more comfortable
There is no one right treatment for eczema in children. What works for another child may not work for yours. You may have to go through several treatments or combinations of treatments in partnership with your doctor before you find one that helps manage your childs symptoms. Be persistent and patient as treating eczema can take several weeks or longer before you see real progress.
Recommended Reading: How To Calm Down Eczema
What Does Baby Eczema Look Like
Eczema doesn’t look the same on every baby. In babies with light skin, it usually shows up as patches of red skin. In darker-skinned babies, the rash might look purplish, brownish, or grayish. Eczema can be harder to see on babies with dark skin.
These patches are almost always dry, itchy, and rough.
Babies can get the condition just about anywhere on their body. Most often, it affects their cheeks and the joints of their arms and legs.
Its easy to confuse baby eczema with cradle cap. But there are some key differences.
Cradle cap is much less itchy and irritated. It generally clears up by age 8 months and usually appears on the scalp, sides of the nose, eyelids and eyebrows, and behind the ears. See a photo of what cradle cap looks like.
Which Is The Best Emollient For My Baby

Emollients treat dry skin by providing a surface film of oils. This increases water in the upper layer of the skin, restoring and providing a robust skin barrier, to prevent the entry of environmental agents or triggers.
Emollients soften the skin and reduce itch. If they are used regularly to maintain skin hydration, they can reduce the frequency of eczema flares. Leave-on emollients include lotions, creams,ointments and gels.
The emollient advised or prescribed for your baby should prevent dry skin and not cause irritation. You might need to try several products until you find the right one. Apply leave-on emollients regularly, throughout the day for example, at every nappy change and after bathing.
Use the product liberally . To apply the product, dot it all over the skin, and then smooth it in, using a gentle, downward, stroking motion rather than rubbing in.
Recommended Reading: Is Chocolate Bad For Eczema
What Is The Cause Of Eczema In Children And Babies
There is often no obvious cause of eczema in children, which often appears in the first five years of a childs life. However, there are some identifiable triggers, and managing flare-ups of the condition can be easier if you can pinpoint what these are for your child.
Whilst the exact cause of eczema in children is unknown, research has shown that it is largely down to a combination of your childs genes and triggers in their environment.
These environmental factors can range from the foods they eat to washing powders, cigarette smoke, soaps, stuffed animals, or simply the weather. You may find that your childs eczema tends to get worse in the winter due to the air being drier. Additionally, your babys saliva can cause irritation on their cheeks, chin and neck due to drooling.
These triggers in the environment cause the immune system to switch on unnecessarily. This in turn causes your childs skin cells not to behave as they should, which is what makes their skin so red and angry looking.
Your child is more likely to develop eczema, particularly atopic dermatitis, if your family has a history of the condition, but also if there is a history of asthma or hay fever.
How Often Should I Bathe My Baby
If your baby has eczema, a daily bath with an emollient will help soothe the eczema and reduce dry skin and itching, while cleansing the skin, removing dirt and repairing the skin barrier. Use leave-on emollients instead of soaps, baby washes or bubble bath, or alternatively use emollient wash products or bath additives. Avoid any perfumed products and keep the water tepid, as heat can aggravate eczema.
Recommended Reading: Why Do Newborns Get Eczema
How Can Parents Help
Help prevent or treat eczema by keeping your child’s skin from getting dry or itchy and avoiding triggers that cause flare-ups. Try these suggestions:
- Kids should take short baths or showers in warm water. Use mild unscented soaps or non-soap cleansers and pat the skin dry before putting on cream or ointment. Teens should use unscented makeup and oil-free facial moisturizers.
- Ask your doctor if it’s OK to use oatmeal soaking products in the bath to help control itching.
- Kids should wear soft clothes that “breathe,” such as those made from cotton. Wool or polyester may be too harsh or irritating.
- Keep your child’s fingernails short to prevent skin damage from scratching. Try having your child wear comfortable, light gloves to bed if scratching at night is a problem.
- Kids should avoid becoming overheated, which can lead to flare-ups.
- Kids should drink plenty of water, which adds moisture to the skin.
- Get rid of known allergens in your household and help your child avoid others, like pollen, mold, and tobacco smoke.
- Stress can make eczema worse. Help your child find ways to deal with stress .
What Foods Should I Eat Or Avoid To Reduce My Risk Of Eczema
The connection between eczema and food allergies is unclear. If you have food allergies, then one of the reasons why you must avoid that food is that it may cause or worsen dermatitis. Examples of common allergies include peanuts, dairy, eggs, sugar, alcohol and gluten. Pay attention to what you eat. If your eczema flares up after you eat a certain food, then you might have an allergy to it.
If you dont have a food allergy then there are no foods, including chicken, that will cause or worsen your eczema.
You May Like: Can Black People Get Eczema
When To Seek Medical Advice
See a GP if you have symptoms of atopic eczema. They’ll usually be able to diagnose atopic eczema by looking at your skin and asking questions, such as:
- whether the rash is itchy and where it appears
- when the symptoms first began
- whether it comes and goes over time
- whether there’s a history of atopic eczema in your family
- whether you have any other conditions, such as allergies or asthma
- whether something in your diet or lifestyle may be contributing to your symptoms
Typically, to be diagnosed with atopic eczema you should have had an itchy skin condition in the last 12 months and 3 or more of the following:
- visibly irritated red skin in the creases of your skin such as the insides of your elbows or behind your knees at the time of examination by a health professional
- a history of skin irritation occurring in the same areas mentioned above
- generally dry skin in the last 12 months
- a history of asthma or hay fever children under 4 must have an immediate relative, such as a parent, brother or sister, who has 1 of these conditions
- the condition started before the age of 2
What Is The Cause Of Eczema In Children
Eczema is a common problem in young children and infants. About one-fifth of the worlds children under the age of five suffer from some form of eczema. It is a skin disease characterized by rash and itching which can be very uncomfortable. This article will help you understand eczema, its causes, symptoms, and treatment methods.
Also Check: How Long Does An Eczema Breakout Last
What Are The Symptoms Of Eczema
Eczema is a chronic condition which causes red, itchy areas on the skin. Sometimes the itching is very severe. When skin is scratched it can break open, ooze and then crust over. Symptoms of eczema can come and go. Babies with eczema often have it on their cheeks, forehead and scalp. Older children often have it on their hands, wrists, ankles, feet, and on the inside folds of their elbows and knees.
How Is Facial Eczema In Children Diagnosed
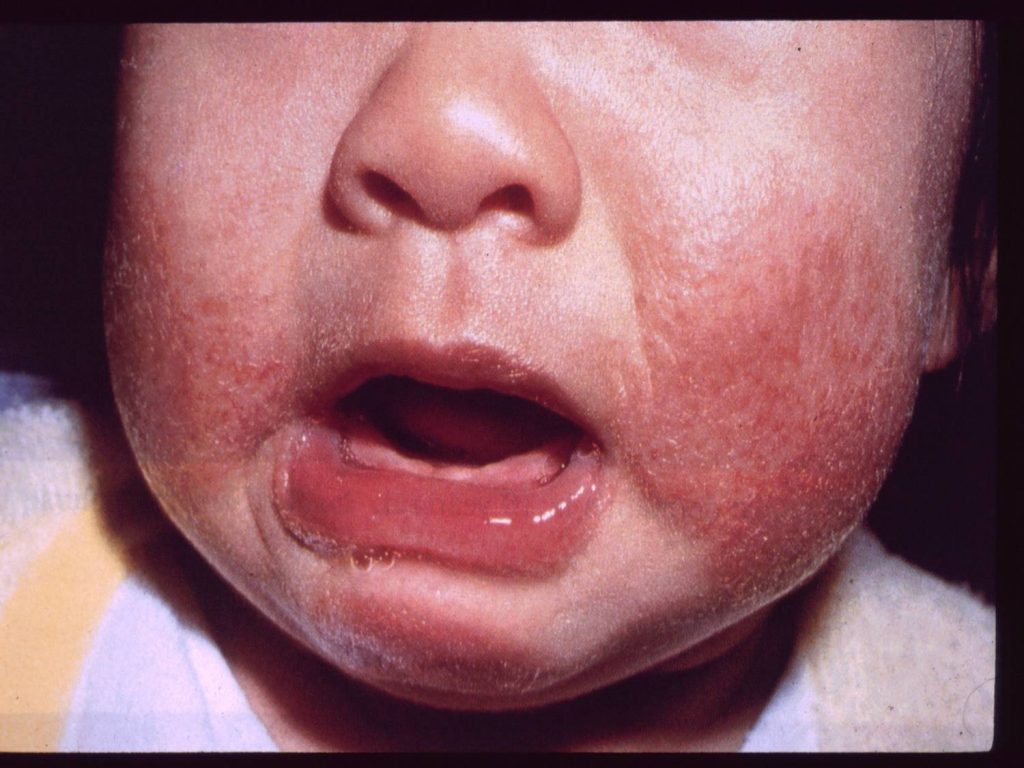
The National Eczema Association estimates that 9.6 million children in America have eczema, which is also known as atopic dermatitis.
Doctors and other healthcare professionals usually diagnose it by looking at the rash and asking questions about triggers and other symptoms like itching.
Its possible that allergy testing, such as skin prick or scratch tests, may be needed to make sure the rash isnt caused by an allergic reaction.
. What your child needs will depend on the severity of the condition and your childs age and overall health.
Here are some common treatment options:
Recommended Reading: Hand Sanitizer For People With Eczema
How Is Eczema Treated
There is no cure for eczema. But treatments can help with symptoms. The doctor will recommend different treatments based on how severe the symptoms are, the child’s age, and where the rash is. Some are “topical” and applied to the skin. Others are taken by mouth.
Topical moisturizers. Skin should be moisturized often . The best time to apply moisturizer is after a bath or shower, with the skin patted dry gently. Ointments and creams are best because they contain a lot of oil. Lotions have too much water to be helpful.
Topical corticosteroids, also called cortisone or steroid creams or ointments. These ease skin inflammation. It’s important not to use a topical steroid prescribed for someone else. These creams and ointments vary in strength, and using the wrong strength in sensitive areas can damage the skin, especially in infants.
Other topical anti-inflammatory medicines. These include medicines that change the way the skin’s immune system reacts.
Medicine taken by mouth. These can include antihistamines to help itchy kids sleep better at night, antibiotics if a rash gets infected by bacteria, and corticosteroid pills or other medicines that suppress the immune system.
Other types of treatment can include:
- wet wraps: damp cloths placed on irritated areas of skin
- bleach baths: bathing in very diluted bleach solution
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Eczema
There are steps you can take that may prevent eczema outbreaks:
- Establish a skin care routine, and follow your healthcare professionals recommendations for keeping your skin healthy.
- Wear gloves for jobs where you have to put your hands in water. Wear cotton gloves under plastic gloves to absorb sweat, and wear gloves outside, especially during the winter months.
- Use mild soap for your bath or shower, and pat your skin dry instead of rubbing. Apply a moisturizing cream or ointment immediately after drying your skin to help seal in the moisture. Reapply cream or ointment two to three times a day.
- Take baths or showers with tepid rather than hot.
- Drink at least eight glasses of water each day. Water helps to keep your skin moist.
- Try to avoid getting too hot and sweaty.
- Wear loose clothes made of cotton and other natural materials. Wash new clothing before wearing. Avoid wool.
- Avoid sudden changes in temperature and humidity.
- Learn to recognize stress in your life and how to manage it. Regular aerobic exercise, hobbies and stress-management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, might help.
- Limit your exposure to known irritants and allergens.
- Avoid scratching or rubbing itchy areas of skin.
Read Also: How To Prevent Dyshidrotic Eczema