Remember Treatment Is Possible
If you’re suffering from red, flaky skin as an adult, there’s both good news and bad news. “We can’t cure eczema, but we can keep it under control,” says Zeichner, who typically treats eczema in adults the same way as in children. It all starts with getting the skin barrier in good shape while reducing inflammation. And it may, depending on the eczema’s severity, be completely treatable via topical prescriptions when paired with certain over-the-counter products.
“For all ages, moisturizing and supporting the skin barrier is the mainstay of maintenance,” says Hadley King, a board-certified dermatologist in New York City. “That means using moisturizers that contain humectants to hydrate, emollients to support the skin barrier, and occlusives to lock in the moisture, several times daily.”
Root Causes Of Eczema & How To Treat It Naturally
Anyone whos ever dealt with the terrible dry, itchy, red skin caused by eczema has probably wondered What the heck is causing this?!
I dont blame you, it can be incredibly frustrating. And when its your child struggling with the painful symptoms, it can be heartbreaking to feel theres nothing you can do to help.
Fortunately, you dont have to just continue suffering or watching your child suffer. Once you know whats causing the symptoms you can actually put a stop to them for good.
So what is causing this skin condition that affects over 30 million Americans?
What Causes Eczema In Adults Look At The Adrenals
Of all the chronic skin conditions, eczema is the one that seems the most temperamental and unpredictable. It appears to be triggered by such diverse and seemingly unrelated causes:
- Metals, in particular, nickel
- Certain fabrics such as wool and polyester
- Irritants such as soaps, detergents, shampoo, bubble bath
- Changes in the weather such as cold and dry weather, dampness
- Allergens such as house dust mites, pet fur, pollen, and molds
- Stress
We all take this as being normal and do not question it. But this easily triggered sensitivity points to also having adrenal weaknesses, since the adrenal glands are responsible for producing anti-inflammatory steroids that keep our bodies in check in response to external changes in chemistry.
More here on Adrenal Fatigue Natural Treatment for Adrenal Fatigue
Also Check: What Does An Eczema Rash Look Like
Alcohol And Nummular Dermatitis
Heavy alcohol use can exacerbate or cause many types of skin lesions. Nummular dermatitis appears more frequently in people who abuse alcohol or drink heavily, especially in those who have abnormal liver function tests, which occur when alcohol damages the liver cells. People with this condition should consult their doctors about the risks of drinking alcohol.
Differences In Rash Appearance By Age
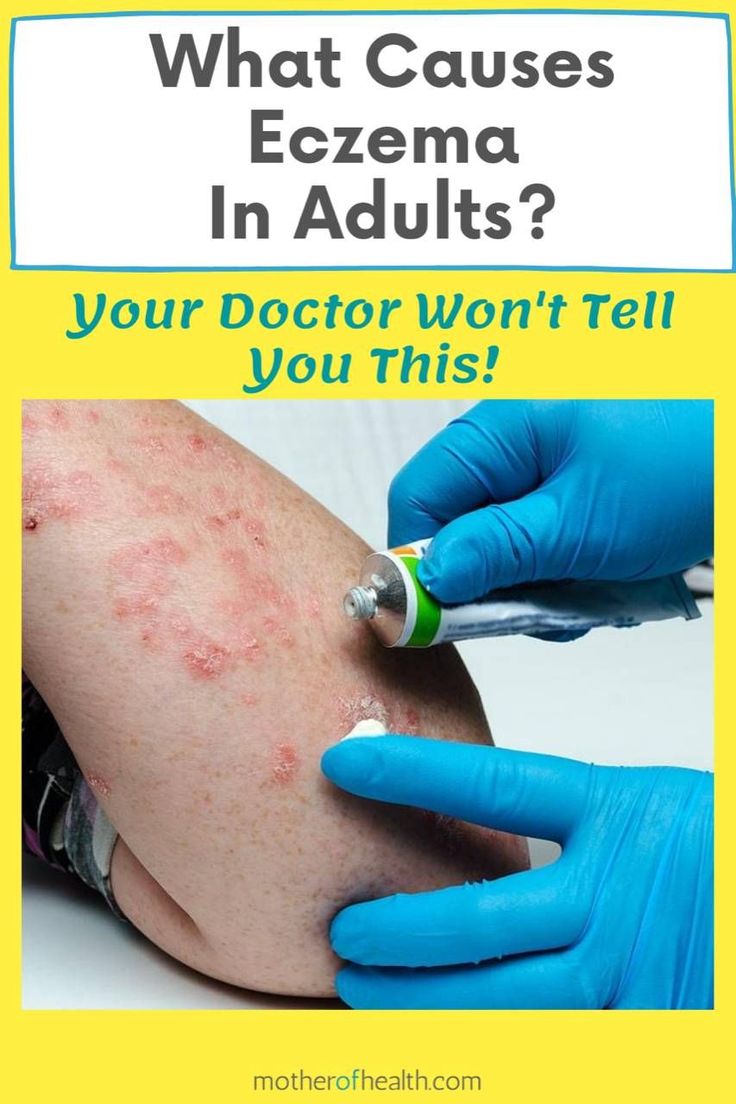
The appearance of atopic dermatitis may depend on your age. In fact, one of the biggest differences between childhood and adult eczema is how it looks on the skin:
- Infants tend to have rashes on the scalp and face, particularly on the cheeks, chin, scalp, and forehead. Skin usually looks weepy and red.
- Babies between 6 months and 12 months often develop eczema on their knees and elbows because of irritation from crawling.
- Toddlers also experience irritation around the knees and elbows but may develop a rash on their ankles, hands, and wrists. A rash around the eyes and mouth is also common in kids under 5. The rash is also more likely to appear scaly.
- Children over 5 typically have rashes behind the knees and in the folds of the elbows. At this age, some people have rashes only on their hands.
- In adults, rashes may appear in these areas but are more common on the hands and eyelids. People who have had lifelong eczema may have thick patches of skin that are darker or lighter than other areas.
Recommended Reading: Why Is My Eczema Burning
Emollients For Washing And Bath/shower Equipment
Soaps, shower gels and bubble baths can dry out the skin. Its best to use an emollient soap substitute or a cream-based leave-on emollient as a soap substitute.
Your GP may refer you to the Community Occupational Therapy Service if you need special bath/shower equipment for safety or if you have difficulty getting in or out of the bath/shower. They can fit a bath seat, grab-rails, a seat in the shower or an alarm if you get into difficulties.
Bath emollients make the shower tray and bath more slippery. Use non-slip bath mats to help reduce the risk of slipping. Support bars fixed to the wall in the shower or by the bath will provide extra safety when showering/bathing. Pour bath emollient into the bath after you get in rather than before. As an extra precaution its a good idea to empty out bath water before getting out of the bath. Be careful not to knock your legs, as this could lead to ulcers. Use a bandage or pad under support stockings for extra protection.
For more detailed information on emollients for moisturising and washing, please download our Emollients factsheet.
What Are The Current Treatment Options For Adults With Eczema
There are various types of treatments to manage eczema. A doctor can go over the different options with you and create a treatment plan that works for your specific type of eczema and symptoms.
Treatments can include lifestyle changes, medications , and alternative treatments. Well discuss each of these options in more detail below.
Recommended Reading: Que Es Bueno Para La Eczema En La Piel
How Is Eczema Treated What Medications Are Used
Treating eczema can be difficult if the cause is something you cant control, like genetics. Fortunately, you may have some influence over your environment and stress levels. Do your best to figure out what triggers or worsens your eczema, and then avoid it. The goal is to reduce itching and discomfort and prevent infection and additional flare-ups.
Consider these treatment tips:
If your child has skin problems, such as eczema, you can:
- Avoid long, hot baths, which can dry the skin. Use lukewarm water instead and give your child sponge baths.
- Apply lotion immediately after bathing while the skin is still moist. This will help trap moisture in the skin.
- Keep the room temperature as regular as possible. Changes in room temperature and humidity can dry the skin.
- Keep your child dressed in cotton. Wool, silk and manmade fabrics such as polyester can irritate the skin.
- Use mild laundry soap and make sure that clothes are well rinsed.
- Watch for skin infections. Contact your healthcare provider if you notice an infection.
- Help them avoid rubbing or scratching the rash.
- Use moisturizers several times daily. In infants with eczema, moisturizing on a regular basis is extremely helpful.
Causes Of Atopic Eczema
The exact cause of atopic eczema is unknown, but it’s clear it is not down to one single thing.
Atopic eczema often occurs in people who get allergies. “Atopic” means sensitivity to allergens.
It can run in families, and often develops alongside other conditions, such as asthma and hay fever.
The symptoms of atopic eczema often have certain triggers, such as soaps, detergents, stress and the weather.
Sometimes food allergies can play a part, especially in young children with severe eczema.
You may be asked to keep a food diary to try to determine whether a specific food makes your symptoms worse.
Allergy tests are not usually needed, although they’re sometimes helpful in identifying whether a food allergy may be triggering symptoms.
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Eczema On Scalp
Causes Of Atopic Dermatitis
The exact cause of AD is unknown, but most cases are a combination of genetics and triggers 2
- There are several genetic factors which may lead to AD:
- Individuals who have a parent with a history of AD, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop AD 3
- Some people have a mutation in the CARD11 gene, which affects immune system cells 3
- Some people with AD have a mutation in the gene responsible for creating filaggrin, which is a protein that helps create a healthy outer layer of skin 3
- There are multiple things that may trigger AD symptoms including:
- Providers may also prescribe phototherapy 8
Treatment For Adult Eczema
Dermatologists emphasize that moisturizing twice a day with one of the many over-the-counter emollient lotions or creams is the cornerstone of eczema treatment, along with the application of nonsteroidal creams to inflamed lesions or flared areas of the body.
Corticosteroid ointment, either OTC or prescription strength, should be used judiciously and for no longer than one to two weeks at a time. Antihistamines help to relieve itch.
For serious flare-ups, oral medications such as Prednisone are used to reduce inflammation. Topical calcineurin inhibitors , which are steroid-free medications that affect specific cells of the immune system, help lessen redness, itch and swelling.
Another class of topical medication, known as PDE4 inhibitors, block an enzyme linked to inflammation. For very severe cases of atopic dermatitis, systemic immunosuppressant drugs may be used.
Because older adults tend to have comorbidities multiple medical conditions these powerful medications must be used with caution. Phototherapy is also useful.
Dupilumab , the first injectable biologic drug approved for moderate to severe eczema, blocks the actions of key substances involved in the inflammatory process and also influences nerves in the skin, reducing the perception of itch. Alexis says it’s a very safe and effective drug that typically works well in older people, with few or no side effects.
Don’t Miss: Scalp Eczema And Hair Loss
Whats The Difference Between Dermatitis And Psoriasis
Psoriasis and dermatitis can appear similar. Both cause patches of red skin. However, in psoriasis, the scales are thick and the edges of those scales are well-defined.
Discuss with your healthcare provider your questions about which type of skin condition you have. You can have more than one skin condition at a time. Treatments for one may not work for the other.
Questions To Ask Your Childs Doctor
After your child is diagnosed with atopic dermatitis, you may feel overwhelmed with information. It can be easy to lose track of the questions that occur to you.
Lots of parents find it helpful to jot down questions as they arise- that way, when you talk to your childs doctors you can be sure that all of your questions are answered. If your child is old enough, you may want to suggest that she writes down what she wants to ask her health care provider too.
The commitment and compassion with which we care for all children and families is matched only by the pioneering spirit of discovery and innovation that drives us to think differently, to find answers, and to build a better tomorrow for children everywhere.
Don’t Miss: What Can I Do For Eczema
Economic Burden Of Atopic Dermatitis
- The total annual cost of AD increased to estimated $5.3 billion in 2015 10
- The direct costs associated with AD were over $1 billion annually in 2004 9
- $636 million for office visits 9
- $154 million for prescription medications 9
- $108 million for outpatient hospital visits 9
- $105 million for emergency department visits 9
- $6 million for inpatient hospital stays 9
- The indirect costs associated with AD were $619 million in 2004 9
Per person, the average cost of treating AD is $3,302 more than for a person without the disease 11
References
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis In Adulthood
When you say eczema, most people think of atopic dermatitis. Thats for good reason: atopic dermatitis is the most common type of eczema. Its hallmark is the itch-scratch-rash cycle. First, you feel an itch, and you scratch it. Then you develop a red, swollen rash, which may then crack, weep or bleed. Afterward, the rash will crust over and form scaly patches. Sometimes, youll go into a period of remission, without any flare-ups of eczema, only to experience an exacerbation later on down the road.
As many as 60% of people who had atopic dermatitis as children go on to experience it in adulthood. If you first developed this form of eczema as a baby or young child, as many people with eczema do, youre well acquainted with the cycle. Youve probably dealt with it countless times over the years. And youve probably developed a successful routine for managing any exacerbations.
If you developed atopic dermatitis as an adult, however, it may take you some time to recognize the telltale itch and be prepared for the rash. Your doctor can talk to you about the appropriate treatment, which usually starts with topical corticosteroid creams. Youll have to learn how to treat your skin carefully, which includes regular moisturization. Youll also have to work on resisting the urge to scratch your skin, which can cause further damage and even lead to infections.
Read Also: Best Body Soap For Eczema Skin
Can Eczema Happen In Adulthood
Eczema can and does occur in adults. Sometimes, eczema starts in childhood, clears up for a while, and then returns later on. In other people, it may suddenly appear for the first time as an adult.
According to the National Eczema Association, 1 in 4 adults report that their symptoms first appeared in adulthood. Multiracial or white adults have the highest prevalence of adult-onset eczema, although studies vary on the specific percentages.
Overall, approximately 10 percent of adults in the United States are living with eczema.
Adults can get any type of eczema, including atopic dermatitis. Certain types of eczema are more common in adults. These can include:
Can You Get Eczema As An Adult
Eczema or psoriasis? Managing eczema in summertimeNickel allergySevere atopic dermatitis
Adults can get any type of eczema, including atopic dermatitis , which many people consider a childhood disease.
When AD begins after your 18th birthday, dermatologists call it adult-onset atopic dermatitis. Youd receive this diagnosis if you never had AD before. A peak time for developing adult-onset AD is in your 50s.
AD and the eyes
In adults, atopic dermatitis often develops on skin around the eyes.
Some adults who have AD had it as a child. Its possible for AD to go away in childhood and return years later. When the AD returns, its often much milder.
For some children, the AD never goes away, so its a lifelong disease. This happened to Peter Moffat, the award-winning writer of the British TV series Criminal Justice. You can read about how AD affects his life by going to: Adults with eczema too often suffer in silence
Read Also: Why Is My Eczema Worse In The Morning
Types Of Facial Eczema
Eczema is actually a term for a group of conditions that cause itchy, red, and inflamed skin rashes. The types of eczema that are most likely to appear on the face are:
- Atopic dermatitis: This is the most common type of eczema overall. It is very common on the cheeks and chin, especially in infants. It can also appear around the eyes, on the eyelids, and around the lips. It can, however, occur anywhere on the face or the rest of the body.
- Contact dermatitis: This is also a common type of eczema. It is a skin reaction to a specific irritant. On the face, it is usually found around the eyes, the hairline, and in areas that contact perfumes and jewelry, like the neck and earlobes. But, like atopic dermatitis, this type of eczema can occur anywhere.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: This type most often occurs around the hairline, in the eyebrows, around the ears, and on the sides of the nose.
How To Treat Eczema
1. Emollients
Emollients are medical creams and lotions that can start to heal the open, dry skin from eczema. A true emollient is moisturizing and never contains any fragrances or dyes. Another way you can control that constant itch is with oral medications. Taking an antihistamine, such as Benadryl, can bring down the itching and make you much more comfortable as your skin heals. Because these types of medications can cause fatigue, try taking it at bedtime to see how it affects you.
2. Prescription Eczema Creams
If your eczema continues to worsen and the emollient just isnt cutting it, try an over-the-counter-cream that contains hydrocortisone. Using cortisone for eczema will moisturize your skin while relieving the incessant itching. Failing that, your doctor will most likely prescribe an ointment that contains a steroid. These medications can quickly clear up the itching and inflammation, but you do need to be careful with them. Using them for too long can lead to skin discoloration or thinning. Make sure to wash your hands after applying it and always follow the directions.
3. Phototherapy
Light therapy is an effective way to treat eczema when lotions and steroids alone cant control it. Exposing your skin to natural sunlight is the first step. If you live in a cold climate, natural sunlight may not be an option. Your doctor may then recommend phototherapy, a treatment where light is exposed to areas of the skin affected by eczema.
Read Also: Best Healing Cream For Eczema
The Role Of Infection
Antigen stimulation
Infective organisms play an important role in triggering and aggravating atopic dermatitis. Bacteria and in some patients yeasts contribute to chronic inflammation.
Bacterial infection
People who have atopic dermatitis are particularly prone to skin infections with Staphylococcus aureus.
- This is in part due to breaks in dry, split skin, from scratching and from diminished barrier function.
- They also seem to have a reduced ability to fight these common organisms.
- The bacteria that cause infection are also commonly found on healthy skin. The oil on healthy skin is a protective mechanism against invasive infection because the bacteria are lipophobic . Staphylococcal bacteria thrive and invade dry, atopic skin.
- Antimicrobial peptides on the skin surface normally fight these bacteria but may be deficient in the stratum corneum of atopic dermatitis.
As a result, people with atopic dermatitis frequently suffer from boils, folliculitis and infected eczema.
The infection causes eczema to worsen and become more resistant to the usual treatment with emollients and topical steroids. S. aureus produces enterotoxin. This induces the production of enterotoxin-specific IgE, resulting in proliferation and recruitment of more T cells and aggravating dermatitis.
Antibiotics are often required to eliminate the infection and control eczema. However, antibiotics may reduce the biodiversity of the microbiome.
Viral infections
Fungal infections